Types of Economies
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today, we will explore the fascinating world of economies. Can anyone tell me what an economy is?

Isn't it how people make money and live?

Exactly! An economy is a system by which people earn their livelihood. Now, why do you think different places might have different types of economies?

Maybe it’s because of the resources they have?

Right! Factors like resource availability and societal needs influence the type of economy adopted in a region. Let's dive deeper into the three main types!
Capitalist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s start with the first type, the capitalist economy. Can anyone define what this is?

It’s where private individuals own the businesses and resources.

Great! That's right! In capitalist economies, the profit motive drives the market. Can you name a country that follows this model?

The United States!

Correct! Remember the acronym ‘PFP’ – Private ownership, Freedom, and Profit motive. These are the key features of capitalism.
Socialist Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to the socialist economy. What defines this type of economy?

The government controls everything!

Correct! Here, public ownership is central. What's important here is the lack of a profit motive. Can you think of any examples?

North Korea and Cuba?

Exactly! Reflect on how no competition influences production here, as everything is centrally planned. Use the acronym 'GOW' - Government Ownership, Welfare focus.
Mixed Economy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss mixed economies. Who can tell me what characterizes a mixed economy?

It has both private and public sectors!

Exactly! Government regulates key industries while also allowing private enterprise. Can you name a mixed economy?

India!

Correct! Remember the phrase 'Balance for Growth' as it encapsulates the goals of mixed economies—economic growth and social welfare!
Comparison of Economies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's review what we learned by comparing these economies. What feature separates capitalist from socialist economies?

Ownership! It's private in capitalist and public in socialist.

Exactly! And how does the role of government differ in these economies?

It’s minimal in capitalist and maximum in socialist.

