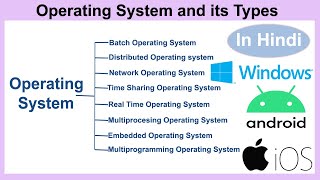
Modern Features of Operating Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Multitasking and Multiprocessing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with multitasking and multiprocessing in modern operating systems. What do you think multitasking means?

I think it means doing multiple things at the same time.

Exactly! Multitasking allows users to run several applications at once. How do you think this affects the way we use computers?

It makes things faster and easier since we don't have to close one program to open another.

That’s correct! And multiprocessing allows the OS to use multiple CPUs to handle these tasks. Remember the acronym M&M for Multitasking and Multiprocessing.

Oh, that’s a good way to remember it!

Great! Can anyone explain the difference between multitasking and multiprocessing?

Multitasking is about running several tasks on one CPU, while multiprocessing uses multiple CPUs.

Exactly! You've got it! In summary, multitasking improves usability, and multiprocessing enhances performance by better utilizing computer resources.
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's dive into the Graphical User Interface, or GUI. Why do you think a GUI is important?

I think it's easier to use because you can see everything visually.

Exactly! A GUI makes user interaction much more intuitive. You don’t need to remember commands like in a command-line interface. Can anyone give an example of a GUI element?

Icons and menus!

Perfect! Icons and menus help users navigate through software. Now, remember the saying: 'What you see is what you get'—this applies to GUIs.

That’s easy to remember!

Good! In summary, GUIs enhance usability by providing visual representation and interaction.
Automatic Hardware Detection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about automatic hardware detection, also known as Plug and Play. What do you understand by this term?

It means connecting devices that automatically work without installing drivers.

Exactly! It's designed to make the user experience much smoother. What’s its advantage?

It saves time, since we don’t have to set things up manually.

Very true! This feature significantly enhances system usability. Remember the acronym PnP for Plug and Play!

That’s a smart way to memorize it!

In summary, Plug and Play technology simplifies hardware configuration, enhancing overall system convenience.
Virtual Memory and Efficient Memory Use
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss virtual memory. What do you think its purpose is?

I think it helps if the RAM is full by using the hard drive?

Absolutely! Virtual memory allows the OS to use hard disk space to simulate additional RAM. Can anyone explain why this is important?

It helps run more applications at the same time without crashing!

Exactly! By managing memory effectively, we can improve performance and multitasking capabilities. Remember the phrase 'More memory, more multitasking.'

I’ll remember that!

In summary, virtual memory plays a crucial role in optimizing computer performance.
Network Connectivity and Security Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s explore network connectivity and security features in modern operating systems. Why are they important?

They allow us to connect and protect our data over the internet.

Correct! Security features help protect data from threats. What are some common threats?

Viruses and malware!

Exactly! The OS implements firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption techniques. A handy mnemonic to remember these is SEC—Security, Encryption, Connectivity.

That’s a helpful mnemonic!

