GPS – Global Positioning System
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
History and Development of GPS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with the history of GPS. Can anyone tell me when GPS was developed?

I think it was developed in the 1970s?

Correct! The U.S. Department of Defense developed GPS in the 1970s, and it became fully operational in 1995. Initially meant for military applications, GPS has since been opened to civilian use. Why do you think that was important?

It expanded its usability to many sectors, right? Such as navigation and surveying.

Exactly! This transition greatly impacts civil engineering and geospatial sciences.
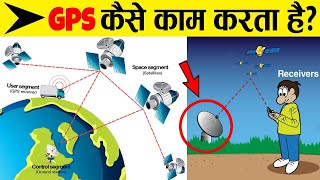
Segments of GPS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into the segments of GPS. Can anyone name the three segments we discussed?

Space, control, and user!

Great! Let's start with the space segment. What does it comprise?

It's made up of at least 24 satellites orbiting the Earth.

Correct! These satellites orbit at about 20,200 km and ensure global coverage. Moving to the control segment, who can tell me its primary functions?

Monitoring satellite health and clock corrections?

Exactly! Now, what about the user segment?

It includes the receivers that calculate positions based on satellite signals.

Correct! This process is essential for civil engineering applications. Can someone summarize why GPS is crucial?

It enhances accuracy for surveying and mapping.

Perfect!
Applications of GPS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss GPS applications in civil engineering. Why do you think GPS is vital for surveying?

It provides rapid and accurate positioning, crucial for surveying and mapping.

Right! GPS improves efficiency and accuracy in site management as well. Can anyone name other applications?

Maybe in disaster management or during construction projects?

Exactly! GPS helps in emergency response and damage assessment too. Let's summarize today's key points.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is integral to accurate global positioning and navigation, initially developed for military applications and later opened to civilian use. This section discusses its historical development, essential components such as the space, control, and user segments, and their relevance in various applications including surveying and infrastructure development.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of GPS - Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a crucial component of the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) framework, specifically designed to provide accurate location and timing information globally. Developed in the 1970s by the U.S. Department of Defense, GPS was deemed fully operational by 1995. While it was originally intended for military applications, its utility was extended to civilian sectors, profoundly impacting areas such as civil engineering, disaster management, and navigation.
Key Components of GPS
- Space Segment:
- Composed of at least 24 satellites orbiting approximately 20,200 km above the Earth in six distinct orbital planes.
- Each satellite completes an orbit around the Earth twice daily, ensuring continuous global coverage.
- Control Segment:
- Managed by a Master Control Station located in Colorado, USA, it includes various ground monitoring stations worldwide.
- Its primary functions include monitoring satellite health, clock corrections, and updating satellite orbits.
- User Segment:
- Involves GPS receivers installed in various mobile devices, surveying equipment, vehicles, etc.
- These receivers utilize signals from satellites to compute three-dimensional geographic positions and precise timing information, thus playing a vital role in various applications, including engineering and mapping.
In summary, GPS demonstrates significant advancements in technology that facilitate accurate positioning, proving essential in contemporary applications ranging from construction management to emergency response.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
History and Development
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s
• Declared fully operational in 1995
• Originally for military use, later opened to civilians
Detailed Explanation
The Global Positioning System (GPS) was developed in the 1970s by the U.S. Department of Defense. Initially designed for military applications, GPS was declared fully operational in 1995. The system was later made available for civilian usage, enabling a wide range of applications beyond military needs, including navigation, surveying, and mapping.
Examples & Analogies
Think of GPS like a tool developed for airplane pilots to navigate during flights. Initially, only pilots could use the tool, but over time, it became available for everyone to assist drivers with directions, hikers in finding trails, and delivery services to optimize routes.
Segments of GPS
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
a) Space Segment
• Comprises a constellation of at least 24 satellites
• Orbiting at ~20,200 km above Earth in 6 orbital planes
• Each satellite orbits Earth twice a day
b) Control Segment
• Master Control Station (MCS) located in Colorado, USA
• Ground antennas and monitoring stations spread globally
• Functions: satellite health monitoring, clock correction, orbit update
c) User Segment
• GPS receivers in mobile devices, surveying equipment, vehicles, etc.
• Receives satellite signals to calculate 3D position and time
Detailed Explanation
GPS systems are divided into three main segments:
- Space Segment: This consists of at least 24 satellites positioned about 20,200 kilometers above the Earth, spread across six orbital planes. Each satellite completes two orbits around the Earth every day, allowing for continuous signal availability.
- Control Segment: This includes the Master Control Station located in Colorado and various ground antennas and monitoring stations worldwide. Its role encompasses monitoring the health of the satellites, correcting their clocks, and updating their orbits to ensure accuracy.
- User Segment: This refers to the devices that receive GPS signals, including mobile phones, surveying equipment, and vehicles. These devices utilize satellite signals to determine their three-dimensional location on Earth as well as the precise time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the GPS as a complex city. The satellites are like streetlights that constantly provide information; the Master Control Station is the city hall ensuring everything runs smoothly and that lights function correctly. The residents are the GPS devices that rely on the light to find their way in the city.
Key Concepts
-
GPS: A system providing global location and time information.
-
Space Segment: Includes orbiting satellites.
-
Control Segment: Manages satellite functions from the ground.
-
User Segment: Receives signals for positioning.
-
Civil Engineering Applications: Uses GPS for accurate surveying and mapping.
Examples & Applications
Using GPS in surveying to determine property boundaries.
Application of GPS in disaster response for location tracking.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
GPS, oh what a mess, satellites above, guiding us with love.
Stories
Imagine a knight who uses enchanted stars to find his way home. Each star represents a satellite, guiding him with perfect precision.
Memory Tools
Remember 'S-C-U' for Space-Control-User segments.
Acronyms
GPS - 'Global Positioning System' is how we navigate!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that uses a constellation of satellites to provide accurate location and time information anywhere on Earth.
- Space Segment
Comprises the satellites in orbit that provide GPS signals.
- Control Segment
Includes ground monitoring stations that manage satellite operations.
- User Segment
Encompasses devices and equipment that receive GPS signals to determine positioning.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
