Origin of Bitumen
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Natural Bitumen Sources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore natural bitumen. Can anyone tell me where natural bitumen comes from?

Isn't that the stuff found in places like asphalt lakes?

Exactly! Natural bitumen, or asphalt, can indeed be found in asphalt lakes, rock asphalt, and tar sands. These sources are formed through geological processes over millions of years. Can anyone guess some of the steps involved in this process?

Maybe it has to do with dead plants or sea creatures decomposing?

Correct! Organic matter from marine organisms gets deposited in sedimentary basins. That's the first step in the process, leading to what we call anaerobic conditions. Why do you think those conditions are critical?

Because it stops it from decomposing fully, right?

Absolutely! This lack of oxygen preserves the organic material. As we continue, heat and pressure over geological time transform this material into hydrocarbons. Finally, evaporation and oxidation lead to the formation of bitumen. Can anyone name a natural source of bitumen?

Like Pitch Lake in Trinidad?

Yes! Great job! So we have learned how natural bitumen forms and some sources. Remember, the mnemonic 'DOHE' can help remember: Decomposition, Oxygen absence, Heat, and Evaporation.
Petroleum-Derived Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's shift gears and discuss petroleum-derived bitumen. Who can tell me how bitumen is produced from crude oil?

Isn’t it through refining?

Correct! The process begins with crude oil refining where the crude oil, containing various hydrocarbons, undergoes fractional distillation. What do you think is the first step in this process?

Preheating it?

Absolutely! Preheating the crude oil is crucial. It’s heated to around 400°C before entering the distillation column. Can anyone explain what happens next?

Lighter hydrocarbons get separated based on their boiling points!

Exactly! After that, the residue undergoes vacuum distillation to avoid thermal cracking. This residue becomes the feedstock for producing bitumen. To remember these steps, think of the acronym 'PAV': Preheating, Atmospheric Distillation, and Vacuum Distillation!

So the heaviest part is what gets turned into bitumen?

