Reconfigurable Testing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Reconfigurable Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore reconfigurable testing and how it plays a crucial role in modern electronic systems. Can anyone tell me what they think reconfigurable testing means?

Is it about changing how something is tested while it's already in use?

Exactly! Reconfigurable testing allows systems to adapt their testing strategies on-the-fly based on the current operational state. Now, how do you think this could benefit an electronic device?

It would help find and fix issues without needing to stop everything or redesign the device.

That's a great point! This flexibility reduces downtime and enhances overall system reliability.
Adaptive Scan Chains in Depth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve deeper into adaptive scan chains. Can anyone explain what they think adaptive scan chains do?

They change how many scan cells are used based on what faults we’re checking?

That's correct! Adaptive scan chains dynamically alter their configuration to optimize testing for different types of faults. Why might this be preferable than traditional fixed scan chains?

Because different parts of the circuit might need different testing approaches?

Exactly! It leads to better fault coverage and more efficient testing. Remember, adaptive scanning optimizes testing efficiency based on the faults present.
Reconfigurable Hardware Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about reconfigurable hardware. What are examples of reconfigurable hardware that can aid in testing?

FPGAs, right?

Yes, FPGAs! They allow features to be modified or added post-deployment. Why do you think this is beneficial?

It means we can fix or improve the system without starting over from scratch.

Exactly! This capability enhances maintenance and reduces costs, vital for long-term reliability.
Real-World Application of Reconfigurable Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s consider real-world applications. How do you think reconfigurable testing could impact industries like aerospace or healthcare?

In critical systems, it would mean fewer failures because we can adapt testing as the device operates.

And less downtime means better overall performance and safety.

Absolutely! The agility offered by reconfigurable testing can significantly enhance system performance and safety in high-stakes environments. Remember, adapting testing in real-time is not just beneficial; it’s essential.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Reconfigurable testing allows for the adaptation of testing strategies in real-time by utilizing hardware that can be reconfigured post-deployment. This approach assists in optimizing testing processes while accommodating various types of faults effectively, ensuring both efficiency and reliability.
Detailed
Reconfigurable Testing
Reconfigurable testing is a vital advancement in Design for Testability (DFT) as it allows systems to adapt their testability features dynamically based on their current operational state. In this context, two primary concepts emerge:
Adaptive Scan Chains
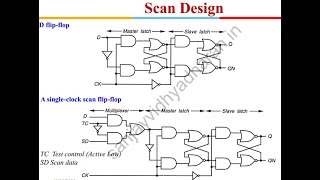
Adaptive scan chains are a key innovation that modifies the scan length and configuration according to the type of fault being tested. For instance, if a specific fault type is detected, the system can change the number of scan cells or adjust the scan chain length to optimize testing efficiency based on different segments of the circuit, resulting in more focused testing.
Reconfigurable Hardware
Systems that incorporate reconfigurable hardware such as FPGAs or dynamic logic circuits allow modifications to testability features even after deployment. This means that engineers can implement post-deployment testing and maintenance without needing to redesign the entire system. Such flexibility can be critical in maintaining performance and reliability in a fast-evolving technological landscape.
The ability to implement reconfigurability not only enhances troubleshooting and maintenance capabilities but also contributes significantly to the overall cost-effectiveness and longevity of electronic systems.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Adaptive Scan Chains
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Adaptive scan chains adjust the scan length and configuration based on the type of fault being tested. For example, the system can dynamically change the number of scan cells or adjust the length of the scan chain to optimize testing efficiency for different parts of the system.
Detailed Explanation
Adaptive scan chains allow systems to modify their testing approach depending on the particular faults they are trying to identify. This means that if a specific type of fault is known to occur, the system can automatically adjust how it tests different sections. For instance, by changing the number of scan cells—essentially the elements that read and write data in the test process—the system can focus more effectively on the areas most likely to have issues. This leads to more efficient testing and quicker fault identification.
Examples & Analogies
Think of adaptive scan chains like a customizable toolbox. If you're working on a specific project that requires different tools, you might adjust which tools you take out based on the tasks at hand. Similarly, adaptive scan chains adjust their configurations based on what faults are present in the system being tested.
Reconfigurable Testing
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Systems with reconfigurable hardware (e.g., FPGAs or dynamic logic circuits) allow testability features to be modified or added after deployment. This reconfigurability enables post-deployment testing and maintenance without the need for redesigning the entire system.
Detailed Explanation
Reconfigurable testing involves hardware like Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), which can be updated or modified even after they are already in use. This is important because it allows engineers to fix or enhance the testing features of a system without needing to go through a complete redesign. For instance, if new testing strategies become available, the hardware can be reprogrammed to utilize them, ensuring that the system remains reliable and maintainable over time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine living in a house where you can change the layout of the rooms whenever you want. If you find that the living room is too small, you could rearrange the walls or add more space without building a new house. Similarly, reconfigurable hardware allows engineers to adapt the system for better testing without starting from scratch.
Key Concepts
-
Reconfigurable Testing: Facilitates adjustments to testing strategies in real-time, allowing efficient fault detection.
-
Adaptive Scan Chains: Modify their configurations dynamically, enhancing testing coverage based on specific faults.
-
FPGAs: Reconfigurable hardware enabling testing strategies to be modified post-deployment for ongoing maintenance.
Examples & Applications
Using adaptive scan chains, a device can configure different scan lengths to test different sections efficiently based on the identified faults.
FPGAs allow engineers to adjust the testing architecture even after the system is deployed, which is crucial for real-time applications.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Reconfigurable testing is a clever way, to test and adjust, come what may.
Stories
Imagine a smart robot that can change its tools when faced with different tasks, enhancing its ability to work effectively.
Memory Tools
Remember 'R.A.R': Reconfigurable Adaptation for Reliability.
Acronyms
RAFT
Reconfigurable Adaptive Fault Testing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Reconfigurable Testing
A testing approach that allows adjustments to testability features dynamically based on current operational states.
- Adaptive Scan Chains
Scan chains that adjust their configurations in real-time to optimize testing for various fault types.
- FPGAs
Field Programmable Gate Arrays, a type of reconfigurable hardware that can have its functionality modified after deployment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