Right again! So, to sum up, we see that each type has its strengths and weaknesses, often leading to many countries adopting a mixed economy approach.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Economies are categorized into capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies based on their ownership of resources, government involvement, and profit motive. Each type has distinct characteristics and examples reflecting various global practices.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we delve into the concept of economies which serve as systems through which people sustain their livelihoods. Economies can be categorized based on ownership and economic freedoms into three primary types: capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies.
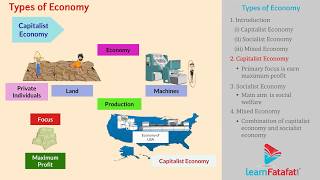
1. Capitalist Economy:
In capitalist economies, private individuals own and control the means of production. The key features include:
- Private ownership of resources.
- Freedom of choice and enterprise.
- The profit motive driving economic activity.
- Minimal government intervention, with prices determined by supply and demand.
Examples of capitalist economies include the United States, Australia, and Japan.
2. Socialist Economy:
Contrarily, socialist economies are characterized by government ownership of production. Key features involve:
- Public ownership of resources.
- Central planning executed by the government.
- A focus on societal welfare instead of profit motives.
- Equal distribution of resources with no competition.
Countries like the Former Soviet Union, North Korea, and Cuba serve as examples.
3. Mixed Economy:
Mixed economies blend elements of both capitalism and socialism, featuring:
- Co-existence of public and private sectors.
- Government regulation of key industries while encouraging private enterprises within certain limitations.
- A balanced approach toward economic growth and social welfare.
Examples of mixed economies include India, the United Kingdom, and France.
Overall, each economy type presents unique merits and limitations contributing to the diverse economic landscape seen globally.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Economies
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An economy refers to a system by which people earn their livelihood. Different countries adopt different types of economies based on their needs, resources, and ideologies.
Detailed Explanation
An economy is fundamentally a system that outlines how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed. It focuses on how people earn their living, and this can vary significantly from one country to another based on various factors, such as the available resources, cultural beliefs, and government policies. Understanding the type of economy in a country helps explain its structure and functionality regarding wealth and resource distribution.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an economy as a recipe for a dish. Different cultures have different recipes based on the ingredients they have available (resources) and the tastes they prefer (ideologies). Just like a chef might adjust a recipe for their restaurant (needs), countries do the same with their economies.
Classification of Economies
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Economies can be classified into the following main types:
1. Capitalist Economy
2. Socialist Economy
3. Mixed Economy
Detailed Explanation
Economies can primarily be divided into three categories based on ownership and control of resources: capitalist, socialist, and mixed. A capitalist economy focuses on private ownership, while a socialist economy is characterized by government control. Mixed economies, as the name suggests, incorporate elements from both. This classification allows for a better understanding of how economic systems operate and the implications each type carries for individuals and society.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the economic systems like different types of games. In some games (capitalist), players compete individually for points (profits), while in others (socialist), everyone works together towards a common goal, ensuring everyone wins something. Mixed economies are like games that have both individual competitions and team objectives.
Capitalist Economy
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Definition: An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by private individuals.
● Main Features:
- Private ownership of property and resources
- Freedom of choice and enterprise
- Profit motive is the driving force
- Minimal government interference
- Prices determined by market forces (demand and supply)
● Examples: United States, Australia, Japan
Detailed Explanation
In a capitalist economy, individuals own and control the production and distribution of goods and services. This system is characterized by private ownership, meaning that people have the freedom to run businesses, choose careers, and make personal financial decisions. The driving force behind these decisions is often the profit motive, which encourages innovation and efficiency. The government plays a limited role, allowing market forces to determine pricing based on supply and demand.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a lemonade stand run by a child (the individual). They source lemons, sugar, and cups (production resources), set their prices based on how many people want lemonade (market forces), and keep the profits they make. This is how a capitalist economy operates at a small scale.
Socialist Economy
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Definition: An economy where the means of production are owned and controlled by the government.
● Main Features:
- Public ownership of property and resources
- Central planning by the government
- No profit motive – welfare of society is the goal
- Equal distribution of income and wealth
- No competition; production decided by government plans
● Examples: Former Soviet Union, North Korea, Cuba
Detailed Explanation
In a socialist economy, the government owns and controls nearly all aspects of production and distribution. Decisions regarding what is produced, how it is produced, and for whom are made through central planning. The focus in this system is more on the welfare of society as a whole rather than individual profit. Income and wealth tend to be distributed more equally among the populace, and competition is often limited.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a big family where parents decide what everyone eats, how much each person gets, and ensure that everyone's needs are met first (social welfare). No one runs their own kitchen for individual gain (competition); instead, everyone works together based on the family plan.
Mixed Economy
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Definition: An economy that has both private and public sector enterprises; it combines features of both capitalist and socialist economies.
● Main Features:
- Co-existence of public and private sectors
- Government regulates and controls key industries
- Encouragement of private enterprise with some restrictions
- Aims for both economic growth and social welfare
● Examples: India, United Kingdom, France
Detailed Explanation
A mixed economy combines elements of both capitalism and socialism. In this system, both private companies and government entities operate, providing a balance between individual entrepreneurship and social welfare. The government typically regulates key industries to ensure public interests are met while also encouraging private enterprise to drive economic growth. This creates a more balanced approach to managing the economy.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community garden where some plots are individually maintained by residents (private sector), while others are managed by the city (public sector). Both aim to create a flourishing garden but have different approaches to resource management and upkeep.
Comparison Table of Economies
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature Capitalist Socialist Economy Mixed Economy
Ownership of resources Private individuals Government Both government and private
Profit motive Yes No Limited
Economic planning No (Market-driven) Yes (Centrally planned) Partial
Role of government Minimal Maximum Moderate
Examples USA, Japan Cuba, North Korea India, UK
Detailed Explanation
This comparison table succinctly outlines key features of the three economic systems: capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies. It contrasts who owns resources, the existence of a profit motive, the nature of economic planning, the role of the government, and real-world examples of each type. This structured comparison helps students identify and differentiate the characteristics of each economy effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this comparison as different types of music genres. Just like how rock, classical, and jazz have unique characteristics (ownership, profit motive, planning), each affecting how the music is played and enjoyed, the economies differ in how they operate and serve their communities.
Conclusion on Economies
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each type of economy has its own merits and limitations. Most countries today follow the mixed economy model to combine the efficiency of the market with the equity of government control.
Detailed Explanation
In conclusion, while capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies all have their strengths and weaknesses, most contemporary nations adopt a mixed approach. This allows them to benefit from market efficiencies while striving for equitable resource distribution through government oversight. Understanding these systems helps us assess economic policies and their implications on society.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a sailboat that uses both wind (market forces) to navigate and an anchor (government control) to maintain balance. Both elements are essential for a successful journey, just as different economic systems contribute to the overall health of a nation.
Key Concepts
-
Capitalist Economy: Owned and controlled by private individuals with minimal government intervention.
-
Socialist Economy: Controlled by the government aimed at societal welfare.
-
Mixed Economy: Combines aspects of both capitalism and socialism, balancing private enterprise with public regulation.
Examples & Applications
The United States and Japan are examples of capitalist economies.
Cuba and North Korea exemplify socialist economies.
India and the United Kingdom are examples of mixed economies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a capitalist space, profits race, in socialism, the government finds its place.
Stories
Imagine a village where everyone shares what they produce freely, that's socialism; but then think of a town where everyone competes to build the best business, that's capitalism!
Memory Tools
To remember the features of capitalism, think 'PFP' - Private ownership, Freedom, Profit.
Acronyms
For socialism, remember 'GOW' - Government Ownership, Welfare focus.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capitalist Economy
An economic system where private individuals own and control the means of production.
- Socialist Economy
An economic system where the means of production are owned and controlled by the government.
- Mixed Economy
An economic system that incorporates elements of both capitalism and socialism.
- Private Ownership
Ownership of resources by private individuals or businesses.
- Public Ownership
Ownership of resources by the government or state.
- Profit Motive
The main driving force in a capitalist economy, focused on earning profits.
- Central Planning
Economic decisions made by the government regarding resource allocation.
- Welfare of Society
The focus in a socialist economy to improve community well-being.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
