Introduction to Packaging Types - 2
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to IC Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the different types of IC packaging. Can anyone tell me why packaging is crucial in electronics?

It protects the components and ensures connections!

Exactly! It not only protects but also supports the electrical connections. Now, let's talk about the three main types of packaging: Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array. Remember the acronym 'THS' to recall these types.

What are the main differences between them?

Good question! Each type has distinct characteristics and is suited for different applications, which we'll explore in detail.
Through-Hole Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s start with Through-Hole packaging. What do you think are its main components?

I think it has long leads that pass through the PCB?

Exactly! The leads are soldered on the opposite side of the PCB. It’s known for its durability and is often used in high-power applications. Can anyone share a disadvantage of this method?

It takes up more space, right?

Correct! Due to its size, it’s bulkier compared to Surface-Mount technology. Great job recalling these details!
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss Surface-Mount Technology. What’s unique about SMT in comparison to Through-Hole?

It doesn't need holes in the PCB.

Right! This leads to a more compact design. SMT allows for higher component density, which is essential in modern electronics. Can someone name an area where SMT is commonly used?

I think it’s used in smartphones!

Exactly! It's perfect for consumer electronics. However, remember that SMT components can be difficult to repair due to their small size.
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The last type we'll cover today is the Ball Grid Array. What distinguishes BGA from the other two types?

It uses solder balls arranged in a grid.

Correct! This design provides a strong electrical connection and helps with heat dissipation. What’s a main challenge with BGA?

Inspecting the solder joints can be hard since they're not visible.

Exactly! That’s a significant challenge in using BGA. Great observations, everyone!
Comparison and Conclusion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve reviewed all three packaging types, can anyone summarize the key differences?

Through-Hole is durable but bulky, SMT is compact but harder to repair, and BGA has high performance but is tricky to inspect!

Fantastic summary! Choosing the right packaging depends on specific requirements, such as size, mechanical strength, and the intended application.

Can we also think about costs when choosing?