In summary, network connectivity and security features are vital for both usability and data protection.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Operating systems today come equipped with features that support multitasking, graphical interfaces, hardware detection, virtual memory, and improved network security, which collectively improve user interaction and system performance.
Detailed
Modern Features of Operating Systems
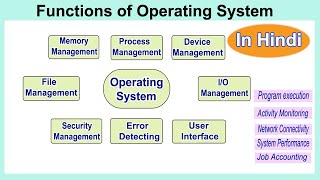
Modern operating systems (OS) provide a range of features that enhance both user experience and the efficiency of hardware utilization. One significant feature is multitasking, which allows the OS to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making it easier for users to switch between applications without interruption. In addition, multiprocessing enables the OS to utilize multiple CPUs for better performance.
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) simplifies user interactions, allowing users to navigate through visual elements rather than relying solely on command lines. This is particularly beneficial for users who may not have extensive computer knowledge. Furthermore, modern OSs support automatic hardware detection, commonly referred to as Plug and Play, which makes it straightforward for the system to recognize and configure connected devices without manual setup.
Another crucial feature is virtual memory, which allows systems to use hard drive space as additional memory, improving the process of managing active applications. Lastly, enhanced network connectivity and security features not only facilitate communication between devices but also protect user data against threats such as malware and unauthorized access. These features constitute a modern OS's response to growing performance demands and user expectations.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Supports Multitasking and Multiprocessing
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Supports multitasking and multiprocessing
Detailed Explanation
Modern operating systems can handle multiple tasks at the same time, known as multitasking. This means you could be typing a document, while a download is in progress, and music is playing. Multiprocessing refers to the ability of the operating system to manage more than one processor at a time, allowing various processes to be executed simultaneously on different processors.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy restaurant kitchen where multiple chefs are cooking different dishes at once. One is frying chicken, another is baking bread, and another is preparing salads. This is similar to multitasking in an operating system where multiple processes are handled simultaneously.
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Graphical User Interface (GUI) for ease of use
Detailed Explanation
Modern operating systems use Graphical User Interfaces, which make it easier for users to interact with the computer. Instead of typing commands, users can point and click on icons, buttons, and menus, making navigation intuitive and user-friendly.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a smartphone screen filled with colorful icons. You simply tap an icon to open an app, similar to how you click on an icon on a computer desktop. This visual interaction is what makes using computers and devices accessible to everyone, even those without technical knowledge.
Automatic Hardware Detection (Plug and Play)
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Automatic hardware detection (Plug and Play)
Detailed Explanation
Automatic hardware detection, often called 'Plug and Play', allows users to connect new hardware devices like printers or USB drives without having to manually install drivers. The operating system automatically recognizes the new device and configures it for use.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a new child joining a school. The school automatically adds them to the class list and gives them necessary supplies without needing manual paperwork. Similarly, when you plug in a new device, the operating system does the heavy lifting to get it ready for you.
Virtual Memory and Efficient Memory Use
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Virtual memory and efficient memory use
Detailed Explanation
Virtual memory is a feature that allows computers to use hard disk space to simulate extra memory. This means that even if your RAM (the computer's short-term memory) is full, the operating system can temporarily store inactive programs on the hard disk to free up RAM for active tasks, enhancing overall performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a classroom where students can only work on a certain number of projects at a time. When a student finishes a project (or steps out for a while), their desk can be cleared for a new project (using the available hard disk space), allowing them to work on a maximum number of projects without getting overwhelmed or running out of desk space.
Network Connectivity and Security Features
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Network connectivity and security features
Detailed Explanation
Modern operating systems offer enhanced network connectivity features that allow devices to connect to the internet and other networks seamlessly. They also include security features to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, such as firewalls and encryption.
Examples & Analogies
Think of your home security system. Just as it helps keep intruders out while allowing you to access your home, network connectivity features in an operating system ensure safe communication over the internet while keeping your personal information secure from cyber threats.
Key Concepts
-
Multitasking: The ability to run multiple applications at the same time.
-
Multiprocessing: Using multiple CPUs for better performance.
-
Graphical User Interface (GUI): A visual interface that enhances user interaction.
-
Plug and Play: Automatic recognition of hardware components.
-
Virtual Memory: Using hard drive space as additional memory.
-
Network Security: Protecting data during network connectivity.
Examples & Applications
Using a web browser while listening to music on a media player demonstrates multitasking.
The automatic setup of a printer when plugged in is an example of Plug and Play functionality.
Operating systems like Windows and macOS use GUIs to allow users to interact more intuitively with their computers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Multitasking and multiprocessing, so fast and shining, run tasks with ease, without you whining.
Stories
Imagine a chef in a busy kitchen (multitasking) while having multiple ovens (multiprocessing) cooking different dishes all at once, making sure everything is perfect without any hold-up!
Memory Tools
Remember SEC for Security, Encryption, Connectivity when discussing network safety.
Acronyms
Remember PnP for Plug and Play, making hardware setup as easy as child's play.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Multitasking
The ability of an operating system to execute multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Multiprocessing
The use of multiple CPUs to manage processes efficiently.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI)
A visual way of interacting with a computer using windows, icons, and menus.
- Plug and Play
A feature that allows the operating system to automatically detect and configure hardware components.
- Virtual Memory
An OS capability that uses disk space as extra memory to enhance performance.
- Network Security
Measures and protocols that protect networked data and ensure privacy against threats.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
