Recap of Cauchy Equations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cauchy's Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today we will explore Cauchy's equations, which are pivotal in fluid mechanics. Can anyone tell me what you already know about these equations?

Aren’t they related to fluid motion and forces acting on fluids?

Yes, and I think they help us understand momentum in a fluid.

Exactly! Cauchy's equations help describe the motion of fluids by relating stress to strain. Remember this: 'Stress equals force per unit area,' which is a fundamental concept in fluid mechanics. Now, let’s delve deeper.
Derivation of Navier-Stokes from Cauchy’s Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we progress, we will derive the Navier-Stokes equations from Cauchy’s equations. Why do you think this derivation is important?

It probably helps in understanding complex fluid flows, like around structures.

That's a great observation! By using Cauchy’s equations, we establish the groundwork for analyzing real-world fluid motion. Let's recap: Cauchy’s equations reveal how different forces and motions translate into fluid behavior.
Velocity, Pressure, and Density in Fluid Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we need to understand how velocity, pressure, and density fields maximize our analysis. Can someone explain how these components are interrelated in fluid dynamics?

I believe they all influence each other. For instance, an increase in flow velocity can lead to changes in pressure and density.

Exactly! This relationship is vital when applying Cauchy’s equations. Remember: understand these components well, and you'll unlock the secrets of fluid behavior.
Applications of Cauchy’s Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the applications of Cauchy's equations in engineering. What real-world problems do you think we can solve using these principles?

Maybe predicting the flow patterns around bridges?

Or designing airplane wings to optimize aerodynamics?

Both excellent examples! Remember, Cauchy’s equations pave the way for understanding and improving designs in various engineering fields. Learning these concepts allows us to tackle today’s complex fluid dynamics challenges.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the mathematical foundations of Cauchy’s equations, which serve as the basis for deriving the Navier-Stokes equations in fluid mechanics. The importance of these foundations in computational fluid dynamics is emphasized, alongside the impact of velocity, pressure, and density fields on real-world fluid flow problems.
Detailed
In fluid mechanics, Cauchy’s equations are crucial as they establish the differential forms of linear momentum equations. This section introduces the derivation process leading to the Navier-Stokes equations while emphasizing the role Cauchy’s equations play as foundational principles for computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Throughout the section, students are encouraged to engage with material from recommended sources such as the Sinzel Simbala and Frankman White books which elucidate fluid dynamics with illustrations and solved examples. The discussion covers various concepts, including scalar components of velocity, the concept of stress tensors within fluid flow, and the continuum hypothesis, which allows for the analysis of fluid flow as a continuous medium. Understanding these equations provides insights into predicting and analyzing flow patterns that are essential in a range of engineering applications.
Youtube Videos







