Introduction to Packaging Types - 2.1
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to IC Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the importance of IC packaging. What do you think happens once an integrated circuit is fabricated?

I think it gets put into a package, but why is that necessary?

Great question! The packaging not only supports the chip physically but also facilitates the electrical connections to other components. Can anyone name the main types of packaging we will cover?

Are we talking about Through-Hole and Surface-Mount technologies?

And Ball Grid Array too, right?

Exactly! Remember the acronym TSB for Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array. We'll look into their characteristics soon!
Through-Hole Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss Through-Hole packaging. Who can describe how it functions?

I believe it has long leads that go through the circuit board.

Right! The component leads pass through holes in the PCB and are soldered on the opposite side. What might be an advantage?

They are more durable and easier to repair.

Exactly! This makes it great for high-power applications or prototypes. What about drawbacks?

They take up more space than surface-mounted ones, right?

Correct! More space and longer assembly time are the trade-offs.
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's transition to Surface-Mount Technology. What distinguishes it from Through-Hole?

Oh, the components sit on the surface of the PCB without through-holes!

That's right! This design leads to higher density. Can anybody elaborate on its advantages?

It's more cost-effective for mass production, and it's easier to automate.

Exactly! SMT is widely used in consumer electronics. However, what challenges do we have with SMT components?

They're harder to repair, especially with fine-pitch components.

Yes! It makes it less favorable for certain applications.
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s cover Ball Grid Array packaging. What’s unique about its design?

It uses a grid of solder balls instead of leads.

Exactly! This allows for a higher number of connections in less space. What are the benefits of BGA?

Improved thermal performance and mechanical strength!

That's right! But can anyone think of why BGA might present challenges?

Inspection and repairs are more complex since solder joints aren't visible.

Good point! Remember, BGA is favored for high-performance applications like processors.
Comparison of Packaging Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let's compare our three packaging types. Can someone give me an advantage and a disadvantage for each?

Through-Hole is durable but takes up more space.

Surface-Mount is compact but harder to repair.

BGA has high performance but is complex for assembly.

Great summaries! Remember, the choice depends on design needs, like size and strength. Always consider the final application!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Integrated circuit (IC) packaging is essential in manufacturing electronic components, impacting performance and design. This section details the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array packaging methods.
Detailed
Introduction to Packaging Types
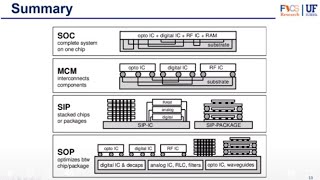
Integrated circuit (IC) packaging is crucial in the production of electronic circuits, offering mechanical support and facilitating electrical connections with external components. The primary packaging types—Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA)—are designed for specific requirements such as performance, size, cost, and application. Each of these methods has unique benefits and drawbacks, which will be explored throughout this chapter.
The Through-Hole technology is one of the earliest methods of mounting electronic components, known for its durability and ease of repair but requires more space and time for assembly. In contrast, Surface-Mount Technology offers a more compact design and is cost-effective for mass production but may not withstand environmental conditions as well as Through-Hole packages. Finally, the Ball Grid Array packaging provides an ideal solution for high-performance ICs, particularly in systems requiring high thermal performance, yet it presents inspection and assembly challenges. Understanding these differences is vital for effective circuit design.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Importance of IC Packaging
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
IC packaging is a critical step in the manufacturing process of integrated circuits (ICs). The packaging not only provides the mechanical support for the IC but also facilitates the electrical connections between the IC and the external components.
Detailed Explanation
IC packaging is essential because it serves two main purposes: first, it physically supports the IC, ensuring it stays safely connected to the circuit board; second, it helps in making electrical connections with other components. Think of the packaging as a protective shell that also provides pathways for electricity to flow between the IC and other parts of the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smartphone, where the battery, screen, and processor are all connected inside a protective case. The case not only keeps everything safe but also allows electrical connections between the parts to work seamlessly. Similarly, IC packaging does both for integrated circuits.
Types of IC Packaging
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are several different packaging types, each designed to meet specific requirements for performance, size, cost, and application. The three most widely used types of IC packaging are Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Each of these packaging technologies has its own advantages, disadvantages, and applications, depending on the specific needs of the circuit design and the end-use application.
Detailed Explanation
IC packaging comes in various types, mainly Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Each type is created with different requirements in mind such as how well it works (performance), how much space it takes up (size), how much it costs (cost), and where it will be used (application). Understanding these types helps designers choose the best option for their specific electronic circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Think of packaging types like different styles of carrying bags. A backpack is great for hauling books (size), a small handbag is perfect for quick trips (cost-effective), and a suitcase has the best protection for clothes during a longer journey (application). Similarly, IC packaging has its unique advantages tailored to various electronic needs.
Exploring Packaging Technologies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this chapter, we will explore the characteristics of these packaging types, their differences, and the specific applications where each is commonly used.
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we'll take a closer look at each packaging type's features, how they differ from one another, and where they are typically used. This exploration helps in understanding why certain ICs are packaged in specific ways and what benefits come along with them.
Examples & Analogies
Consider when you're shopping for shoes—you wouldn’t choose a pair of running shoes for a formal event. Similarly, in electronics, the chosen packaging type serves its purpose depending on the specific needs of the IC, just like different shoes fit different occasions.
Key Concepts
-
Through-Hole (TH): Known for durability and ease of repair but takes up more space and is slower to assemble.
-
Surface-Mount (SMT): Allows for high component density and is cost-effective for mass production but presents challenges in mechanical strength.
-
Ball Grid Array (BGA): Offers higher pin counts and better thermal performance but complicates assembly and inspection.
Examples & Applications
Through-Hole packaging is often used in power supply circuits where mechanical strength is necessary.
Surface-Mount technology is prevalent in consumer electronics such as smartphones due to its compact size.
Ball Grid Arrays are commonly found in high-performance computing devices like graphics cards and CPUs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Through-Hole's sturdy, Surface-Mount's neat, BGA's the fastest in heat.
Stories
Imagine a race where Through-Hole is durable like a sturdy car, SMT is a sleek motorcycle, and BGA is a rocket, all showing different strengths.
Memory Tools
Use 'TSB' to remember Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array for IC packaging!
Acronyms
T.H.E. - Through-Hole is stronger, H.E.M. - High performance in BGA, Easy in SMT for production!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Integrated Circuit (IC)
A set of electronic circuits on a small flat piece of semiconductor material, typically silicon.
- ThroughHole (TH) Packaging
A method where component leads are inserted into holes in a PCB and soldered on the opposite side.
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A method where components are mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A type of surface-mount packaging that uses a grid of solder balls for connections.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
