Conclusion
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Value of Radix-2 FFT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are concluding our exploration of the Radix-2 FFT. Can anyone tell me why we consider the Radix-2 FFT so significant in digital signal processing?

I think it’s because it’s faster than the standard DFT computation.

Right! It reduces the complexity from O(N²) to O(N log N).

Exactly! This efficiency makes it feasible for real-time analysis of large datasets. Does anyone know why the reduction in complexity is important?

Because handling large datasets can be very time-consuming and CPU intensive!

Correct! Smaller operation counts mean faster processing times. Let’s summarize this key point: the Radix-2 FFT is essential for efficient processing in applications like audio and image analysis.
Applications of Radix-2 FFT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss where Radix-2 FFT is applied. What are some fields where this algorithm plays a crucial role?

I know it’s used in audio processing, like for equalization!

It’s also used in image processing and in radar systems.

Good examples! The Radix-2 FFT is indeed widely utilized in audio, image processing, and communications. Can anyone think of a specific technology that uses it?

Wi-Fi and LTE use FFT for their modulation techniques!

Exactly! The use of FFT in technologies like OFDM highlights its importance in modern communication systems. Remember, understanding the applications helps grasp the significance of this algorithm.
The Importance of DFT Understanding
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up, let’s talk about why understanding the DFT is crucial for grasping FFT concepts. Can anyone share their thoughts?

The DFT is the foundational concept upon which FFT is built. If we don’t understand DFT, how can we grasp FFT?

Exactly! It’s like knowing the rules before playing a game.

Right! The DFT gives us the framework of frequency analysis, and FFT optimizes this framework. Let’s conclude by reiterating that mastering the DFT is vital for anyone looking to apply the Radix-2 FFT effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This conclusion summarizes the significance of the Radix-2 FFT algorithm, highlighting its efficiency in transforming the DFT calculation from O(N²) to O(N log N) and its applications in signal processing and real-time analysis of large datasets.
Detailed
Conclusion
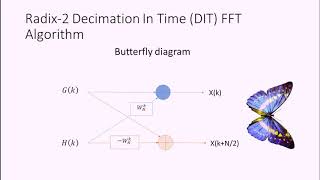
The Radix-2 Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is recognized as one of the most efficient algorithms for computing the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). The ability of the Radix-2 FFT to recursively break down the DFT computation into smaller parts allows it to reduce the computational complexity from O(N²) to O(N log N), which is particularly beneficial for analyzing large datasets in real-time applications. Understanding the Radix-2 FFT’s derivation and its extensive applications in areas like spectral analysis, filtering, and signal compression is crucial for anyone involved in digital signal processing.
Youtube Videos
![Decimation In Time - Fast Fourier Transform [Lec 2]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/XeJXx-Te1Eo/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Radix-2 FFT
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Radix-2 FFT is an efficient and widely used algorithm for computing the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT).
Detailed Explanation
The Radix-2 Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is an algorithm specifically designed to quickly compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of data sequences. The DFT is an important mathematical tool used to analyze the frequencies present in signals, but calculating it via the standard method can be very slow, particularly for large datasets. The Radix-2 FFT streamlines this process by breaking the DFT computation into smaller, more manageable parts, which allows for faster calculations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to calculate how much time each section of a long movie takes. If you listen to the whole movie at once, it takes a significant amount of time. Instead, if you break the movie into smaller scenes and analyze each scene individually, you can get through the entire process much faster. The Radix-2 FFT does something similar with the DFT.
Efficiency of Radix-2 FFT
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
By recursively breaking down the DFT computation into smaller DFTs, the Radix-2 FFT reduces the computational complexity from O(N²) to O(Nlog N), making it feasible to analyze large datasets in real-time applications.
Detailed Explanation
The primary advantage of the Radix-2 FFT is its significant reduction in computational complexity. This means that as the size of the data (denoted as N) increases, the time taken to compute the FFT grows much more slowly compared to the traditional methods. Instead of needing to perform N squared calculations, which can be extremely time-consuming, the Radix-2 FFT requires only around N times the logarithm of N operations. This efficiency is especially crucial for applications that require processing large amounts of data quickly, such as in telecommunications or multimedia.
Examples & Analogies
Consider organizing a large group of people for a concert. If you consider the traditional approach of pairing each person with every other person individually, it becomes a daunting and time-consuming task with a lot of unnecessary steps. However, if you organize them in smaller groups and handle each group separately (like breaking down the data in Radix-2 FFT), you can significantly speed up the process, allowing the concert to get started quickly.
Importance in Signal Processing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The understanding of how the Radix-2 FFT works, its derivation, and its applications is essential for anyone working in signal processing, especially for tasks like spectral analysis, filtering, and signal compression.
Detailed Explanation
For practitioners in the field of signal processing, knowing how to implement and utilize the Radix-2 FFT is fundamental. This algorithm is not only a cornerstone for analyzing frequency components of signals—essential for tasks such as audio processing and communications—but it also plays a crucial role in other areas where signal manipulation is essential. For example, techniques involving filtering (removing unwanted frequencies) or compressing data (for efficient storage) heavily rely on the FFT to operate effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a professional chef who must know different cooking techniques, including chopping, boiling, and frying. Just as a chef relies on their skills to prepare delicious meals efficiently, a signal processing engineer uses the Radix-2 FFT to efficiently analyze and manipulate signals, ensuring high-performance results in tasks such as refining audio quality or optimizing data storage.
Key Concepts
-
Computational Efficiency: The Radix-2 FFT significantly reduces the complexity of DFT calculation.
-
Real-time Application: Its efficiency permits analysis of large datasets in real-time.
-
Signal Processing Applications: FFT is widely used across various fields, enhancing technologies like audio, image processing, and communications.
Examples & Applications
The Radix-2 FFT can compute the DFT of a signal composed of multiple frequencies much faster than traditional methods.
In digital communications, FFT enables efficient modulation and demodulation processes, improving data transmission rates.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every signal we inspect, Radix-2 FFT's what we select.
Stories
Imagine a chef with a recipe, needing to cut vegetables quickly. By using Radix-2 FFT, he divides and conquers, preparing his dish efficiently!
Memory Tools
RAPID – Radix Algorithm Processes Information Dynamically.
Acronyms
FFT – Fast Fourier Transform saves Time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Radix2 FFT
An algorithm that computes the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) efficiently by recursively breaking it down into smaller DFTs.
- Discrete Fourier Transform
A mathematical transformation used to convert a sequence of values into components of different frequencies.
- Computational Complexity
A measure of the amount of computational resources that an algorithm requires, typically measured in terms of time and space.
- Signal Processing
The analysis, interpretation, and manipulation of signals, particularly in digital form.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
