Meaning of Journal
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Journal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we're discussing the Journal in accounting. Can anyone tell me what a Journal is?

Isn't it where we record all the business transactions?

Exactly! The Journal is the primary book of entry where we record transactions consecutively. It serves as the backbone of our accounting records.

What do you mean by 'primary book of entry'?

Great question! It means that before transactions go anywhere else, they first get documented in the Journal. Think of it as the starting point of our accounting journey.

So every transaction is recorded there first?

Yes! Let's remember this with the acronym JET: Journal Entry Tracker. It helps us recall that every financial event is first tracked in the Journal. Any questions before we move on?

No, that makes sense!
Journal Entries - Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into the features of journal entries. Can someone share what details we need?

Do we need the date and the accounts involved?

Great! We record the date, the particular accounts involved, and the amounts for debit and credit, following the double-entry system. This means for every debit entry, there's an equal credit entry.

It's like balancing a scale!

Exactly! And just like 'balancing,' we should remember this idea with the word 'DICE': Date, Information, Credit, and Entry. Let’s practice some examples of how we’d write journal entries. Any thoughts?

Can we see a real example?
Types of Journal Entries
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the types of journal entries we can have. Who can name one type?

Is a simple entry a type?

Yes! A simple entry includes just one debit and one credit. What about compound entries?

That one has multiple debits or credits, right?

Correct! To help remember this, we can use the mnemonic 'SIMPLES'; Simple, Adjustment, Multiple, and Opening for different types of entries. Let's practice identifying different entries from examples.

I think I'm starting to get it!
The Significance of Journals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss the significance of journals. Why do you think they're important in accounting?

They help keep track of everything happening!

Exactly, they create an auditable history of transactions which is crucial for financial transparency!

And they help prepare the Ledger, right?

Yes! Remember: 'Journals feed the Ledger', which helps us in our financial reporting. Good catch! As a summary, let's review the 'JET' and 'DICE' concepts we've learned today. Any final questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In accounting, the Journal serves as the primary record for all business transactions as they occur, capturing extensive details for each entry under a systematic approach. Journal entries follow the double-entry accounting system, providing a foundation for further classification in the Ledger.
Detailed
Meaning of Journal
The Journal is the primary book of entry in accounting, known for recording business transactions in the order of their occurrence. Each transaction is recorded through a journal entry that maintains complete details and follows the double-entry system: every debit must correspond with a credit. This critical component paves the way for further classification of transactions in the Ledger and ultimately leads to the preparation of the Trial Balance. Understanding the Journal's function is essential for grasping how financial data is systematically organized for use in decision-making.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Journal
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Journal is the primary book of entry in accounting. It records business transactions chronologically (i.e., as they occur). Each entry in the journal is called a journal entry.
Detailed Explanation
The Journal serves as the first notebook where all financial transactions of a business are entered. Each transaction is recorded in the order it happens, which means the earliest transactions appear first. This chronological order ensures that anyone reviewing the Journal can easily see what occurred and when. Each individual transaction recorded is known as a journal entry, which contains important information like date, amounts, and details about the transaction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Journal like a diary where you write daily experiences. Just as you might note down what happened every day in your diary—like meeting a friend for lunch or buying groceries—the Journal keeps track of all the financial events of the company in the same sequential manner.
Key Concepts
-
Chronological Record: The Journal records transactions as they occur.
-
Double-Entry Accounting: Each transaction has an equal debit and credit.
-
Journal Entry Structure: Entries include the date, accounts involved, and amounts.
Examples & Applications
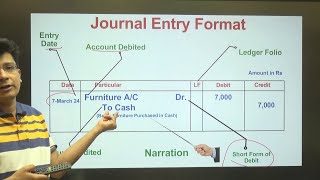
Example of a journal entry: On July 1st, 2025, Goods sold for cash amounts to ₹5,000, recorded as:
01/07/2025 Cash A/c Dr. ₹5,000
To Sales A/c ₹5,000.
Example of an adjustment journal entry: At the end of the period, accruing ₹1,000 in expenses as:
31/07/2025 Expenses A/c Dr. ₹1,000
To Accrued Expenses A/c ₹1,000.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To enter accounting's game, use the Journal and remember the name.
Stories
Once upon a time in business land, there was a Journal that took a stand. It recorded every sale and every trade, ensuring transactions are never delayed.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'JET' for Journal Entry Tracker to keep your transactions ordered.
Acronyms
DICE
Date
Information
Credit
Entry to remember the structure of journal entries.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Journal
The primary book of entry in accounting, where business transactions are recorded chronologically.
- Journal Entry
A record of a transaction made in the Journal documenting the date, accounts involved, and amounts.
- DoubleEntry System
An accounting method where every debit entry has a corresponding credit entry.
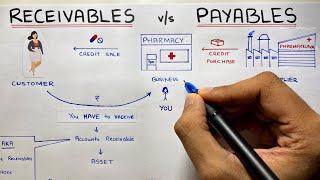
- Ledger
A collection of accounts where transactions from the journal are classified and summarized.
- Trial Balance
A statement showing the balances of all accounts to verify the accuracy of bookkeeping.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
