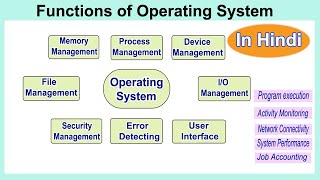
Functions of Operating System
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Process Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with Process Management. Can anyone tell me why it's important for an operating system?

I think it's because it allows us to run several programs at the same time!

Exactly! Process Management ensures that these programs run efficiently without interfering with one another. We often use the acronym 'CPU' to remember that the 'Central Processing Unit' manages these processes. Can someone explain how CPU scheduling works?

Isn't it like taking turns? The CPU gives each program some time to run before switching to the next?

Yes, that's called time-sharing. Great job! It maximizes CPU use.
Memory Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to Memory Management. How does an OS handle memory allocation?

I think it divides the memory into portions for different programs.

That's right! The OS keeps track of which parts of memory are being used and which are free, preventing overlap. Remember the mnemonic M.A.P: 'Manage, Allocate, Protect.' Can anyone explain what that means?

It means the OS manages memory, allocates it to programs, and protects it from unauthorized access!

Well done! Protecting memory is vital for system security.
File Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will discuss File Management. Why do you think it’s an essential function of an OS?

It helps in sorting and organizing the documents we create!

Exactly! The OS organizes files into directories and ensures easy retrieval. There’s a phrase: 'Files First, Folders Follow'. Can someone explain this?

'Files First' means that files are the main components, and 'Folders Follow' indicates how we categorize them!

Great understanding! File management is key to maintaining an organized storage system.
Device Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss Device Management. What role does the OS play in this function?

It controls how devices communicate with the computer, right?

Correct! Operating systems use drivers to facilitate communication with hardware. There’s a helpful mantra: 'Drivers Drive Devices'. Can anyone elaborate?

It means that device drivers are essential for enabling devices to function properly with the system!

Excellent! Device management ensures that all peripherals work smoothly with the OS.
Security and User Interface
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s look at Security and User Interface. Why is security a function of the OS?

To protect our personal data from unauthorized access!

Exactly! The OS implements various security measures. Now, about the User Interface. How does it impact user experience?

A user-friendly interface makes it easier to interact with the computer, like using Windows or icons!

