Adaptive and Reconfigurable Testability
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Adaptive Scan Chains
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's explore adaptive scan chains. Can anyone share what they understand by the term?

Is it about changing how we scan for faults based on their type?

Exactly! Adaptive scan chains modify their length and configuration depending on the fault type detected during testing. This dynamic approach optimizes testing efficiency. For example, if a specific fault type is identified, the system may adjust the number of scan cells used.

So it's like switching between gears depending on the road conditions?

That's a perfect analogy! Just like a vehicle adapts to roads, adaptive scan chains adjust to different fault conditions. Why do you think this flexibility is advantageous in testing?

It probably saves time and resources, right?

Correct! By adapting, we ensure higher test coverage while optimizing resource usage. To remember 'Adaptive Scan Chains', think 'ASC' - Adjusting Scan Chains for efficiency.
Reconfigurable Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into reconfigurable testing. Why do you think it’s essential for systems, especially after deployment?

Maybe to fix issues without needing to redesign the whole system?

Precisely! Reconfigurable testing helps systems adapt their testability features, such as in FPGAs, even after they're deployed. What does this imply for engineers?

They can solve problems more efficiently and update features as needed.

Exactly! This not only affords greater reliability but also accommodates growth in requirements. Remember, think 'RTP' - Reconfigurable Testing for Progress.

So, RTP means we can enhance designs even after they're out in the field?

Absolutely! In conclusion, both adaptive scan chains and reconfigurable testing play vital roles in ensuring our electronic systems can evolve and remain efficient in testing. Well done, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the significance of adaptive scan chains and reconfigurable testing in enhancing the testability of modern electronic systems, enabling real-time adjustments to testing strategies based on current operational states.
Detailed
Adaptive and Reconfigurable Testability
In today’s rapidly advancing electronic systems, the traditional static testing approaches are becoming insufficient. As circuits become more complex and flexible, the demand for adaptive and reconfigurable testability emerges. This sub-section explores two key concepts: Adaptive Scan Chains and Reconfigurable Testing.
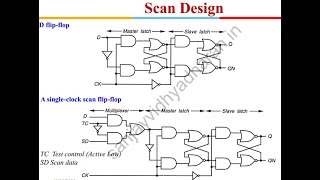
Adaptive Scan Chains
Adaptive scan chains enable a dynamic response to varying fault types. This means that depending on the detection of specific faults, the testing apparatus can modify the length and configuration of the scan chain. For instance:
- If a system detects a hard fault, it may decide to utilize a longer scan chain for a deeper level of debugging.
- Conversely, when testing less severe faults or during routine checks, the system might shorten the chain for efficiency.
Reconfigurable Testing
Reconfigurable testing applies to systems with adaptable hardware elements such as FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays). These systems allow enhancements in their testability features post-deployment. This ability is crucial as it enables modifications without the need for complete system redesign. Key aspects include:
- Post-deployment adjustments: Engineers can adapt the testing protocols based on performance data or emerging faults, enhancing reliability.
- Growth accommodation: Early-stage designs can evolve meeting new requirements without extensive overhauls to existing infrastructures.
In combination, these adaptive and reconfigurable approaches not only promote higher test coverage but also optimize testing efficiency significantly, making them essential in the landscape of modern electronics.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Adaptive and Reconfigurable Testability
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As systems become more flexible and adaptable, the ability to adjust testing strategies in real-time is becoming increasingly important. Adaptive testing and reconfigurable testability are emerging trends that allow systems to dynamically adjust their testability features based on the current operational state.
Detailed Explanation
In today's electronic systems, flexibility is key. Adaptive testing and reconfigurable testability means that a system can change its testing methods on the fly, responding to different conditions or faults that may arise during operation. This ability ensures that the testing process is not static but instead is responsive to the needs of the system at any given moment.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a car that can switch its diagnostic methods depending on whether it’s on a highway or in a city. In the same way, adaptive testing allows electronic systems to modify their testing strategies based on their current operation.
Adaptive Scan Chains
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Adaptive scan chains adjust the scan length and configuration based on the type of fault being tested. For example, the system can dynamically change the number of scan cells or adjust the length of the scan chain to optimize testing efficiency for different parts of the system.
Detailed Explanation
Adaptive scan chains are specialized systems that can change how they conduct tests based on what they need to check. If a certain type of fault is being looked for, the scan chains can either shorten or lengthen, which helps to focus testing efforts where they are needed most, thereby improving overall efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how a chef might change a recipe based on available ingredients. If a certain spice is missing, they might alter the cooking times or methods. Similarly, adaptive scan chains adjust their configuration based on the specific faults needing examination.
Reconfigurable Testing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Systems with reconfigurable hardware (e.g., FPGAs or dynamic logic circuits) allow testability features to be modified or added after deployment. This reconfigurability enables post-deployment testing and maintenance without the need for redesigning the entire system.
Detailed Explanation
Reconfigurable testing is a very practical and modern approach. It refers to the capability of certain hardware to change its testing features even after the system has been deployed. This means that if a problem arises after a device is already being used, engineers can update the testing methods or add new features without having to reconstruct the entire system.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a smartphone that can receive system updates. Just like how software updates can enhance the phone's functionality after it’s been released, reconfigurable testing enables hardware systems to adapt and improve their testing capabilities post-deployment.
Key Concepts
-
Adaptive Testing: The ability of testing systems to adjust in real-time based on operational State.
-
Reconfigurability: The design property that allows enhancements or modifications after a system is deployed.
Examples & Applications
An adaptive scan chain that changes its configuration to handle different types of circuit faults without manual intervention.
Utilizing an FPGA that enables updates in testing protocols based on system performance data acquired post-deployment.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Scan it short, or make it long, adjust the test where it belongs!
Stories
Imagine a smart testing robot that changes its arm's length based on the tools it needs for each task, optimizing its movement effortlessly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'ART' for Adaptive and Reconfigurable Testing.
Acronyms
‘ASC’ stands for Adaptive Scan Chains, helping you remember its dynamic nature.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Adaptive Scan Chains
Dynamic testing frameworks that adjust their length and configuration based on the type of fault detected.
- Reconfigurable Testing
Testing methods that allow systems to modify or enhance their testability features after deployment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
