Differential GPS (DGPS)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Concept of DGPS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll be exploring Differential GPS, or DGPS. Can anyone explain what they think DGPS is?

Is it a system that uses satellites like regular GPS?

Exactly! DGPS is indeed based on GPS technology, but it utilizes a base station with known coordinates to make corrections. Who can tell me what kind of errors GPS might have?

There can be satellite clock errors and atmospheric delays.

Great points! DGPS helps correct those errors by sending precise correction signals from a stationary base. This enhances accuracy. Can anyone tell me how accurate DGPS gets?

I think it can improve to about 1 to 3 meters!

Right! DGPS can indeed achieve that level of accuracy. To remember that, think of '1-3' as 'one tree' — just like that tree in the park which needs precise positioning for planting. Let's continue to explore its applications.
Applications of DGPS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about where DGPS is used. What industries do you think might benefit from its accuracy?

Maybe in farming? They need accurate data for planting.

Correct! Precision farming is a perfect application of DGPS. It allows farmers to maximize productivity. Can anyone think of another application?

How about marine navigation?

Absolutely! Safe navigation in oceans requires precise location data, and DGPS greatly enhances that. To remember marine navigation, think of it like a captain steering a ship directly to a safe harbor: every meter counts!

So, DGPS is used in construction as well, right?

Yes! In construction surveys, accurate positioning ensures that structures are built correctly. It’s vital for maintaining design specifications. Remember, DGPS is critical in these industries for safety and efficiency.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
DGPS utilizes a base station with known coordinates to transmit correction signals, significantly improving GPS positioning accuracy to within 1–3 meters. It finds applications in various fields including marine navigation and precision farming.
Detailed
Differential GPS (DGPS)
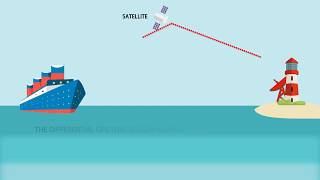
Differential GPS (DGPS) is an enhancement to the standard GPS technology that aims to improve its accuracy. This system operates by using a base station that has known, fixed coordinates. This base station measures the difference between its known location and the location calculated based on GPS signals. By transmitting correction signals to neighboring mobile or rover receivers, DGPS can significantly reduce the errors associated with GPS measurements, achieving an impressive accuracy level of 1 to 3 meters.
Key Applications of DGPS
DGPS is predominantly utilized in areas such as:
- Marine navigation, which requires high precision for safe navigation of vessels.
- Precision farming, where farmers use DGPS in equipment to optimize planting patterns and enhance agricultural productivity.
- Construction surveys, which need accurate positioning to ensure that structures are built to design specifications.
Overall, DGPS represents a critical advancement in GPS technology that significantly supports various industries relying on accurate geolocation.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Concept of DGPS
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Uses a base station with known coordinates to correct errors
• Transmits correction signals to rover receivers
Detailed Explanation
Differential GPS (DGPS) is a system that improves the accuracy of GPS positioning by using correction signals. It involves two main components: a base station and rover receivers. The base station is set up at a location with known coordinates, meaning its precise position is already determined. This station calculates any errors in the GPS signals it receives and sends correction information to the rover receivers, which are often mobile units used in various applications. The rover receivers then incorporate these corrections to enhance their positional accuracy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the base station like a teacher who corrects a student's math test answers. The student (rover receiver) has the answers but needs the teacher (base station) to point out any mistakes so they can accurately understand how to reach the right solution.
Accuracy Improvement with DGPS
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• DGPS can enhance accuracy to 1–3 meters
Detailed Explanation
One of the key benefits of using DGPS is its ability to significantly improve positioning accuracy compared to standard GPS alone. While regular GPS might provide location information that can be off by several meters, DGPS can narrow that down to within 1 to 3 meters. This increased precision is particularly beneficial in applications where exact positioning is crucial—such as in surveying, agriculture, and marine navigation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to hit a target with a dart. Without corrections, you might miss the bullseye by several feet. But with adjustments from DGPS, it's like having a guide that shows you exactly where to aim your dart, increasing your chances of landing right in the center of the target.
Applications of DGPS
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Used in marine navigation, precision farming, construction surveys
Detailed Explanation
DGPS has various applications across different sectors. In marine navigation, it helps vessels determine their precise location, ensuring safe travel across waters. In precision farming, farmers use DGPS to optimize the planting and harvesting processes, ensuring they make the best use of their land and resources. Construction surveys benefit from DGPS by providing high accuracy in determining layouts and boundaries, which is critical for meeting project specifications and ensuring safety.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a precise farmer who uses DGPS in their fields. Just like a chef measuring ingredients accurately to perfect a recipe, the farmer uses DGPS to ensure that every seed is planted at the right spot, leading to better yields and more efficient use of resources, significantly impacting the overall productivity of the farm.
Key Concepts
-
Base Station: A known location that corrects GPS data for other receivers.
-
Rover Receiver: A mobile device that receives corrected GPS signals.
-
Accuracy Improvement: DGPS achieves greater positioning accuracy through corrections.
Examples & Applications
A farmer uses DGPS to optimize planting patterns to improve crop yields.
A shipping vessel employs DGPS for precise navigation through treacherous waters.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In farming fields so wide and clear, DGPS helps steer without fear.
Stories
A captain stood on his ship, reliant on DGPS, knowing every meter made a difference as he navigated through choppy waters safely.
Memory Tools
Remember DGPS as 'Daring GPS', as it bravely corrects our paths with precision.
Acronyms
DGPS
'Dynamic Guidance for Precision Safety'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Differential GPS (DGPS)
An enhancement to GPS that improves its accuracy by using correction signals from a fixed base station with known coordinates.
- Base Station
A stationary GPS receiver with a known location that sends correction signals to rover GPS receivers.
- Rover Receiver
A mobile GPS receiver that receives correction signals from a base station to improve positioning accuracy.
- Accuracy
The degree to which the computed position matches the true position.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
