Transition and Path Delay Faults
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Transition Faults
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into transition faults. Does anyone know what a transition fault is?

Is it when the signal takes too long to change from one state to another?

Exactly! Transition faults occur when signals do not transition between logical states at the required speed. This delay can disrupt circuit function.

Why is that a problem in high-speed circuits?

Great question! In high-speed circuits, even a slight delay can cause timing violations, leading to critical errors. Think of it like a race where even one slow runner can affect the overall result.

How do we address these faults?

Good point! We use advanced fault modeling techniques to detect and analyze these faults methodically.

Can you give an example of such a technique?

Sure. Techniques like transition fault testing allow us to simulate and identify where these delays might occur.

To summarize, transition faults are timing issues in circuits that can lead to malfunctions, especially in high-speed applications. Utilizing fault modeling helps us identify and mitigate these risks.
Exploring Path Delay Faults
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore path delay faults. Who can tell me what this means?

Is it related to the overall delay across multiple gates?

Correct! Path delay faults refer to the delays that occur along the path between two points in the circuit. It's crucial for ensuring that the data transfer happens correctly.

What happens if one path has a significant delay?

If one path is delayed, it could mean that other paths may finish earlier. This discrepancy can cause data corruption or misinterpretation.

How do we test for these faults effectively?

We employ advanced testing techniques, including dynamic simulation and timing analysis, to accurately model the possible delays.

So, implementing these tests helps prevent potential failures?

Exactly! Proper testing and validation of paths help ensure overall circuit reliability and performance.

To summarize, path delay faults can severely impact circuit functionality due to propagation delays along paths. Employing advanced testing techniques allows us to ensure system integrity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section focuses on transition and path delay faults, which can severely affect circuit performance by causing signals to delay beyond required parameters. It highlights the necessity for advanced fault models to identify and mitigate these timing issues in modern electronic designs.
Detailed
Transition and Path Delay Faults
Transition and path delay faults are critical considerations in modern circuit designs as they pertain to the integrity of timing in complex systems. These faults arise when signals take longer than specified to propagate through a circuit, potentially leading to timing violations and, consequently, malfunctioning systems.
Importance of Modeling
Advanced fault models specifically designed for detecting transition and path delay faults have become essential tools for engineers. These models enable the identification of subtle timing issues in high-speed circuits and facilitate corrections, leading to more reliable designs. By addressing the nuances of signal propagation, engineers can ensure enhanced performance and reduced errors, making these models vital in the context of comprehensive Design for Testability (DFT) strategies.
Youtube Videos

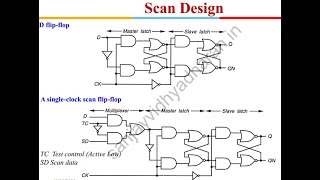

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Transition and Path Delay Faults
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These models focus on ensuring that the timing of signal transitions is correct across all paths, particularly in multi-clock or high-speed systems.
Detailed Explanation
Transition and path delay faults relate to the way signals travel through a circuit. When a signal transitions from one state to another (like from off to on), it needs to do so within a specific time frame. If it takes too long, the circuit can malfunction, typically in high-speed or multi-clock systems where timing is critical. This section discusses how the fault models can help to ensure that these timings are correct across all parts of the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a relay race where runners must exchange the baton smoothly as they pass the finish line. If one runner is slow to make the handoff, the team could lose the race. Similarly, if a signal is delayed in a circuit, it may not function correctly, just as miscommunication can cause a race team to falter.
Impact of Delay Faults
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These faults occur when signals do not propagate through the circuit within the required timing parameters, which can lead to malfunctioning systems.
Detailed Explanation
Delay faults are significant because when signals are delayed beyond acceptable limits, they can cause circuits to behave unpredictably. This could mean that a device might freeze, crash, or work improperly, which is especially troublesome in high-speed applications like computers or telecommunications systems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how traffic lights work in busy intersections. If one light takes too long to change, it can cause confusion and traffic jams. Similarly, in a circuit, if signals don't arrive when they're supposed to, it can lead to system failures, much like a poorly timed traffic light can lead to chaos on the road.
Key Concepts
-
Transition Faults: Delays in the signal changing from one state to another.
-
Path Delay Faults: Delays in the signal propagation through circuit paths.
-
Fault Modeling: A technique used to simulate and detect faults.
-
Timing Violations: Occurrences where actual signal timing does not meet specifications.
Examples & Applications
In a high-speed flip-flop circuit, if the clock signal transitions too slowly, it can cause a transition fault resulting in incorrect data being latched.
A digital design with multiple paths may experience a scenario where one path has a delay, causing misalignment in output signals, showcasing path delay faults.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When signals delay, count the ways, transition faults cause dismay!
Stories
Imagine a runner who trips on a delayed signal in a relay race. This misstep represents a transition fault, where timing can derail the entire race outcome.
Memory Tools
Think of 'P' for Path and 'D' for Delay to remember Path Delay Faults.
Acronyms
Use TOS for Transition and Operating Speed to remember the essence of transition faults.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Transition Faults
Delays that occur when signals do not transition between logical states within the required timing parameters.
- Path Delay Faults
Delays in the signal propagation along paths in a circuit from one point to another, which can affect overall circuit performance.
- Fault Modeling
A methodology for identifying potential faults in circuits through simulated analysis.
- Timing Violations
Situations where a signal's propagation does not adhere to the designated timing requirements, potentially leading to circuit malfunctions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
