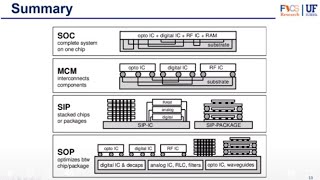
Structure of BGA Packaging
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to BGA Structure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the structure of Ball Grid Array packaging. Can anyone tell me what we know about BGA so far?

I think it's a type of surface mount technology that uses solder balls instead of leads!

Correct! BGA uses a grid of small solder balls. This design helps in maximizing the pin connections. Let’s remember it with the acronym 'BGA' - Balls for Grid Array. Can anyone explain how these solder balls are used?

They’re melted during the assembly process, right?

Exactly! This process is known as reflow soldering. It allows for robust connections. Can anyone think of an advantage this might provide?

Maybe better thermal management because of more direct contact with the PCB surface?

Spot on! This is a crucial aspect of BGA. So, the next time you think of a BGA, remember: 'BGA = Balls for Grid Array, and better performance'.
Advantages of BGA Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the structure, let’s explore the advantages of BGA. Why do you think having a higher pin count is beneficial?

More pins mean we can connect more functions to the chip, right?

Exactly! BGA allows for many connections, which is essential for high-performance applications. It’s perfect for CPUs and GPUs. What about thermal performance?

Since the BGA connects more surface area to the PCB, it helps with spreading heat.

Great observation! This robust design enhances thermal management. A simple way to remember: 'More Balls = More Connections and Better Cooling'.
Challenges with BGA Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now discuss some of the challenges BGA poses. Can anyone guess why inspection might be more difficult compared to other packages?

Because the solder joints are underneath, right? You can’t see them easily.

Well pointed out! That requires specialized X-ray techniques for proper inspection. What do you think about the assembly process?

It sounds complicated since you need precise alignment.

Correct! Precision is key. Remember: 'BGA = Blind to flaws without proper tools'. Always ensure your team is equipped for this!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explores the detailed structure of BGA packaging, which uses a grid of solder balls as the connection method instead of traditional leads. It emphasizes the advantages of BGA technology, including improved thermal performance and higher pin counts, as well as assembly considerations.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of the Structure of BGA Packaging
The Ball Grid Array (BGA) packaging represents an advanced method of connecting integrated circuits (ICs) to printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional surface-mounted devices that use leads or pads, BGA utilizes an arrangement of small solder balls in a grid pattern located on the underside of the package. This innovative approach allows for greater connectivity and performance, suitable for high-density applications.
Key Components of BGA Structure:
- Ball Grid: A series of solder balls replace standard leads, providing a compact connection that maximizes the number of interconnections per unit area.
- Reflow Soldering: During assembly, the balls are melted using reflow soldering techniques, forming robust electrical connections with the PCB.
Significance:
BGA packaging’s structural design offers multiple advantages, including improved thermal efficiency, increased mechanical strength, and higher pin counts—crucial for high-performance ICs. Understanding these components is essential for engineers and designers when selecting packaging technology for electronic devices.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Ball Grid Structure
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Ball Grid: Instead of leads or pads, BGA components have an array of small solder balls arranged in a grid pattern on the bottom of the package. These balls serve as the connection points for the IC to the PCB.
Detailed Explanation
In a Ball Grid Array (BGA) packaging, the traditional connection method of using leads or pads is replaced by a grid of tiny solder balls. These balls are strategically arranged on the bottom of the package, and they act as the points where the integrated circuit (IC) connects to the printed circuit board (PCB). This grid arrangement allows for a compact design, enabling a higher pin count in a smaller space, which is crucial for high-performance applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a BGA like a chessboard where each square (solder ball) represents a place where a chess piece (IC connection) can be positioned. Just like a chessboard allows for multiple pieces to fit in a limited area efficiently, a BGA allows many connections in a compact space.
Reflow Soldering Process
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Reflow Soldering: The BGA is soldered to the PCB using reflow soldering, where the solder balls melt and form a strong electrical connection between the IC and the PCB.
Detailed Explanation
The connection of a BGA to the PCB is achieved through a process known as reflow soldering. In this process, the PCB is heated up so that the solder balls on the BGA package melt. As they melt, they create a strong electrical bond between the IC and the PCB, solidifying as they cool. This method ensures reliable connections that can withstand thermal and mechanical stress, which is key for high-performance electronics.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine melting chocolate chips to make cookies. When the chocolate chips melt, they mix with the dough, and as they cool, they harden and create a solid cookie. Similarly, in reflow soldering, the heating melts the solder balls, creating strong connections when they cool down.
Key Concepts
-
Ball Grid: A pattern of solder balls used instead of leads in BGA packaging.
-
Reflow Soldering: Heating method used for melting solder balls to create connections.
-
Thermal Performance: Enhanced heat dissipation due to the larger contact area.
-
Higher Pin Count: Ability to connect more pins in a smaller area, allowing for more functionality.
Examples & Applications
High-performance processors often use BGA packaging due to the need for numerous connections and efficient thermal management.
Smartphones utilize BGA for compact design and enhanced performance, allowing for advanced features in a small form factor.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a grid, the balls are set, connections strong, no regret.
Stories
Imagine a basketball game, where every ball represents a connection. Each ball connects to the hoop — simply put, BGA arrays work like this, ensuring the IC excels in performance!
Memory Tools
Remember 'BGA': Balls for better Grid Array — highlighting solder balls and advantages.
Acronyms
BGA
Balls = Grid = Array of connections.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- BGA (Ball Grid Array)
A type of surface-mount packaging that uses a grid of solder balls as connection points.
- Reflow Soldering
A soldering process where solder is melted to create connections between components and the PCB.
- Thermal Management
The method of controlling the temperature of electronic devices to ensure optimal performance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