Absolutely! Cost-effectiveness plays a crucial role in the decision-making process. Great discussion today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
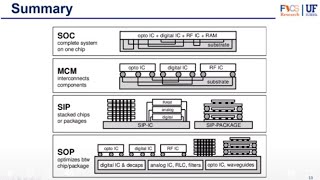
The section introduces the essential concept of integrated circuit (IC) packaging, focusing on Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA) types. It covers the structural characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications of each packaging type, providing insights into their respective roles within electronic device manufacturing.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section serves as an introduction to the various types of integrated circuit (IC) packaging, which is a crucial component in the manufacturing of electronic devices. IC packaging not only gives mechanical support to the components but also ensures effective electrical connections with external circuits. The three primary types of IC packaging discussed are Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA).
Key Details:
- Through-Hole Packaging:
- Involves inserting component leads through drilled holes in the PCB and soldering on the opposite side.
- Advantages: Enhanced durability, ease of repair, and higher power handling.
- Disadvantages: Requires more space on the PCB, leading to bulkier designs and longer assembly times.
- Applications: Often used in high-power devices and prototyping.
- Surface-Mount Technology (SMT):
- Components are mounted directly on the PCB surface without the need for holes.
- Advantages: Higher component density, suitable for automated assembly, improved performance, and cost-effectiveness for mass production.
- Disadvantages: Lower mechanical strength compared to TH, challenging repairs on multi-layer boards.
- Applications: Commonly used in consumer electronics and compact high-density boards.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA):
- Features a grid of solder balls for connections, eliminating conventional leads.
- Advantages: Supports higher pin counts and offers superior thermal and mechanical performance.
- Disadvantages: Difficult to inspect for solder joint quality and requires precise assembly techniques.
- Applications: Utilized in high-performance processors and mobile devices.
This section emphasizes the importance of understanding these packaging types to design more efficient and reliable electronic systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of IC Packaging
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
IC packaging is a critical step in the manufacturing process of integrated circuits (ICs). The packaging not only provides the mechanical support for the IC but also facilitates the electrical connections between the IC and the external components.
Detailed Explanation
Integrated circuit (IC) packaging is essential because it plays two vital roles: it supports the physical structure of the IC and ensures that it can connect to other components effectively. Think of IC packaging as the protective casing and linking point that allows the chip to interact with other electronic parts, making it functional within a device.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smartphone as a puzzle. Each piece of that puzzle is an electronic component, and the packaging of the IC is like the individual puzzle piece that fits into a larger picture. Without proper packaging, the piece wouldn't fit well, which means the entire puzzle wouldn't work.
Types of IC Packaging
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are several different packaging types, each designed to meet specific requirements for performance, size, cost, and application.
Detailed Explanation
Different packaging types exist because electronic components have varied demands. For instance, some circuits require compact designs while others need to handle high power. The choice of packaging affects the size, cost, and performance of the final product, which must be tailored to the intended use.
Examples & Analogies
Think of packaging types like different types of containers for food. You wouldn't use a large pot for a small serving of soup or a tiny jar for storing a picnic feast. Similarly, electronic components require appropriate packaging based on their specific requirements.
Three Main Packaging Types
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The three most widely used types of IC packaging are Through-Hole (TH), Surface-Mount (SMT), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Each of these packaging technologies has its own advantages, disadvantages, and applications, depending on the specific needs of the circuit design and the end-use application.
Detailed Explanation
The three dominant types of IC packaging—Through-Hole, Surface-Mount, and Ball Grid Array—each serve different purposes based on the characteristics of the electronic components. Understanding these differences allows engineers to choose the most suitable packaging that aligns with performance expectations and manufacturing processes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider three athletes who excel in different sports: a marathon runner, a sprinter, and a decathlete. Each athlete has strengths that suit their sport. Similarly, each packaging type has unique advantages that make it better for specific applications in electronics.
Overview of Chapter Content
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this chapter, we will explore the characteristics of these packaging types, their differences, and the specific applications where each is commonly used.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter intends to delve deeper into each packaging type, discussing their unique features, how they differ from one another, and common scenarios where each type is effectively employed. This comprehensive understanding is crucial for anyone involved in electronic design and manufacturing.
Examples & Analogies
It's like taking a road trip where you plan your route based on different terrains. You wouldn't take the same road for a beach trip as you would for a mountain expedition. Similarly, understanding the characteristics of each packaging type helps designers select the right path for their specific electronic applications.
Key Concepts
-
Through-Hole Packaging: A method providing strong mechanical connections due to leads passing through PCB holes, suitable for high-power applications.
-
Surface-Mount Technology: A modern technique allowing for higher component density and efficiency in PCB assembly, ideal for compact electronic devices.
-
Ball Grid Array: A surface-mount package type with enhanced thermal and mechanical performance, primarily used in high-performance electronics.
Examples & Applications
Through-Hole packaging is often found in components like resistors and capacitors in high-power power supply designs.
Surface-Mount Technology is widely used in smartphones and laptops for compact designs with many features.
Ball Grid Array packaging is utilized in high-performance GPUs and microprocessors due to their high pin counts.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Through-Hole stands tall, for power it handles all; SMT's compact flair, in devices, it’s everywhere.
Stories
Imagine a sturdy tree (Through-Hole), compact shrubs (SMT), and a vibrant grid of flowers (BGA) in a tech garden—all serving unique purposes in nature's design.
Memory Tools
Think of 'THS' for packaging: T for Through-Hole, S for Surface-Mount, G for Grid in Ball Grid Array.
Acronyms
Use ‘HPC’ for remembering packaging advantages
for High power
for Performance
for Compact!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ThroughHole Packaging (TH)
A technology for connecting electronic components by inserting leads through holes in a printed circuit board (PCB).
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB without requiring drilled holes.
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A type of surface-mount packaging that utilizes an array of solder balls arranged in a grid pattern for connections.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
