Conclusion
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of IC Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are wrapping up our discussion on IC packaging. Can anyone tell me why selecting the appropriate type of packaging is so crucial in electronic design?

I think it's about durability and how well components can handle stress.

That's a great observation! Through-Hole packaging, for example, offers strong mechanical bonds, making it suitable for high-stress applications. Does anyone remember other factors to consider?

Maybe size and power handling?

Exactly! Size and power capabilities can differ greatly between packaging types. Always remember the mnemonic 'SHAPE' for Size, Heat management, Applications, Performance, and Ease of repair!

How does that apply in real applications?

Excellent question! It helps define which packaging you'll use based on the specific needs of the device. Let’s summarize: understanding these facets aids in designing reliable systems.
Reviewing Packaging Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we conclude, who can recall the advantages of Surface-Mount Technology?

It has higher component density and is cost-effective for mass production!

Right! And what about its downsides?

Less mechanical strength compared to Through-Hole?

Exactly. When deciding between SMT and BGA, what would guide your decision?

I'd look at the needed pin count and power performance.

Well said! BGA shines in high-performance roles due to high pin counts and better heat distribution.

Thanks for the recap, it helps to see the comparisons!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
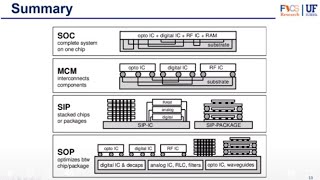
The conclusion synthesizes the key points from the chapter, emphasizing the significance of understanding various packaging technologies. Each type—Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array—offers unique advantages tailored to specific applications, highlighting the need for careful consideration in design.
Detailed
In the conclusion of Chapter 2, we distill the essential learnings about IC packaging types—Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Understanding these packaging technologies is vital for the efficient design and manufacturing of electronic systems. Each packaging type comes with distinct advantages tailored for specific applications, influenced by factors such as size, mechanical strength, thermal management, and intended device functions. By understanding these characteristics, designers can make informed choices that enhance the performance and reliability of electronic products.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of IC Packaging
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding the different types of IC packaging is crucial for designing efficient and reliable electronic systems.
Detailed Explanation
This sentence emphasizes that knowing about different IC packaging types is essential for effective electronic system design. Knowledge of these packages helps engineers choose the right one based on performance, reliability, and specific application needs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like choosing the right container for food. If you have soup, you wouldn’t put it in a basket; you’d use a bowl with a lid. Similarly, electronic components need the right type of packaging to perform efficiently.
Distinct Advantages of Packaging Types
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Through-hole, surface-mount, and ball grid array packaging each offer distinct advantages and are suited for different applications.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk identifies the three main types of IC packaging—through-hole, surface-mount, and ball grid array—that have unique benefits. Understanding these advantages allows designers to select the appropriated packaging for specific applications, such as durability or compactness.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're packing for a trip. If you're going hiking, you might choose a sturdy backpack (through-hole) for heavy gear. If you're going to a fancy dinner, a small stylish bag (surface-mount) would be better. For something like a mobile phone, a compact and multi-functional case (ball grid array) is ideal.
Factors Influencing Packaging Choice
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The choice of packaging technology depends on factors such as size, mechanical strength, thermal management, and the specific needs of the device.
Detailed Explanation
Here, we recognize that the selection of packaging technology is influenced by multiple factors. For instance, if a device needs to be small, surface-mount packaging might be preferred, while a device requiring more strength will benefit from through-hole packaging. Each aspect—like size and thermal management—plays a crucial role in determining the ideal packaging.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like choosing a vehicle for travel. If you're driving through a crowded city, a small car (surface-mount) is efficient. But if you're hauling heavy equipment, you’ll need a truck (through-hole). Each choice depends on your travel needs and conditions.
Key Concepts
-
IC Packaging: The critical step of encapsulating integrated circuits providing support and connections.
-
Through-Hole Packaging: Strong mechanical bonds for durability in high-stress applications.
-
Surface-Mount Technology: Efficient space usage and suitability for automated production.
-
Ball Grid Array: Higher density of connections with improved thermal performance.
Examples & Applications
Through-Hole packages are commonly used in power supplies where high current handling is required.
Surface-Mount components are prevalent in smartphones due to their compact design.
Ball Grid Arrays are often found in high-performance graphics cards for better heat dissipation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Through-Hole's large but can be slow, while SMT offers a compact flow.
Stories
Imagine designing a smartphone; you need it sleek and fast. You'd choose SMT for compactness, while a robust power supply needs the strength of Through-Hole.
Memory Tools
SHAPE = Size, Heat management, Applications, Performance, Ease of repair.
Acronyms
BGA = Big Grid Array, remember it has many small balls to connect.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ThroughHole Packaging
A method of mounting electronic components with leads that pass through holes in the PCB.
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A technique where components are mounted directly on the surface of a PCB without the need for drilled holes.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A surface-mount packaging that uses a grid of solder balls for connections, providing high performance.
- Mechanical Strength
The ability of a component or package to withstand physical stress.
- Thermal Management
Techniques to control the temperature of electronic devices to ensure their performance and reliability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
