Definition - 2.3.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Capitalism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today, we will discuss the concept of a capitalist economy. Can anyone tell me what they think a capitalist economy is?

Isn't a capitalist economy where private individuals own things like businesses?

Exactly! In a capitalist economy, the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals. This leads to what we call 'private ownership.'

What are some other features of a capitalist economy?

Great question! Other features include freedom of choice and enterprise, a profit motive driving economic actions, and minimal government interference. Remember, we can summarize these features with the acronym 'PFP' — Private ownership, Freedom, Profit motive!

Can you give us examples of capitalist economies?

Sure! Countries like the United States, Australia, and Japan are prime examples of capitalist economies. They operate mainly on market principles.

In summary, a capitalist economy is marked by private ownership and minimal government control, leading to market-driven economic activities. Any questions?
Market Forces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about market forces in a capitalist economy. Who remembers how demand and supply affect prices?

I think if demand goes up and supply stays the same, prices increase?

Correct! This is known as the law of supply and demand. Prices fluctuate based on how much of a product is available compared to how much people want it.

So, does that mean the government doesn’t control prices in a capitalist economy?

Exactly! In a capitalist economy, prices are determined by the market itself rather than by government regulation. This leads to a truly free market.

To summarize, market forces play a critical role in determining prices and resource allocation in a capitalist economy. Any final questions?
Benefits and Drawbacks of Capitalism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s review the benefits and drawbacks of capitalism. Can anyone share a benefit they see in this system?

Maybe the innovation because companies compete to create better products?

Absolutely! Competition drives innovation and efficiency, leading to better products for consumers. That’s a huge advantage!

What about the drawbacks, though?

Good point! One drawback can be economic inequality, where wealth is concentrated among a few. It can lead to significant social disparities.

To summarize, capitalism encourages innovation and efficiency, but it can also create inequality. These are essential aspects to consider in our economic discussions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
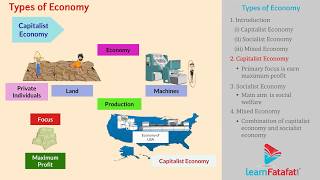
In this section, a capitalist economy is defined as one where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals. Key features include private ownership, freedom of enterprise, and minimal government interference, with examples of countries exhibiting this economy.
Detailed
Definition of Capitalist Economy
In economics, a capitalist economy is defined as an economic system where the means of production—such as land, labor, and capital—are predominantly owned and controlled by private individuals. This system operates on the principles of free market where the allocation of resources is determined by market forces, specifically through the dynamics of supply and demand. The major characteristics that distinguish a capitalist economy include:
- Private Ownership: Individuals have the right to own and control properties and resources.
- Freedom of Choice and Enterprise: Consumers and producers are free to make their own choices regarding what to produce, sell, or purchase.
- Profit Motive: The pursuit of profit motivates individuals and businesses, serving as a driving force for economic activity.
- Minimal Government Interference: The government plays a limited role in the economy, primarily focusing on maintaining law and order rather than controlling markets.
- Market-Driven Prices: Prices of goods and services are determined through the interplay of demand and supply in the market.
Examples of capitalist economies include advanced countries such as the United States, Australia, and Japan, each exemplifying varying degrees of capitalism with market-driven governance.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Capitalist Economy
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
Detailed Explanation
A capitalist economy is characterized by the idea that private individuals have ownership over businesses and resources. This means that people can buy, sell, and manage their own enterprises as they see fit. The driving force behind a capitalist economy is the profit motive, meaning individuals and companies are motivated to earn money and maximize their profits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bakery owned by an individual. This owner decides what to bake, how to sell it, and what price to charge. The owner’s goal is to make a profit by selling as many baked goods as possible. If the bakery starts to lose money, the owner might change recipes or start offering new products to attract more customers. This scenario illustrates how decisions in a capitalist economy are driven by individual choices and the goal of making a profit.
Key Concepts
-
Private Ownership: Economies where the means of production are owned by individuals.
-
Free Market: Economic system driven by supply and demand without government interference.
-
Profit Motive: The driving force behind production and consumption in capitalist economies.
-
Market Forces: The influences of supply and demand affecting prices and resource allocation.
Examples & Applications
The United States operates under a capitalist economy where individual entrepreneurship is encouraged.
In Japan, innovation driven by competitive markets leads to technological advancements.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In capitalism, you'll see, it's ownership that's key. Profit does drive, and markets thrive!
Stories
Imagine a marketplace where every shopkeeper decides what to sell and the price, leading to a buzzing economy full of choices and innovation.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PFP' for Capitalism: Private ownership, Freedom, Profit motive.
Acronyms
CAPITA
Capital
Assurance of property
Profit motive
Individual ownership
Trade freedom
and Advancement.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
- Private Ownership
The right of individuals to own and control properties and resources.
- Profit Motive
The reason individuals engage in economic activity to earn personal profits.
- Market Forces
The supply and demand theories that determine prices and resource allocation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
