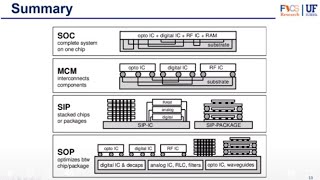
Applications of Surface-Mount Technology
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Surface-Mount Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into Surface-Mount Technology, commonly referred to as SMT. Can anyone tell me what makes SMT different from other packaging technologies like through-hole?

I think SMT components are placed on the surface of the PCB rather than inserted into holes.

Exactly! SMT allows for a denser arrangement of components which means smaller devices. Remember, SMT stands for Surface-Mount Technology, so right away you can link 'Surface' with how components are mounted.

What kind of products use SMT then?

Great question! SMT is frequently used in consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops. It's critical in applications where size and component density are key!
Advantages of SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think are some advantages of using SMT in electronic circuit boards?

I guess it's easier to automate the assembly process since they don't need holes in the PCB.

Absolutely! Automation not only reduces labor costs but also improves consistency. Plus, the layout is much more compact, allowing for more features in a smaller size.

How does that affect performance?

Excellent observation! Smaller components with shorter interconnections lead to faster signal transmission and reduced signal loss. We can summarize with the acronym 'C.A.P.' for Compact, Automated, and Performance-enhanced.
Applications of SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss where SMT is most commonly applied. Can anyone mention an area where SMT has become essential?

I think it's used a lot in smartphones!

Correct! Beyond smartphones, SMT is integral in automotive electronics and medical devices, especially where high-density setups are imperative. Remember: 'High-density designs' is a key phrase for SMT advantages!

What about network equipment?

Spot on! SMT is crucial in network equipment due to the high-speed processing needs. SMT's compact nature supports the increasing demand for functionality in confined spaces.
Final Notes on SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To sum up, Surface-Mount Technology enhances the performance, cost-effectiveness, and density of circuit boards. Who can remember the top applications we've discussed?

Consumer electronics and automotive applications!

And it helps in medical devices and networking too!

Exactly, well done! Remember, SMT is foundational in modern electronics and understanding its applications is key to future design considerations.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the applications of Surface-Mount Technology (SMT), emphasizing its significance in consumer electronics and high-density boards. SMT allows for compact designs, making it the preferred choice for automotive electronics, medical devices, and network equipment, among others.
Detailed
Applications of Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronic manufacturing process by enabling components to be mounted directly on the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technique not only enhances the overall component density but also reduces the size of devices.
SMT finds extensive applications in various fields:
- Consumer Electronics: SMT is prevalent in devices like smartphones, laptops, and home appliances, where compact design and functionality are crucial.
- High-Density Boards: It is ideal for automotive electronics, medical devices, and networking equipment, all of which require high-density layouts paired with efficient performance. The choice of SMT is influenced by its advantages such as smaller form factors, lower production costs due to automation, and improved electrical performance due to shorter interconnection lengths, thus gaining traction in fast-paced technological domains.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Consumer Electronics Applications
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Consumer Electronics: Widely used in consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and home appliances.
Detailed Explanation
Surface-mount technology (SMT) is extensively utilized in the production of consumer electronics. This includes devices like smartphones, laptops, and home appliances. SMT allows for a more compact design since the components can be placed directly on the surface of the printed circuit boards (PCBs) without needing drilled holes. This results in lighter and smaller devices with more features crammed into them.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine packing your suitcase for a trip. The more efficiently you arrange your clothes and items, the more you can fit into the suitcase. Similarly, SMT organizes electronic components efficiently, making it possible to incorporate many features into smaller devices like smartphones.
High-Density Boards Applications
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● High-Density Boards: Ideal for applications requiring compact designs with a high component density, such as automotive electronics, medical devices, and network equipment.
Detailed Explanation
SMT is particularly suited for high-density boards, which are essential in applications where space is at a premium. For instance, in automotive electronics, devices need to be compact yet perform multiple functions. Similarly, medical devices must be reliable and often space-constrained, benefiting from SMT's capacity to place many components efficiently on a small board. Network equipment, like routers and switches, also requires high-density designs to support numerous connections for fast data processing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy city where every square meter of land is utilized for buildings, parks, and roads. Just like urban planners maximize space to fit many functions into a limited area, SMT does the same for electronic components, ensuring that each board can carry out numerous tasks within a confined space.
Key Concepts
-
Surface-Mount Technology: A mounting technique for electronic components that enhances density and reduces size.
-
High-Density Designs: Essential for applications in modern electronics where space is at a premium.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Automation in SMT reduces labor costs and enhances production efficiency.
Examples & Applications
Smartphones utilizing SMT for compactness and efficiency.
Automotive control units that rely on high-density PCBs to manage various functionalities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In today's tech, surfaces we mount, SMT means small, that's what it's about.
Stories
Imagine a tiny smartphone that could pack more features because its components were tightly placed on its surface. This storytelling connects SMT with its real-world benefits.
Memory Tools
Remember 'C.A.P.' for Compact, Automated, Performance-enhanced for thinking about SMT benefits.
Acronyms
SMT = S for Surface, M for Mount, T for Technology.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A method for mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB, allowing for higher component density and smaller device sizes.
- PCB
Printed Circuit Board, a board that connects and supports electronic components.
- Component Density
The number of components per unit area on a PCB, which influences the size and performance of electronic devices.
- Automation
The use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention, particularly in manufacturing and assembly processes.
- Interconnection Lengths
The physical distances between connections of components on a PCB, affecting performance and signal integrity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
