Civil Engineering Case Example: Convolution in Structural Dynamics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Convolution in Structural Dynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss how convolution is applied in civil engineering, particularly in understanding how buildings respond to dynamic loads, such as earthquakes. First, can anyone tell me what convolution signifies in this context?

I think convolution combines two functions to show how one influences the other over time!

Exactly! Great job! When we have a building's impulse response function and the ground motion function from an earthquake, convolution helps us determine the building's displacement. Let's move to the formula that expresses this relationship.

What is the formula, as I was not following fully?

It’s expressed as: y(t) = (f ∗ h)(t). This integral integrates the product of the ground motion and the impulse response over time. Remember, y(t) is crucial for analyzing how the building reacts!

So, f(t) is where the seismic activity comes in and h(t) shows how the building behaves?

Spot on! f(t) represents ground motion, and h(t) signifies the building's response. This encapsulates how seismic forces affect our structures.
Examples of Ground Motion and System Response
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss concrete examples of f(t) and h(t). What could an expression for ground motion look like?

Could it be something like f(t) = e^{-t} imes ext{sin}(t)?

Yup! That's correct. It's a common representation for ground motion. Now, what's the implication of using a specific form for h(t)?

It would determine how the structure reacts to the given f(t).

That's right! By specifying h(t) as something like \( h(t) = \frac{1}{m \omega} \sin(\omega t)e^{-\zeta t} \), we help model the damping effect of our structure.

And it helps in designing the building to handle potential earthquake impacts!

Exactly, insightful observation! This use of convolution aids in ensuring buildings can endure seismic activities.
Importance of Convolution in Seismic Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As aspiring engineers, understanding how convolution helps in earthquake preparedness is vital. Why do you think response spectrum analysis is important?

Isn’t it about determining how a building will respond across a range of frequencies?

Yes! It captures different seismic waveforms' impacts on a structure, utilizing convolution principles. Why might this be critical, do you think?

So that we can design buildings that are safer and respond better to real-world conditions!

Correct! Such analyses are integral to civil engineering, ensuring the longevity and safety of the structures we create.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section focuses on a practical application of convolution in civil engineering, specifically demonstrating how a building's displacement response to earthquake ground motion can be calculated using convolution of the ground motion function and the building's impulse response function. It emphasizes the significance of this analysis in seismic design.
Detailed
In this section, we explore the application of convolution in structural dynamics, particularly for civil engineering contexts such as earthquake analysis. When a building is subjected to ground motion, denoted as f(t), its displacement response y(t) can be modeled through convolution with a known impulse response function h(t). The mathematical representation of this relationship is expressed as:
$$ y(t) = (f ∗ h)(t) = \int_0^t f(\tau)h(t-\tau) d\tau $$
Here, f(t) represents the ground motion, and h(t) signifies the system response, given a specific form such as \( h(t) = \frac{1}{m \omega} \sin(\omega t)e^{-\zeta t} \). Understanding this convolution allows engineers to predict how a structure behaves during seismic events, which is critical for designing safe and resilient buildings. This principle underpins response spectrum analysis, showcasing its importance in ensuring civil structures' durability against dynamic loading conditions.
Youtube Videos