Yes! And this understanding helps engineers tailor the bitumen’s properties for specific applications. Always remember, both natural and petroleum-derived routes are essential to our bitumen supply!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Bitumen can originate from natural processes involving organic matter and geological conditions, or it can be derived from the refining of crude oil. It plays a crucial role in road construction, with various sources contributing to its availability and quality.
Detailed
Origin of Bitumen
Bitumen, used extensively in road construction, has two main sources: natural bitumen and petroleum-derived bitumen.
1. Natural Bitumen:
Natural bitumen, or asphalt, forms over millions of years through geological processes. Key steps include:
- Decomposition of Organic Matter: Organic materials from marine organisms are deposited in sedimentary basins.
- Anaerobic Conditions: The lack of oxygen hinders decomposition, resulting in organic-rich layers.
- Heat and Pressure: Over time, heat and pressure convert this organic matter into hydrocarbons.
- Evaporation and Oxidation: Under certain conditions, lighter fractions evaporate, and oxidation thickens the residue into bitumen.
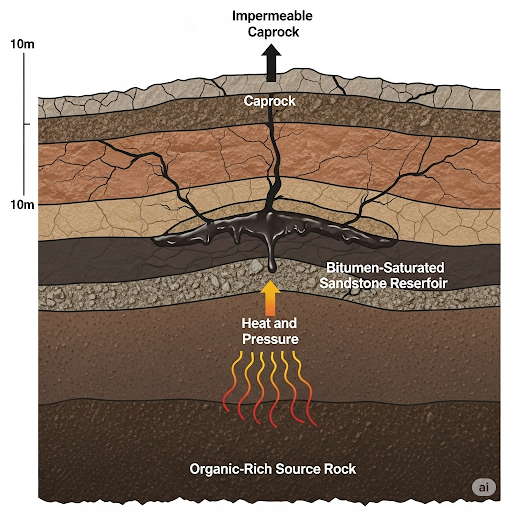
Natural sources of bitumen include Pitch Lake in Trinidad, Alberta Oil Sands in Canada, and deposits at the Dead Sea.
2. Petroleum-Derived Bitumen:
Most of the bitumen used in construction today is obtained from crude oil refining. Crude oil, which contains a mix of hydrocarbons, undergoes fractional distillation where the heaviest residue left after refining becomes the feedstock for bitumen production. Understanding the origins of bitumen is essential for effective application in highway engineering.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Natural Bitumen Overview
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural bitumen, also known as asphalt, occurs in nature in deposits like asphalt lakes, rock asphalt, and tar sands. These are the result of natural geological processes over millions of years involving:
Detailed Explanation
Natural bitumen, often referred to as asphalt, is found in various forms in nature. These include sites known as asphalt lakes, rock asphalt, and tar sands. The formation of these natural bitumen deposits happens over millions of years through specific geological processes. The key processes include the decomposition of organic materials, the lack of oxygen to fully break down those materials, the application of heat and pressure over time, and finally, the evaporation and oxidation that leads to the thickening of the material into bitumen.
Examples & Analogies
Think of natural bitumen like fossilized plants that have turned into coal. Just as those plants took millions of years to become coal through heat and pressure, the organic materials that form bitumen go through similar natural transformations. You can visualize asphalt lakes as natural pools of sticky, black goo formed in these special environments, much like how syrup gathers at the bottom of a pancake stack.
Geological Processes of Origin
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Decomposition of Organic Matter: Organic materials from dead marine organisms are deposited in sedimentary basins.
- Anaerobic Conditions: Absence of oxygen prevents full decomposition, resulting in organic-rich layers.
- Heat and Pressure: Over geological time, these layers are subjected to intense heat and pressure, transforming the organic matter into hydrocarbons.
- Evaporation and Oxidation: In certain conditions, lighter fractions evaporate, and oxidation thickens the residue into bitumen.
Detailed Explanation
The origin of natural bitumen involves several steps. First, organic matter from marine organisms is deposited in sedimentary basins. Without oxygen (anaerobic conditions), this organic material cannot decompose completely. Over millions of years, heat and pressure alter the structure of this organic matter, turning it into hydrocarbons, the foundational element of bitumen. Finally, environmental conditions may lead to the evaporation of lighter components, while heavier materials oxidize and thicken, resulting in bitumen.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a pressure cooker that's been sealed tight with delicious ingredients inside. When you apply heat to it, everything inside transforms into a rich stew. Just like the organic materials that would eventually become bitumen, the ingredients change under heat and pressure, creating something entirely new. Similarly, the absence of air in the seal keeps certain elements from spoiling, paralleling how lack of oxygen allows organic-rich layers to remain preserved underground.
Examples of Natural Bitumen Sources
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples of natural bitumen sources:
- Pitch Lake, Trinidad
- Alberta Oil Sands, Canada
- Dead Sea Deposits
Detailed Explanation
Natural bitumen is sourced from specific locations known for their deposits. Notable examples include Pitch Lake in Trinidad, known for its vast surface area of natural asphalt; the Alberta Oil Sands in Canada, which contain extensive deposits of bitumen mixed with sand; and the Dead Sea Deposits, known for their unique geological features. These places are mining hotspots due to their rich natural resources.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these natural bitumen sources like treasure chests where the earth keeps its valuable resources. Just as a treasure chest might contain ancient coins or jewels, Pitch Lake and the Oil Sands are like giant vaults filled with a thick, black liquid ready to be refined and used in construction. If you pile up sand and mix it with syrup, you might see something similar to Alberta, where bitumen and sand co-exist.
Petroleum-Derived Bitumen Overview
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Most of the bitumen used in construction today is a byproduct of crude oil refining. Crude oil contains a wide range of hydrocarbons, from light gases to heavy residues. Bitumen is obtained from the heaviest fraction left after refining processes like fractional distillation.
Detailed Explanation
Unlike natural bitumen, most of the bitumen utilized in today's construction comes from the refining of crude oil. This crude oil is a complex mixture of different hydrocarbons, from lighter gases to heavier substances. During the refining process known as fractional distillation, the crude oil is separated into various components based on their boiling points. The heaviest fraction remaining after these processes is what becomes bitumen, ready for use.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef creating multiple dishes from a single pot of mixed ingredients. The chef uses different heat levels to cook off lighter ingredients first, leaving behind the thicker residue that’s perfect for a rich gravy. In this way, the refining of crude oil is similar; it isolates lighter fuels first, ultimately producing the heavy bitumen needed for paving roads or making roofs.
Key Concepts
-
Decomposition of Organic Matter: The initial step in the formation of natural bitumen.
-
Anaerobic Conditions: Essential for the preservation of potential bitumen from organic matter.
-
Heat and Pressure: Factors that convert organic matter into hydrocarbons over geological time.
-
Petroleum Refining: The process that turns crude oil into usable bitumen as a byproduct.
Examples & Applications
Pitch Lake in Trinidad is a prime example of a natural bitumen source.
The Alberta Oil Sands are a significant site for extracting petroleum-derived bitumen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When natural bitumen is on the scene, decomposition keeps it clean.
Stories
Imagine the journey of sea creatures turning into rock asphalt, preserved through time under heat and pressure.
Memory Tools
Remember 'DOHE' for Decomposition, Oxygen absence, Heat, and Evaporation in natural bitumen formation.
Acronyms
PAV stands for Preheating, Atmospheric Distillation, and Vacuum Distillation in petroleum refining.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Natural Bitumen
A crude form of bitumen found in nature, also known as asphalt.
- PetroleumDerived Bitumen
Bitumen that is a byproduct of refining crude oil.
- Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon, crucial in forming bitumen.
- Evaporation
The process by which lighter fractions of liquid bitumen turn into vapor.
- Anaerobic Conditions
Environmental conditions lacking oxygen, important for preserving organic matter.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
