Vibration Control using TMDs (Tuned Mass Dampers)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to TMDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss Tuned Mass Dampers, or TMDs. A TMD is specifically designed to reduce the vibrations of structures during seismic events or high winds. Can anyone tell me what major role TMDs play in structural engineering?

They help stabilize buildings during earthquakes by reducing vibrations.

Exactly! By tuning the frequency of the damper to match the building's frequency, we can effectively mitigate the vibrations. Remember the term 'natural frequency'—it’s crucial for successful TMD design.
Design Considerations for TMDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When designing a TMD, the first consideration is the natural frequency. What do you think happens if the TMD's frequency is not correctly tuned?

It might not work as intended or could even amplify the vibrations, right?

Right! This leads to the importance of tuning. Can anyone provide an example of where such dampers are used?

In skyscrapers, like the Tokyo Skytree!

Correct! It minimizes movement during strong winds and seismic shaking, ensuring structural safety. Remember the acronym 'TMD' — it stands for Tuned Mass Damper.
Application and Effectiveness of TMDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

TMDs are widely used in various structures. Why do you think they are preferred in tall buildings?

Because tall buildings are more vulnerable to wind and seismic forces?

Exactly! The damping effect helps control oscillations. Quick tip: think of TMDs as 'balancers'—they counteract the forces acting on the building.

So, having them is crucial for occupant comfort, especially in high-rise buildings?

Absolutely! Always consider the comfort and safety of the occupants when integrating structural dampers.
Operational Principles of TMDs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Think about how TMDs operate. They consist of a mass, spring, and damper. Can anyone explain why the spring is essential?

The spring allows the damper to oscillate, right?

Exactly! The spring's tension must balance the forces from the structure’s movement. Continuous tuning is a critical factor.

So if the building shifts, the TMD shifts in the opposite direction to reduce motion?

Correct! This interaction is what allows TMDs to be so effective. In summary, TMDs are vital for enhancing structural resilience.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the design considerations and operational principles of Tuned Mass Dampers (TMDs). It discusses how TMDs can effectively mitigate vibrations in structures like skyscrapers and towers by providing a mechanical counterbalance, reducing peak displacements and accelerations during seismic events.
Detailed
Vibration Control using TMDs
A Tuned Mass Damper (TMD) is a device used in buildings and structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. It works by using a secondary mass attached to the structure via a spring and damper system, where the natural frequency of the TMD is tuned to match the frequency of the primary structure's vibrations.
Design Considerations
- Natural Frequency Tuning: The TMD must be designed such that its natural frequency closely matches the dominant mode of vibration of the structure it is installed in.
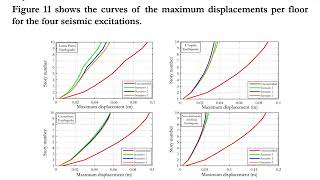
- Peak Reductions: Proper tuning can significantly reduce peak displacements and accelerations during seismic excitation, ensuring that the structure remains safe and comfortable for occupants.
- Applications: TMDs are widely utilized in tall buildings, chimneys, and bridges to enhance stability and reduce the risk of resonance effects from wind or seismic activities.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of TMDs is crucial for engineers working on seismic design and vibration control, contributing to safer and more resilient structural systems.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Tuned Mass Dampers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
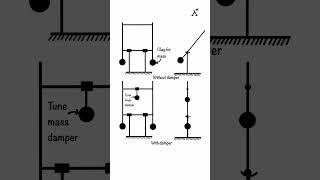
A tuned mass damper is often modeled as a 2-DOF system where one of the masses represents the structure and the second represents the damper.
Detailed Explanation
A tuned mass damper (TMD) is a mechanical device used to reduce vibrations in structures. It involves a system where one mass represents the main structure (like a tall building), while the second mass represents the mass of the damper itself. In a simplified model, we treat this arrangement as a two degree of freedom (2-DOF) system, which helps us analyze how the damper interacts with the structure's natural frequency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a TMD like a pendulum hanging from a moving vehicle. If the vehicle suddenly accelerates or slows down, the pendulum sways back and forth. Similarly, a TMD is designed to sway in a way that counteracts the vibrations of the main structure, much like how the pendulum tries to stabilize the motion of the vehicle.
Design Considerations for TMDs
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• The damper's natural frequency is tuned to the dominant mode of the main structure.
• Proper tuning reduces the peak displacement and acceleration during seismic excitation.
• Widely used in skyscrapers, chimneys, and towers.
Detailed Explanation
For a TMD to effectively minimize vibrations, its natural frequency must be set to match the dominant vibration frequency of the primary structure, like a skyscraper. This process is known as tuning. When this tuning is achieved, the damper effectively absorbs the energy from vibrations, which minimizes movements (displacement and acceleration) caused by seismic activities or wind forces. TMDs are particularly useful in tall structures, where lateral movements during earthquakes can lead to significant discomfort and damage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are at a concert holding a suspended microphone. If the artist moves back and forth at a consistent rhythm, the microphone will sway in sync and stabilize the sound. If you alter the rhythm slightly, the mic might creep too close to your head or sway too much. This is like tuning—if the TMD’s frequency is just right, it stabilizes and minimizes excessive swaying by absorbing energy from the vibrations.
Key Concepts
-
Tuned Mass Damper (TMD): A device used to reduce vibrations by tuning its own frequency to match that of a structure.
-
Natural Frequency: The inherent frequency of a system, crucial for tuning the TMD to synchronize with a structure's oscillations.
-
Damping: The process of reducing vibrational energy to enhance stability and comfort in structures.
-
Resonance: A condition where oscillations amplify due to matching frequencies, which TMDs aim to control.
Examples & Applications
The Taipei 101 uses a massive TMD to stabilize against typhoon winds.
Many modern skyscrapers incorporate TMDs to ensure occupant comfort during seismic events.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Dampers keep buildings from shakes and quakes, keeping structures safe for all our stakes!
Stories
Once there was a tall tower named Sky High. Whenever the wind blew fiercely, it wobbled and shook. To save the tower, clever engineers created a TMD, which counterbalanced the movements, allowing Sky High to stand still and proud against the storm!
Memory Tools
To remember TMD: Tune, Mass, and Damper. Think of a musical band where each member must be in tune!
Acronyms
TMD
Tuning Mass Dampens vibrations effectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Tuned Mass Damper (TMD)
A device used to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations in structures by using a secondary mass tuned to the natural frequency of the structure.
- Natural Frequency
The frequency at which a system oscillates when not subjected to a continuous or repeated external force.
- Damping
The process through which vibrational energy is dissipated, helping to reduce the amplitude of motion over time.
- Resonance
The phenomenon that occurs when a system is driven at its natural frequency, leading to increased amplitude of oscillation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
