Definition - 2.5.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of an Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with the fundamental question: What is an economy?

Isn't it just a way for people to earn a living?

Exactly! An economy is the system by which people earn their livelihood. It's how resources are managed and distributed in society.

Why do different countries have different economies?

Good question! Different countries adopt different types based on their needs, resources, and ideologies. This brings us to the classification of economies.

What categories do economies belong to?

There are three main types: capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies. Let’s explore these in depth!

To remember this, think of the acronym CSM—Capitalist, Socialist, Mixed.

CSM! That's helpful!
Classification of Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s define the first type of economy: the capitalist economy. Who can tell me its characteristics?

I think it has private ownership, right?

Yes! In a capitalist economy, the means of production are owned by private individuals. What other features come to mind?

There's freedom of choice and a profit motive!

Perfect! Minimal government interference allows prices to be determined by supply and demand. Can anyone name a country with a capitalist economy?

The United States?

Correct! Now, how does this compare to a socialist economy?
Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In a socialist economy, who owns the means of production?

The government, right?

That's right! The goal is the welfare of society rather than profit. What else can you tell me about its features?

There's public ownership and central planning, and no competition!

Exactly! This leads to equal distribution of income and wealth. Can anyone give me an example of a country that follows this model?

North Korea?

Yes! Lastly, let's look at the mixed economy. What do you know about it?
Mixed Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

A mixed economy combines elements from both capitalism and socialism. Can someone explain how this works?

It has both private and public sectors, right?

Exactly! It encourages private enterprise but also maintains some government control, especially in key industries.

What’s the aim of a mixed economy?

The aim is to achieve economic growth while ensuring social welfare. Can anyone name a country that exhibits this type of economy?

India!

Well done! Remember, mixed economies aim to blend the best features of both systems for better results.
Conclusion and Comparison
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s review the main characteristics of capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies. What are the ownership dynamics in each?

In capitalism, it's private ownership; in socialism, it's public ownership; and in mixed, it's both!

Great summary! Where does profit motive fit in?

It's strong in capitalism, none in socialism, and limited in mixed economies!

Excellent! Finally, let's remember that each type has its own merits and limitations, making mixed economies increasingly popular worldwide.

Can we conclude that most economies strive for this mixed model?

Absolutely! As we integrate these concepts, remember them by relating CSM to their features.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The economy is defined as a system through which people earn their livelihood. Different types of economies (capitalist, socialist, and mixed) are classified based on ownership, goals, and government intervention, influencing how resources are managed and distributed in society.
Detailed
Definition of an Economy
An economy is defined as the system through which people earn their livelihood and manage resources. Different countries establish various economic structures according to their unique needs, ideologies, and resources.
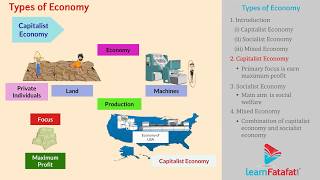
Types of Economies
- Capitalist Economy: This type of economy is characterized by private ownership of production means, minimal government involvement, and market-driven pricing influenced by supply and demand.
- Socialist Economy: Here, the government owns and controls production means, aiming for equitable resource distribution and the welfare of society, often with central planning and no profit motive.
- Mixed Economy: Combining elements of both capitalist and socialist systems, mixed economies feature both public and private sector enterprises, with the government playing a regulatory role to promote both economic growth and social welfare.
Understanding these definitions and classifications is critical as they lay the foundation for examining how different economies operate and influence individuals' livelihood strategies.
Youtube Videos









Key Concepts
-
Capitalist Economy: Characterized by private ownership of production.
-
Socialist Economy: Government ownership of means of production for social welfare.
-
Mixed Economy: Combines features of both capitalism and socialism.
-
Profit Motive: The drive for financial gain influencing economic behavior.
Examples & Applications
The United States exemplifies a capitalist economy.
North Korea is a prominent example of a socialist economy.
India represents a mixed economy, balancing private and public sectors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In capitalism, we strive for gain, while in socialism, the people train. Mixed economies blend the two, ensuring growth and welfare too.
Stories
Once in a land of varied riches, there lived three towns—one ruled by private hands, the second by the government, and the last by both. The private town flourished with ideas, the government town shared equally, and the last one balanced growth and care for all.
Memory Tools
Remember CSM for types of economies: Capitalist, Socialist, Mixed!
Acronyms
Use CSM to recall Capitalist, Socialist, Mixed economies and their features.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where the means of production are privately owned and operated for profit.
- Socialist Economy
An economic system where the government owns and controls the means of production, aiming to achieve social welfare.
- Mixed Economy
An economic system that incorporates both private and public enterprise, balancing elements from capitalism and socialism.
- Profit Motive
The incentive for individuals or businesses to act in their own interest to achieve financial gain.
- Public Ownership
When the means of production are owned by the government or state.
- Private Ownership
When the means of production are owned by private individuals or corporations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