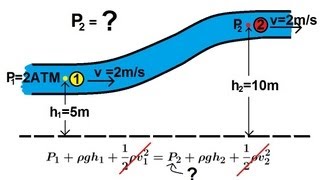
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Cauchy Equations
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Before deriving the Navier-Stokes equations, we derive Cauchy equations, which are very important equations when you go for the differential form of linear momentum equations.
Detailed Explanation
Cauchy equations are foundational in fluid mechanics and represent the differential form of the linear momentum equation. They are critical for understanding fluid motion and form a basis for the more complex Navier-Stokes equations that govern fluid flow. By deriving Cauchy equations first, students gain insight into the fundamental principles of fluid dynamics.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Cauchy equations as the fundamental rules of driving on a road, where each vehicle's speed and direction need to be understood before setting traffic rules (like speed limits). Just as traffic rules help manage flow on the roads, Cauchy equations help manage the flow of fluids.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cauchy equations form the basic foundations of computational fluid dynamics. Today you can see what are the challenging problems we have been solving in this era.
Detailed Explanation
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve problems that involve fluid flows. Cauchy equations are integral to this computational approach, as they describe the physical behavior of fluid motion. They lay the groundwork for approximating solutions to complex flow problems that can be modeled and analyzed using CFD tools.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to predict how a river flows around a bend. Just as knowing the basic rules of water movement helps predict the river's behavior, understanding Cauchy equations enables engineers to model and predict fluid movements in complex systems, such as air around airplane wings.
Velocity Fields and Control Volumes
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Here we have used a CFD software... how the velocity fields are changing.
Detailed Explanation
The concept of velocity fields is pivotal in fluid mechanics. It refers to how the speed and direction of fluid particles change over time and space. In CFD, a control volume is a defined space where calculations are made to evaluate these changes. By analyzing velocity fields, engineers can determine how fluids behave around objects like bridge piers or within sections of a pipeline.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water slide where the speed of water varies at different points due to the slide's shape. By breaking down the slide into segments (like control volumes), you can understand how fast the water will flow at each point, which is crucial for designing safe and effective water parks.
The Role of Stress and Deformations
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When you apply the load on a solid you will have stress formations... reflected in terms of stress components.
Detailed Explanation
Stress in fluid mechanics refers to the internal resistance forces that develop when fluid particles move, similar to how solid materials respond to forces. As fluid flows, changes in stress can lead to deformations, which are essential to understanding how fluids respond to forces. Recognizing these stress components allows engineers to predict how fluids will react under various conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how a sponge behaves when you squeeze it. The stress and resulting deformation help you understand how much liquid the sponge can absorb. Similarly, in fluid mechanics, understanding how forces apply to moving fluids can help predict their changes in shape and flow.
Momentum Flux and Control Volume Analysis
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Now if you look at the computations..., the change of momentum flux within the control volume.
Detailed Explanation
Momentum flux refers to the amount of momentum passing through a unit area per unit time. When analyzing fluid behavior, engineers use control volumes to capture and calculate changes in momentum within defined spaces. This analysis is crucial for deriving conservation laws and equations governing fluid motion, leading to the Cauchy equations.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a busy highway where cars (momentum) move in and out of lanes. By observing how many cars pass a certain point (momentum flux), you can make decisions about traffic management. In fluid dynamics, analyzing momentum flux allows engineers to optimize systems, such as pipelines or airflows, just as traffic engineers optimize highway designs.
Concluding Thoughts
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cauchy equations derived almost 200 years back... Thank you.
Detailed Explanation
Cauchy equations have a historical significance in fluid mechanics, having been derived nearly 200 years ago. Their continued relevance underscores the importance of foundational theories in advanced applications such as CFD. Understanding these equations allows students to tackle modern challenges in fluid dynamics with confidence.
Examples & Analogies
Much like how classic literature can shape modern storytelling, the foundational equations of fluid dynamics like the Cauchy equations shape the way we understand and solve complex fluid flow problems today.
Key Concepts
-
Cauchy Equations: Describe the motion of fluids and are a foundation for fluid mechanics.
-
Navier-Stokes Equations: Govern the dynamics of fluid flow and are essential to computational fluid dynamics.
-
Stress Tensor: Represents internal forces in a fluid and is crucial for analyzing flow patterns.
Examples & Applications
Understanding flow around structures like bridge piers using Cauchy's equations.
Using Navier-Stokes equations in predicting weather patterns through fluid motion analysis.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In fluid flows, Cauchy takes the lead, describing stress in every need.
Stories
Imagine a river flowing around a rock; the way pressure changes tells the story of Cauchy’s equations at work.
Memory Tools
Remember: Cauchy = Continuous, Navier = Nurturing the flow's journey.
Acronyms
C.M.P - Cauchy, Momentum, Pressure
Key elements of fluid behavior.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cauchy Equations
Equations that describe the motion of continuous media and relate stress to strain in fluid mechanics.
- NavierStokes Equations
A set of equations that describe the motion of viscous fluid substances, derived from the principles of Newton's laws of motion.
- Scalar Components of Velocity
Measures of velocity in a fluid that correspond to the three spatial dimensions.
- Stress Tensor
A mathematical representation of internal forces within a fluid, defined in terms of stress components acting on different planes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
