Summary of Key Concepts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to TCL in Coded Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will delve into the role of TCL in chip design automation. Can someone tell me what TCL stands for?

Tool Command Language!

Exactly! TCL is an interpreted scripting language. It’s great for automating tasks in EDA tools. What do you think are some features of TCL?

Is it easy to use?

Yes, TCL’s syntax is indeed simple and intuitive. This ease of use, along with its integration capabilities, makes it popular. Can anyone summarize a task TCL is often used for in chip design?

Automating tool setup and running simulations!

Well done! TCL helps in managing the setup and execution, allowing more efficiency. Let’s mark this as a mnemonic: TCL = Tasks, Control, Language. Remember that!

To wrap up, TCL helps automate EDA tasks and is adaptable across different environments.
Introduction to Perl in Coded Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss Perl. Who can tell me what makes Perl distinct compared to TCL in our context?

Its text processing capabilities!

That's right! Perl excels at handling strings and parsing large amounts of data, making it suitable for generating reports. Can anyone think of a real design task where Perl shines?

Extracting performance metrics from simulation logs!

Perfect! Perl is great at that. Let’s remember: Perl = Parse, Extract, Report. Who can tell me which scripting tasks Perl handles?

File parsing and data extraction!

Absolutely! The strengths of TCL and Perl complement each other well in automation, enabling robust design workflows. Remember this synergy!
Benefits of Automation Scripts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, why automate tasks in chip design? What are the benefits?

It reduces manual effort and errors!

Exactly! Automation through scripts enhances consistency. What about efficiency?

It saves time by handling repetitive tasks!

Exactly right! By automating simulation and synthesis, we can focus on more critical design aspects. What can we say about combining TCL and Perl?

Using both together can enhance our design workflows!

Well put! By leveraging both languages, we craft a robust strategy for tackling design challenges.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the roles of TCL and Perl in chip design automation, highlighting their unique features and advantages. It emphasizes how these languages improve efficiency and reliability in complex design workflows by automating various processes.
Detailed
Summary of Key Concepts
In this section, we explore the significance of TCL (Tool Command Language) and Perl within the domain of chip design automation. Both are widely utilized scripting languages that automate tasks, thereby enhancing the efficiency of chip design processes which are increasingly complex.
Key Points:
- TCL's Role: Primarily for automating interactions with Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools. It offers features like ease of use, cross-platform support, and extensibility.
- Perl's Role: Excels in text manipulation and integration with external systems, making it ideal for file parsing and report generation.
- Automation Benefits: Scripts crafted in these languages streamline design tasks such as simulations, synthesis, and verification, allowing designers to integrate workflows more effectively and improve productivity.
- Combining Strengths: Utilizing both languages together can result in robust strategies for handling chip design and verification tasks, making the overall design process more efficient.
Youtube Videos

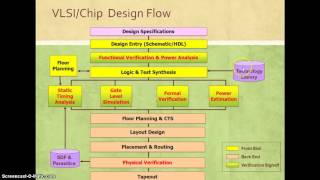
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Scripting Languages in Chip Design
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● TCL and Perl are both widely used scripting languages for automating tasks in chip design automation.
Detailed Explanation
TCL (Tool Command Language) and Perl are two widely recognized scripting languages utilized in the semiconductor industry. They play a crucial role in automating various tasks associated with chip design, making the design process more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of TCL and Perl as powerful assistants in a busy kitchen. Just as a skilled chef relies on sous chefs to automate certain tasks—like chopping vegetables or measuring ingredients—designers use these scripting languages to automate repetitive tasks in chip design.
TCL's Role in Automation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● TCL is commonly used for interfacing with EDA tools, while Perl excels at file parsing and report generation.
Detailed Explanation
TCL is primarily utilized for direct interaction with Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools, enabling designers to automate technical tasks such as simulations and tool configurations. In contrast, Perl is particularly adept at parsing text files and generating reports, making it ideal for managing outputs from simulations and extracting useful data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine TCL as the technician who operates the machines in a factory and Perl as a data analyst who follows up by analyzing the data produced and creating reports. Together, they enhance productivity in the factory (design process).
Benefits of Automation in Design Processes
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Automation scripts help streamline design processes, such as simulation, synthesis, and verification.
Detailed Explanation
Using automation scripts reduces the time and effort required for repetitive tasks in chip design. These scripts facilitate quicker simulations, effective synthesis of designs, and thorough verification processes, all of which are essential for ensuring the quality of the final product.
Examples & Analogies
Consider automation scripts like conveyor belts in a manufacturing setting. Just as conveyor belts move items through various stations efficiently, automation scripts help guide design tasks smoothly through different stages of development.
Integrating TCL and Perl for Enhanced Workflows
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● By combining the strengths of both TCL and Perl, designers can create robust, efficient workflows for chip design and verification tasks.
Detailed Explanation
Integrating both scripting languages allows designers to leverage the strengths of each. TCL's strengths in interacting with EDA tools complement Perl's capabilities in data handling and reporting. This synergy creates an efficient workflow that can adapt to various challenges in chip design.
Examples & Analogies
Think of combining TCL and Perl as a team of experts in a project: one member excels at operating machinery (TCL), while another is great at analyzing results and presenting them (Perl). This collaboration leads to superior results and smoother processes.
Key Concepts
-
TCL and Perl are scripting languages used in chip design automation.
-
TCL is primarily used for EDA tool interfacing.
-
Perl is known for text processing and report generation.
-
Automation increases efficiency and consistency in design workflows.
-
Combining TCL and Perl enhances design automation strategies.
Examples & Applications
A TCL script automating the setup of a simulation environment, improving consistency and efficiency.
A Perl script parsing simulation logs to extract performance data for reporting.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
TCL for the tasks we see, makes design easier and error-free!
Stories
Imagine a factory where tools make all the parts quickly and precisely; TCL guides them like a conductor.
Memory Tools
For TCL, remember: Tasks Control Language. For Perl, it's Parse Extract Report.
Acronyms
TCL - Tasks, Control, Language; Perl - Parse, Extract, Report.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- TCL (Tool Command Language)
An interpreted scripting language widely used for automating tasks in Electronic Design Automation (EDA).
- Perl
A high-level, interpreted programming language known for its powerful text processing capabilities.
- EDA (Electronic Design Automation)
Software tools used to design electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards.
- Simulation
The process of modeling operations of a system to assess its performance under various conditions.
- Automation
Using technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, increasing efficiency and reliability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
