MEMS Process Flow
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to MEMS Process Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to learn about the MEMS process flow. MEMS stands for Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems, which are essential for many modern devices, including sensors and actuators.

What makes MEMS so important?

Great question! MEMS devices are critical because they integrate mechanical components with electronics at a micro scale, which allows for enhanced functionality and miniaturization.

How do you start the MEMS fabrication?

The process begins with surface micromachining, which includes depositing layers that will play different roles during fabrication.
Sacrificial Layer in MEMS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive deeper into the sacrificial layer. Can anyone tell me what a sacrificial layer is?

Is it a layer that gets removed later?

Exactly! We often use SiO₂ as the sacrificial layer. It helps define the structure of the MEMS device.

What happens to that layer after it's used?

It gets removed during etching, usually with Hydrofluoric acid, allowing the final MEMS structure to be exposed.
Etching Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the etching process. Who can tell me why etching is important?

It's how we remove layers, right?

Correct! Etching is crucial for shaping the MEMS device. We often use materials like HF for this step.

Are there any safety concerns with using HF?

Yes, HF is highly corrosive and requires precautions, including proper protective equipment. Always handle with care!
Impact of MEMS Process Flow on Device Functionality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at how our MEMS process flow impacts device functionality. What do you think?

The way we fabricate it affects how well it works?

Yes! Each step, from layer deposition to etching, has to be precise to maintain performance and reliability in MEMS applications.

So, if one step goes wrong, it can mess up the whole device?

Exactly! That's why understanding the entire MEMS process flow is essential.
Summarizing MEMS Process Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

And how these steps affect the final device!

That's right! Each aspect must be done with precision to ensure proper functionality.

What would be our next steps for understanding MEMS further?

Great question! Next, we can explore specific MEMS applications and how innovations are changing the landscape.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
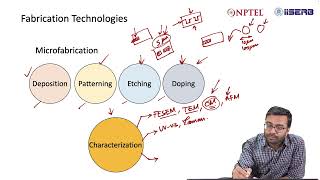
The MEMS process flow primarily involves surface micromachining techniques, which include the critical step of sacrificial layer etching, specifically using SiO₂ in HF. Understanding this flow is essential for producing MEMS devices, highlighting how each step contributes to the final product.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) process flow consists of a series of highly specialized steps that transform raw materials into functional MEMS devices. At the core of this process is surface micromachining, which is a crucial technique in MEMS fabrication. Surface micromachining typically involves the deposition of layers of materials, where certain layers act as sacrificial layers.
Key Aspects of Surface Micromachining
- Sacrificial Layers: A sacrificial layer is a material that is intentionally removed during processing to create space or a specific structure in the device. In the MEMS process, SiO₂ (silicon dioxide) is frequently used as a sacrificial layer.
- Etching Process: The etching process, particularly utilizing Hydrofluoric acid (HF), is employed to selectively remove the sacrificial layer, allowing the desired mechanical elements to be realized in silicon or other substrate materials.
- Device Functionality: This step is critical in achieving the intended functionality of MEMS devices, and it enables the creation of intricate three-dimensional architectures vital for sensor and actuator technologies.
With continued advancements in MEMS technology, a clear understanding of the process flow is essential for future innovations in the field.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Surface Micromachining
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Surface micromachining:
Detailed Explanation
Surface micromachining is a key technique in the fabrication of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS). It involves building structures on the surface of a substrate, typically silicon, by adding and etching layers. This process allows for the creation of complex mechanical devices at the microscale, which are essential for various applications such as sensors and actuators.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a miniature city on a flat table, where each building represents a layer of material deposited. Just like how you can create intricate designs using building blocks, surface micromachining allows engineers to construct fine features that can move or sense things, resembling a tiny ecosystem of machines.
Sacrificial Layer Etching
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sacrificial layer etching (e.g., SiO₂ in HF).
Detailed Explanation
Sacrificial layer etching is a crucial step in surface micromachining that involves creating a temporary layer that will be removed later, allowing for the release of mechanical parts. In this process, a material like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) is placed down first to form a layer. After fabricating the desired structures on top, the sacrificial layer is etched away using hydrofluoric acid (HF), freeing the moving parts of the MEMS device.
Examples & Analogies
Think of making a sandcastle with a moat. First, you build the castle (the structures you want) on top of a pile of sand that represents the sacrificial layer. Once the castle is finished, you dig out the sand around it (etching away SiO₂ with HF), allowing the castle to stand free and sturdy, just like a MEMS component that can function independently.
Key Concepts
-
MEMS: Integration of mechanical and electronic elements at micro scale.
-
Sacrificial Layers: Material removed during processing to create structures.
-
Etching Process: Method used to remove unwanted layers, shaping MEMS devices.
-
Surface Micromachining: Technique involving the manipulation of layers on a substrate to achieve desired structures.
Examples & Applications
An example of MEMS devices includes accelerometers used in smartphones to detect orientation and motion.
A practical application of sacrificial layers is seen in fabricating gyroscopes, where the removal of SiO₂ enables precise rotor mechanisms.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In MEMS, layers fall, it's how we make them small!
Stories
Imagine building a castle with sand. First, you create walls (sacrificial layers) and, when finished, wash away the sand to reveal a beautiful structure, just like how MEMS devices are created!
Memory Tools
Remember: 'SEMS' - Sacrificial, Etching, MEMS Structure, to recall the process steps!
Acronyms
S.E.M.S. - Sacrificial Layer, Etching, MEMS Process. Use this to remember the key steps in the flow!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- MEMS
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems; devices that integrate mechanical and electronic components at the micro scale.
- Sacrificial Layer
A layer that is intended to be removed to create a specific structure in a device.
- Etching
The process of removing material from a substrate, often used to shape device structures.
- Surface Micromachining
A fabrication technique that involves layering materials to create structures on a substrate.
- SiO₂
Silicon dioxide; commonly used as a sacrificial layer in MEMS fabrication.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