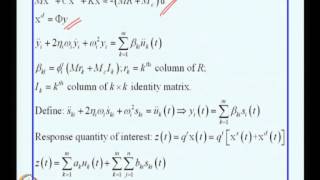



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Displacement Response Formula
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A building subjected to ground motion f(t) due to an earthquake has a known impulse response function h(t). The displacement response y(t) of the building is given by:
Z t
y(t)=(f ∗h)(t)= f(τ)h(t−τ)dτ
0
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we look at how the displacement response of a building during an earthquake is calculated using convolution. The formula y(t) represents the total response of the building at any time t. The integral involves the ground motion function f(τ) and the system's impulse response h(t−τ), which accounts for the effect of past movements on the current response.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a trampoline (the building) being jumped on (the earthquake). The way the trampoline moves (its response) depends on how hard and fast the people are jumping (the ground motion). Each jump affects the trampoline's fabric in a way that you can calculate based on how the trampoline naturally responds to any force applied to it.
Functions of Ground Motion and System Response
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If:
• f(t)=e−tsint: ground motion
• h(t)= 1 sin(ωt)e−ζt: system response
mω
Detailed Explanation
Here, we define two important functions: f(t), which models the ground motion during an earthquake, and h(t), which represents the building's impulse response. The function f(t) combines an exponential decay and a sine wave, indicating that the ground motion is oscillatory and dampening over time. The function h(t) also contains sine waves and decay factors, modeling how the building dissipates energy from the earthquake, given parameters such as mass (m) and damping ratio (ζ).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a swing in a park. When you push it (the ground motion), the swing moves back and forth. The way the swing reacts to your push depends on how heavy the swing is (mass) and how much it resists motion (damping). The equations we see here are just like those physics rules that tell us how far the swing will go and how quickly it will stop swinging before coming to rest.
Practical Application of Convolution
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Then using convolution, you can determine how the building will behave over time during and after the earthquake.
Detailed Explanation
Using convolution allows engineers to predict the building's behavior as the earthquake progresses and how it continues to move afterward. By integrating the effects of the ground motion over time against the building's impulse response, they can obtain a comprehensive view of the building's displacement response at each moment. This predictive capability is essential for ensuring safety and structural integrity during seismic events.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a firework exploding in the night sky. The way the colored lights spread and fade can be likened to how a building responds to ground motion. Just as the trajectory and brightness of the firework depend on how and when it was ignited (the impulse response), the building's displacement over time is calculated based on how the initial earthquake force affects it and how it subsequently behaves.
Foundation of Response Spectrum Analysis
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This approach is the foundation of response spectrum analysis in seismic design.
Detailed Explanation
Response spectrum analysis is a method used in engineering to understand how structures respond to seismic activities. By employing the principles of convolution, engineers can create a response spectrum that characterizes how different buildings will behave under varying earthquake conditions. This analysis helps in designing structures that can withstand seismic forces, optimizing materials, and ensuring safety.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine preparing for a sports game by analyzing past performances of your team under different weather conditions. Just like team strategies adjust based on the weather, engineers use response spectrum analysis to adapt building designs based on predicted earthquake forces, ensuring that structures remain resilient and stable under stress.
Key Concepts
-
Impulse Response Function: Describes a system's response to impulse input.
-
Ground Motion: Ground movement data captured during seismic events.
-
Convolution: Blending of two functions to analyze their combined effect.
-
Displacement Response: Movement of a structure due to external forces.
-
Response Spectrum Analysis: Study of how structures respond across various frequencies.
Examples & Applications
f(t) = e^{-t} imes ext{sin}(t) represents ground motion during an earthquake.
h(t) = \frac{1}{m \omega} \sin(\omega t)e^{-\zeta t} models structural response.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Convolution's mix, helps buildings fix, ground shocks in their midst.
Stories
Imagine a building braving an earthquake's shake, its design and impulse response working together like a dance, ensuring it doesn't fall.
Memory Tools
Frog on the Roof: f(t) for ground motion (Frog), h(t) for impulse (Roof), together they produce y(t) - the response.
Acronyms
GREAT
Ground motion (G)
Response (R) through E = Convolution A (Analysis) T (Time).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Impulse Response Function
A function that describes how a system responds over time to an impulse input.
- Ground Motion
The motion of the ground typically resulting from seismic activity, expressed mathematically to assess its impact on structures.
- Convolution
A mathematical operation that blends two functions, showing how one influences the other over time.
- Displacement Response
The motion experienced by a structure in response to an external force, such as an earthquake.
- Response Spectrum Analysis
A method used in earthquake engineering to analyze a building's expected response to different frequencies of seismic waves.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