Absolutely! Interfaces transform complex commands into something manageable. Summary time: the OS functions we discussed today ensure efficiency, security, and ease of use, which are vital for users!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the primary functions of an operating system, including process management, memory management, file management, device management, security, and user interface. Each function is essential for the overall performance and usability of a computer system.
Detailed
Functions of Operating System
Operating systems (OS) play a pivotal role in managing computer resources and providing a user interface. Here's a detailed look at their core functions:
- Process Management: This involves running multiple programs efficiently and ensuring each process has enough resources to execute while maintaining system stability.
- Memory Management: The OS allocates memory to different tasks and keeps track of each byte in a computer's memory, ensuring efficient utilization to avoid conflicts.
- File Management: Operating systems organize files and folders on storage devices, managing data access for users and applications effectively.
- Device Management: This function controls the operation of input/output devices like keyboards and printers, ensuring seamless interaction between hardware and software.
- Security: An OS protects data from unauthorized access, helping to maintain privacy and the integrity of information.
- User Interface: Operating systems offer graphical (GUI) or command-line interfaces (CLI) for user interaction, making it easier for individuals to work with computers.
Understanding these functions is critical for both users and developers, as they form the foundation for software applications and hardware interactions.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Process Management
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Process Management: Runs multiple programs efficiently
Detailed Explanation
Process management is a vital function of an operating system that ensures multiple programs can run at the same time without interfering with each other. The OS manages the creation, scheduling, and termination of processes. This means when you open several applications, the OS allocates CPU time and resources efficiently, allowing them to operate smoothly together.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant where multiple chefs are preparing different dishes at the same time. Each chef (process) needs a designated cooking station (resources) to work efficiently, and the restaurant manager (OS) ensures that all chefs can cook without bumping into each other.
Memory Management
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Memory Management: Allocates memory to different tasks
Detailed Explanation
Memory management is the process by which the operating system manages the computer's memory resources. Each running program needs a certain amount of memory, and the OS allocates space for each one. It keeps track of which part of the memory is being used and which is free, ensuring that tasks do not interfere with each other or run out of memory.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a library where different books represent running programs. The librarian (OS) must keep track of who is borrowing which book (allocating memory). If there are too many requests for popular books (programs), the librarian ensures that each visitor finds what they need without wasting time looking for lost items.
File Management
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● File Management: Organizes files and folders on storage devices
Detailed Explanation
File management involves the way the operating system handles data storage. It allows users to create, delete, edit, and keep track of files and folders. The OS provides a structured way to organize these files, making it easy for users to find and manage them. This also allows applications to store and retrieve the data they need.
Examples & Analogies
Think of file management like a filing cabinet in an office. Each drawer holds different folders (directories) and documents (files). An organized filing system means you can quickly locate the necessary documents without rummaging through heaps of paper.
Device Management
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Device Management: Controls input/output devices like printers and keyboards
Detailed Explanation
Device management refers to how the operating system interacts with hardware like printers, keyboards, and external drives. The OS acts as a mediator, ensuring that processes can send and receive data from these devices smoothly. It manages the communication between the hardware and software, allowing for efficient input and output operations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a conductor of an orchestra who ensures that all musicians (devices) play together harmoniously. The conductor ensures that each instrument is used at the right time and that the music (data) flows smoothly to create a cohesive performance.
Security
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Security: Protects data from unauthorized access
Detailed Explanation
Security is a critical function of an operating system, aimed at protecting the computer and its data from unauthorized access, breaches, and malware. The OS employs various strategies, including user authentication, password protection, and encryption, to safeguard information and keep the system secure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of your house, which has locks on the doors (security features). Just as a locked door prevents strangers from entering, the OS uses digital locks (security measures) to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information on the computer.
User Interface
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● User Interface: Provides graphical or command-line interfaces for interaction
Detailed Explanation
The user interface is how users interact with the operating system. It can be graphical (GUI), where users can click icons and navigate using the mouse, or command-line, where users type commands into the terminal. An effective user interface makes it easier for users to perform tasks and interact with the computer.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a vending machine. A graphical interface is like a machine with pictures of snacks you can press with a button, while a command-line interface is like giving verbal commands to a staff member at a snack bar. Both get you snacks, but one is more visually engaging and user-friendly.
Key Concepts
-
Process Management: Coordinates execution of concurrent programs.
-
Memory Management: Allocates and tracks memory usage efficiently.
-
File Management: Organizes data storage in a user-friendly manner.
-
Device Management: Ensures smooth operation and communication with hardware.
-
Security: Protects user data from threats and unauthorized access.
-
User Interface: The medium through which users interact with the system.
Examples & Applications
An example of process management is a user running a word processor while also listening to music.
When a user saves a document, the OS's file management system organizes the file in a specified folder.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Manage your processes, memory’s divine, Files organized well and devices align.
Stories
Imagine an orchestra, where each musician is a process. The conductor, the OS, ensures they play in harmony without clashing. Memory is like the music sheets, allocated perfectly so each musician knows their part.
Memory Tools
To remember the functions: P.M.F.D.S.U - Please Manage Files, Devices Securely and Uniformly.
Acronyms
M.U.S.E
Memory
User Interface
Security
and Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Process Management
The part of the operating system that handles multiple programs simultaneously.
- Memory Management
The function of the OS that allocates and manages memory for various tasks.
- File Management
The organization and control of data storage within the operating system.
- Device Management
The OS function that manages and controls hardware devices.
- Security
Measures taken by an OS to protect data from unauthorized access.
- User Interface
The means by which users interact with an operating system, either through GUI or CLI.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
