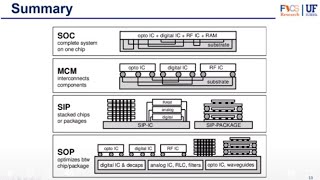
Comparison of Packaging Types
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Packaging Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to compare three main types of IC packaging: Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array. Each of these serves different needs in electronic design. Can anyone tell me why IC packaging is important?

It provides mechanical support and electrical connections!

And it helps manage heat too, right?

Exactly! The packaging not only supports the chip physically but also facilitates how it interacts with other components. Let’s dive into each type, starting with Through-Hole packaging.
Through-Hole Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Through-Hole technology has its roots in earlier electronic designs. What can anyone tell me about its advantages?

I think it's durable, which is good for high-stress environments!

Correct! Strong mechanical bonds make it suitable for high-power applications. What about its downsides?

It's bulkier and takes more time to assemble.

Good points! The size and assembly time make it less ideal for compact designs.
Surface-Mount Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss Surface-Mount Technology. What do you think gives SMT its popularity today?

It allows for a higher density of components, making devices smaller!

Exactly! This high density is ideal for consumer electronics. But what’s a potential downside?

It might not be as strong mechanically, right?

Yes, especially in applications involving vibration. Let’s move on to the Ball Grid Array.
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Ball Grid Array packaging is known for its high pin count. Why is that important?

It allows for more connections in a compact space, which is great for advanced processors!

Exactly! But what is a challenge associated with BGA?

The solder joints are hidden, making it hard to inspect!

Right! Inspection and complex assembly can be tricky, especially in space-constrained devices.
Summary and Comparison
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, how would you summarize the three types of packaging we discussed?

Through-Hole is durable but bulky, SMT is compact but less strong, and BGA has high connectivity but is hard to inspect.

Perfect summary! Each packaging type serves distinct roles in electronics. Remember the advantages and disadvantages as they are critical for making design choices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delves into the three primary IC packaging types—Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array—highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications. Each packaging type serves specific needs in electronic design.
Detailed
Comparison of Packaging Types
In the field of integrated circuit (IC) packaging, various types are utilized to meet specific design requirements. This section reviews the three main packaging types: Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Each type has distinct advantages and disadvantages:
- Through-Hole (TH): Known for its mechanical durability and ease of repair, it is ideal for high-power, military, and prototype applications. However, its larger size and slower assembly time present challenges.
- Surface-Mount (SMT): Offers compact sizes and automated assembly, making it a cost-effective choice for consumer electronics and medical devices. Nonetheless, SMT components can lack mechanical strength and be difficult to repair.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA): Provides a high pin count and superior thermal performance, suitable for high-performance processors and mobile devices. However, its inspection difficulty and complex assembly can pose challenges.
Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the appropriate packaging for electronic systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Through-Hole Packaging
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Through-Hole Packaging
Advantages: Strong mechanical bonds, easier to repair
Disadvantages: Larger size, slower assembly, more costly
Applications: High-power, military, prototype applications
Detailed Explanation
Through-hole packaging is known for its strong mechanical bonds, which means that the components are firmly attached to the PCB. This makes them easier to repair because they can withstand physical stress. However, they take up more space on the board and the assembly process is more time-consuming and costly compared to other methods. Common uses for through-hole packaging include high-power applications, military electronics, and in prototyping where components may need to be replaced frequently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a model using large, sturdy blocks instead of small, delicate pieces. The large blocks (through-hole packaging) are easier to handle and connect securely, making repairs simple. However, they take up more space on your table (larger size), and placing them in position takes more time (slower assembly).
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
Advantages: Compact, high-density, cost-effective, automated
Disadvantages: Less mechanical strength, difficult to repair
Applications: Consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices
Detailed Explanation
Surface-mount technology enables components to be attached directly on the surface of the PCB without the need for holes. This allows for a higher density of components on the board and makes the manufacturing process more automated, which reduces costs. However, SMT components are less mechanically strong than through-hole components, and repairing them can be more challenging. SMT is commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and medical devices where space efficiency is critical.
Examples & Analogies
Think of SMT as fitting as many small toys into a compact box instead of using larger toys which take up more space. The compact toys (SMT components) allow for more items to be included in a single box (the PCB), but if one toy breaks, it's harder to get out (difficult to repair) compared to a larger toy that can be easily removed.
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
Advantages: High pin count, better thermal and mechanical performance
Disadvantages: Difficult inspection, complex assembly
Applications: High-performance processors, mobile devices
Detailed Explanation
Ball Grid Array packaging uses an array of small solder balls for connections, allowing for a high pin count in a compact space. This makes BGAs ideal for high-performance applications because they perform better thermally and mechanically compared to other packages. However, inspecting and repairing BGAs can be difficult since the solder joints are not visible, and the assembly process is complex. BGAs are often found in high-performance processors and mobile devices where performance is essential.
Examples & Analogies
Think of BGAs as a high-tech puzzle where the pieces fit together very tightly and compactly. While this allows for a more intricate design with lots of connections (high pin count), it makes checking if every piece is perfectly placed tricky (difficult inspection). It's like trying to find a specific piece in a jigsaw puzzle that cannot be easily viewed because they are stacked on top of each other (complex assembly).
Key Concepts
-
Through-Hole Packaging: Ideal for high-power applications due to its mechanical strength.
-
Surface-Mount Technology: Allows high-density component placement but can be less robust mechanically.
-
Ball Grid Array: Offers high pin count suitable for complex devices but poses assembly challenges.
Examples & Applications
Example of Through-Hole: Used in military applications requiring durable equipment.
Example of SMT: Found in consumer electronics such as smartphones and laptops.
Example of BGA: Utilized in high-performance processors and graphics cards.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For circuits that need to withstand, Through-Hole's a durable hand. But for gadgets that tiny and sleek, SMT is what we seek.
Stories
Imagine a knight (Through-Hole), a nimble dancer (SMT), and a wise sage (BGA) at a festival. The knight can withstand battles but takes up space, the dancer moves smoothly among the crowd, but might stumble without support, and the sage has powerful connections but is hard to see. Each has their role in the grand tale!
Memory Tools
THS (Through-Hole Strength), SMS (Surface-Mount Sleek), and BGS (Ball Grid Sage) - remember their roles in the packaging kingdom!
Acronyms
BGA - stands for 'Big Grid Array' for all the pins it can accommodate.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ThroughHole Packaging
A mounting method where component leads pass through PCB holes and are soldered on the opposite side.
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A method of mounting components directly on the PCB surface with solder pads, allowing for compact designs.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A packaging technology that uses an array of solder balls for connections, providing high performance for advanced ICs.
- IC
Integrated Circuit, a set of electronic circuits on a small chip.
- PCB
Printed Circuit Board, a board used for connecting electronic components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
