Main Features - 2.4.2
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the main features of a capitalist economy. Can anyone define what a capitalist economy is?

Isn't it where private individuals own the businesses and resources?

Exactly! In a capitalist economy, private ownership is key. What else do you think drives businesses in this system?

The profit motive, right? They want to make as much money as possible.

Correct! The profit motive is a primary driver. Now, how are prices determined in this economy?

By supply and demand. If there’s a high demand, prices go up.

Very well explained! Remember, less government interference means more freedom in business choices. Let’s recap: capitalist economies emphasize private ownership, profit motive, market-driven prices, and minimal government interference.
Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift to the socialist economy. Who can tell me about the ownership of resources in a socialist economy?

The government owns everything, right?

Correct! Public ownership of resources is fundamental. What’s the primary goal of production in this system?

It’s to benefit society rather than to earn profits.

That’s an important point. Socialism is focused on societal welfare, not profit. Additionally, how does the government play a role here?

The government plans everything, right? There’s no competition?

Exactly! Without competition, production is determined by government plans. Let’s summarize: a socialist economy features public ownership, government planning, no profit motive, and aims for equitable wealth distribution.
Mixed Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss the mixed economy. What does this type of economy involve?

It has both private and government enterprises!

Correct! It combines different sectors. Why is government regulation important in a mixed economy?

To ensure that key industries are controlled and that there is no monopoly?

Exactly! Government control helps maintain a balance. How does a mixed economy aim to benefit its citizens?

By promoting economic growth while also looking at social welfare.

Great! To summarize, a mixed economy features both public and private sectors, government regulation, a balance between growth and welfare, and it exemplifies countries like India and the UK.
Comparison of Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have understood each type of economy, let's compare their key features. How does ownership differ among these economies?

Capitalist has private ownership, socialist has public ownership, and mixed has both.

Well done! And what about profit motives?

Capitalist economies seek profit, socialists don’t care about profit, and mixed economies have limited profit motives.

Excellent! And what is the role of government in each of these economies?

Minimal in capitalist, maximum in socialist, and moderate in mixed economies.

Perfect! Lastly, can someone recap some real-world examples of each type?

We have the USA and Japan for capitalist, Cuba and North Korea for socialist, and India and the UK for mixed!

Great job, everyone! Remember these comparisons as we move forward. They will help us understand economic policies better.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The key features of capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies are explored in this section, emphasizing aspects such as ownership of resources, government roles, and the profit motive. This critical comparison helps students understand each system's advantages and disadvantages.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we define and compare three prominent types of economies: capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies. Each system has unique characteristics that dictate how resources are owned, how economic planning is conducted, and the extent of government involvement.
Main Features of Economic Systems
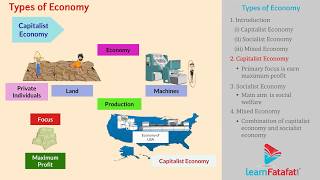
- Capitalist Economy:
- Private Ownership: Resources and production are owned by private individuals.
- Profit Motive: The primary goal of businesses is to generate profit.
- Market Forces: Prices are determined by supply and demand without significant government intervention.
- Freedom of Enterprise: Individuals are free to choose how to conduct their businesses.
- Examples: The United States, Australia, and Japan exemplify capitalist economies.
- Socialist Economy:
- Public Ownership: The government owns and controls most resources and production.
- Welfare Focus: The aim is to enhance social welfare rather than profit generation.
- Central Planning: Economic activities are coordinated through government planning, without competition.
- Income Equality: Efforts are made to ensure equal distribution of wealth.
- Examples: North Korea, Cuba, and the former Soviet Union are notable examples.
- Mixed Economy:
- Combination of Ownership: Both private and public sectors coexist.
- Regulation: The government regulates key industries while encouraging private enterprise.
- Balanced Goals: Aims to achieve economic growth alongside social welfare.
- Examples: India, the United Kingdom, and France represent mixed economies.
Conclusion
Understanding the main features of these economic systems is essential in appreciating how different countries approach economic management and societal welfare.
Youtube Videos









Key Concepts
-
Capitalist Economy: An economy driven by private ownership and profit motive.
-
Socialist Economy: An economy focused on public ownership and social welfare.
-
Mixed Economy: A combination of both capitalist and socialist features, balancing private and public sectors.
Examples & Applications
The United States operates primarily as a capitalist economy, valuing individual freedom and competition.
Cuba represents a socialist economy where the state controls resources for societal benefit.
India exemplifies a mixed economy, balancing growth and social equity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In capitalism, ownership is private, profit is the drive, the markets are alive!
Stories
Imagine a neighborhood with a café owned by a local where everyone has a say in its menu—this represents a mixed economy with both private café owners and public involvement in community decisions.
Memory Tools
CSP - Capitalism, Socialism, and Public ownership help you recall the essential features of each economy by their initials.
Acronyms
MOP - Motive, Ownership, Planning signifies the key factors in comparing economies.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where private individuals own and control the means of production.
- Socialist Economy
An economic model where the government owns and controls the production and distribution of goods.
- Mixed Economy
An economic system that combines features of both capitalism and socialism.
- Profit Motive
The drive for businesses to increase their profits.
- Government Regulation
Rules set by the government to control business practices.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
