Impact of Depreciation on Financial Statements
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Financial Statements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today, we're going to explore the impact of depreciation on financial statements. Can anyone tell me how depreciation might show up in these statements?

I think it affects the income statement, right?

Exactly! Depreciation is listed as an expense in the income statement, which reduces the net profit. It's crucial to ensure we represent profits accurately. Who can think of a reason why this is important?

It gives a clearer picture of how much money the company is actually making!

Correct! Understanding this allows management to make informed financial decisions and show the true profitability of the business.
Lasting Impact on Balance Sheet
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss its impact on the balance sheet. Can someone summarize how depreciation appears there?

It shows a reduction in the value of fixed assets, right?

That's right! If a company has a provision for depreciation, that provision is also shown as a deduction. What effect does this have on stakeholders reviewing the balance sheet?

It makes the assets look less valuable, which could affect decisions made by investors.

Spot on! It can influence investor perceptions. Seeing these accurate asset values is crucial for making investment decisions.
Understanding Net Profit Reduction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Who's ready to delve deeper into how depreciation affects net profit? Remember, it’s recorded as an expense. How does this affect overall profitability?

It decreases the profit we can report!

Exactly! By reducing reported earnings, we must ensure stakeholders understand that this does not mean cash has left the business. How might investors react to such financial statements?

They might be cautious if they don't understand depreciation.

Precisely! That’s why providing clear explanations in financial reporting is so vital.
Conclusion: Depreciation's Role in Financial Representation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In conclusion, we’ve learned how depreciation influences both our income statement and balance sheet. Why is it essential for us to understand this as future managers?

So we can make better financial decisions and analyze the company’s performance accurately!

Absolutely! Understanding these principles helps us maintain transparency and aids in strategic planning for asset management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains how depreciation is recorded as an expense on the income statement, leading to lower reported profits, and how it impacts the balance sheet by presenting assets at their depreciated value, influencing stakeholders' perception of the company's financial health.
Detailed
Impact of Depreciation on Financial Statements
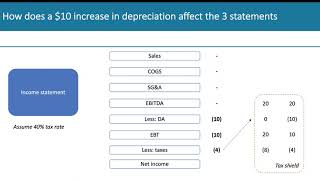
Depreciation plays a crucial role in the preparation of financial statements, influencing both the income statement and balance sheet significantly.
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Account)
- Expense Treatment: Depreciation is accounted for as an expense, which directly reduces the net profit reported by a company.
Balance Sheet
- Asset Valuation: The value of assets is shown at a reduced amount reflecting their depreciation. If a provision for depreciation exists, it is recorded as a deduction from the gross assets.
In summary, depreciation is not just a routine accounting entry; it impacts the financial portrayal of a business, influencing decision-making for management, investors, and other stakeholders.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Depreciation in the Income Statement
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Income Statement (Profit and Loss Account)
• Depreciation is treated as an expense.
• Reduces net profit.
Detailed Explanation
In the income statement, depreciation is classified as an expense. This means it is deducted from the total revenue generated by the company to calculate the net profit. By including depreciation as an expense, companies reflect the fact that assets are losing value over time, which affects overall profitability. This accounting treatment ensures that the income statement presents an accurate view of the company's financial performance over a period.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a company as a restaurant. Just like how every meal has a cost that needs to be accounted for, the restaurant needs to recognize the cost associated with using its kitchen appliances, furniture, and other equipment. If they ignore these costs (like depreciation), their profits would look higher than they actually are, misleading them about their actual financial health.
Depreciation in the Balance Sheet
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Balance Sheet
• Shown as a reduction in the value of the asset.
• If provision is used, shown as a deduction from gross asset.
Detailed Explanation
On the balance sheet, depreciation is represented as a reduction in the value of fixed assets. This reduction is necessary because it reflects the fact that assets lose value over time due to wear and tear or obsolescence. If a provision for depreciation is created, it is displayed as a deduction from the gross asset amount, providing a clearer picture of the asset's net book value. This helps stakeholders understand the actual worth of assets held by the company.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine buying a brand-new car for $20,000. Over the years, as you drive it, the car loses value; it’s like showing a used car's value. On your financial statements, you would show the car's reduced value instead of its original price. This way, anyone looking at your financials can see how much you actually might get if you sold that car today, reflecting its current market value.
Key Concepts
-
Depreciation impacts net profit negatively.
-
Depreciation reduces asset values on balance sheets.
-
Understanding depreciation is crucial for accurate financial representation.
Examples & Applications
A company has an asset valued at $10,000 with a life of 5 years and a residual value of $1,000. Under the straight-line method, the annual depreciation is ($10,000 - $1,000) / 5 = $1,800, reducing net income by this amount yearly.
In a balance sheet, if a fixed asset worth $10,000 has accumulated depreciation of $4,000, it will appear as an asset value of $6,000, reflecting its reduced value.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Depreciation takes a toll, on profit it's not whole, the balance shows it steady, making numbers look ready.
Stories
Once in a bustling marketplace, a merchant bought a new machine for $10,000. Each year, it would wear down and lose value, represented on paper not just as a cost, but as a loss of income, guiding the merchant on wise investments!
Memory Tools
D.I.S. - Depreciation Impacts Statements! Remember this to recall depreciation's role.
Acronyms
D.E.P.R. - Depreciation Effects Profit and Reporting
way to remember the key impacts of depreciation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Income Statement
A financial statement that reports a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period, including revenues and expenses.
- Balance Sheet
A financial statement that presents a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Net Profit
The total revenue of a company minus its expenses, taxes, and costs, indicating the company's profitability.
- Depreciation Provision
The amount set aside in the accounts to cover future depreciation charges.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
