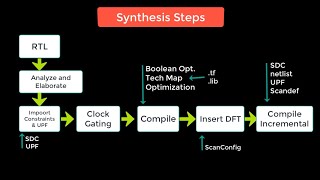
Technology Mapping
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Technology Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Alright class, today we are delving into technology mapping, which is essential in the logic synthesis process. Can anyone explain what technology mapping does?

Isn't it about converting Boolean functions into actual gates?

Exactly! Technology mapping transforms minimized Boolean logic into standard cell representations, ensuring designs are ready for manufacturing. Remember the acronym MAP - **M**apping **A**lgorithms for **P**erformance.

Interesting! So, what types of mapping are there?

Great question! There are two main types: cell-based mapping, which directly utilizes standard cells, and technology-independent mapping that optimizes without considering specific gates initially.

What’s the advantage of technology-independent mapping?

It often leads to better logic simplification. However, it can be more computationally intensive. Remember, more optimization can mean more processing power required!

So, it’s a balance between efficiency and simplicity?

Precisely! Balancing these aspects is crucial in designing efficient VLSI circuits.
Cell-Based Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive deeper into cell-based mapping. Can anyone remind us how this approach functions?

It directly maps Boolean functions onto cells from the technology library, right?

Exactly! We use algorithms like the A* search to find the most efficient configurations of gates. This process is like playing a puzzle, where you fit pieces together for optimal performance.

Why is finding an efficient configuration important?

Well, efficient configurations can minimize area and improve performance, which are both crucial in VLSI design. Think of it as optimizing space in your backpack for school—every inch counts!

So, less area means less cost?

Exactly! Reducing area can lead to cheaper chip manufacturing costs, essential in the competitive tech industry.
Technology-Independent Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s explore technology-independent mapping. Who can summarize its key characteristics?

It first optimizes Boolean functions without worrying about actual gates and only maps them afterward.

Right! This approach allows for potentially better performance optimization since it simplifies logic before committing to a specific technology.

Are there any downsides to this approach?

Yes, it can be computationally expensive, requiring more processing time and resources. Keep in mind the balance of optimization and performance!

So, in the end, both methods have their pros and cons?

Absolutely! Engineers must decide which method to apply based on the specific project requirements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details the process of technology mapping within logic synthesis, highlighting two main categories: cell-based mapping and technology-independent mapping. It discusses their approaches, advantages, and how they aim to efficiently implement logic while meeting area and performance constraints.
Detailed
Technology Mapping
Technology mapping is a pivotal component in the logic synthesis process, transitioning from minimized Boolean functions to actual gate implementations using standard cells from a technology library. This process is essential for ensuring that the logical design aligns with physical constraints and performance metrics.
Two Main Categories of Technology Mapping:
- Cell-Based Mapping:
- This method directly assigns Boolean functions onto available cells from the technology library.
- Algorithms, such as the A* search algorithm, are used to identify optimal implementations of the functions in terms of the number of gates and their interconnections.
- Technology-Independent Mapping:
- Here, Boolean functions are first optimized without reference to specific gates, allowing for greater logical simplification.
- The mapping to specific gates occurs later, which can be more efficient overall, although it may involve higher computational complexity.
In conclusion, technology mapping is crucial for transforming logical representations into manufacturable designs, ensuring that the final implementation adheres to both area and performance requirements.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Technology Mapping
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Once Boolean functions are minimized, the next step in logic synthesis is mapping these functions to actual gates from a given technology library. Technology mapping ensures that the logic is implemented using standard cells (e.g., AND gates, OR gates, multiplexers) in a way that meets both area and performance requirements.
Detailed Explanation
Technology mapping is the process that comes after we minimize the Boolean functions of a digital circuit. Its purpose is to assign these functions to real hardware components, which we call standard cells, like AND gates or OR gates. This process needs to consider both how much physical space the circuit will take on a chip (area) and how fast it can perform its functions (performance).
Examples & Analogies
Think of technology mapping like assembling furniture from a flat-pack kit. After you’ve planned out the design of the furniture and figured out what pieces you need (minimized functions), you have to put it all together with the right screws and joints (mapping to gates) to ensure it fits and is sturdy (area and performance).
Main Categories of Technology Mapping Algorithms
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The two main categories of technology mapping algorithms are:
● Cell-Based Mapping: This approach maps Boolean functions directly onto cells from the technology library. Algorithms like the A search algorithm* are used to find the most efficient way to realize the Boolean function in terms of gates and connections.
● Technology-independent Mapping: This approach first optimizes the Boolean function without considering the actual gates available, and only later maps them to specific gates. This approach can be more efficient in terms of logic simplification but can be computationally expensive.
Detailed Explanation
There are two primary ways to execute technology mapping. In cell-based mapping, the Boolean functions are directly linked to specific components or gates from the technology library. Here, algorithms, like the A search algorithm, help identify the best configuration for implementing the circuit efficiently. On the other hand, technology-independent mapping focuses first on simplifying the Boolean functions without worrying about which gates to use. After simplification, it determines the appropriate gates to implement. While this method may simplify the logic, it might take more time and computing resources.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're organizing a collection of books. In the first approach (cell-based mapping), you put them directly onto shelves of specific sizes you’ve already decided on. In the second approach (technology-independent mapping), you first reorganize the books by type and size, and only after that do you look for the right shelves. While reorganizing might help you later, it takes longer at the start.
Key Concepts
-
Technology Mapping: The transition from Boolean functions to standard cells.
-
Cell-Based Mapping: A direct mapping strategy that utilizes gate libraries.
-
Technology-Independent Mapping: Optimization first, mapping later approach.
Examples & Applications
Using a combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates to implement a simplified logic function based on a truth table.
Mapping a minimized Boolean logic function to specific gates in a technology library to create an efficient circuit design.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To map and define, optimize in time—cell or tech wise, design without lies.
Stories
Imagine an architect who optimizes a building's design before selecting materials. Similarly, technology-independent mapping focuses on improving the logic before choosing specific gates.
Memory Tools
Remember MAP: Mapping Algorithms Profitable—they help in efficient technology mapping.
Acronyms
Use CITE for cell-based mapping
**C**ell
**I**mplementation
**T**ech-library
**E**fficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Technology Mapping
The process of converting minimized Boolean functions into actual gates from a technology library.
- CellBased Mapping
A method that maps Boolean functions directly to standard cells available in a chosen technology library.
- TechnologyIndependent Mapping
A mapping approach that first optimizes Boolean functions without considering specific gate implementations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
