Joint Fillers
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Function of Joint Fillers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about joint fillers in concrete pavements. Can anyone tell me what a joint filler is?

Is it something that fills gaps?

Exactly! Joint fillers are compressible materials that fill the gap, allowing for expansion and helping in absorbing compressive forces. They remain in place during the pavement's life.

Why is it important to use them?

Great question! They prevent damage caused by temperature changes and ensure that joints do not become filled with debris or water, which can deteriorate the pavement.

Can anyone remember the mnemonic for the desirable properties of joint fillers? It starts with 'C' for compressibility.

C-R-D-W-R! It stands for Compressibility, Recovery, Durability, Water resistance!

That's right! Wonderful job!

In summary, joint fillers are essential for absorbing forces and ensuring longevity in pavements.
Desirable Properties of Joint Fillers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s dive deeper into the desirable properties of joint fillers. Can anyone mention what makes a good joint filler?

It should be durable!

Correct! And it should also have high compressibility and recover well after being compressed. This ensures it can withstand movement without failing.

Are there other characteristics?

Yes, it should be non-absorbent or have low water absorption to resist decay. Remember, the acronym C-R-D-W to recall these properties: Compressibility, Recovery, Durability, Water resistant.

To summarize, these properties ensure joint fillers perform effectively under varying conditions.
Common Materials Used as Joint Fillers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about the materials used for joint fillers. Who can name one?

I know bituminous fillers are one type!

Exactly! Bituminous premoulded fillers are common in India and consist of bitumen with fibers. They are effective for many applications.

What about cork? I’ve heard it’s durable.

Yes, cork is natural, compressible, and an excellent choice for various applications. Another interesting material is sponge rubber. It's lightweight and very easy to install.

What about expanded polystyrene?

Good point! EPS is indeed lightweight and resilient. Can anyone remember another one?

Cellulose fiberboard!

Perfect! Remember to evaluate the options based on their characteristics for your projects. Summary: using the right material is crucial for effective joint fillers.
Installation Techniques for Joint Fillers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve covered materials, let’s talk about installation techniques. What are key considerations for installing joint fillers?

They need to be flush with the slab edges, right?

Exactly! They should also cover the full depth of the joint as designed.

What about alignment?

Yes, proper alignment is critical. We want to avoid gaps, which can lead to failure. Remember to consider using bond breakers as well.

In summary, good installation prevents future problems and ensures the effective function of the joint fillers in pavements.
Importance of Joint Fillers in Pavement Maintenance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap up our understanding of joint fillers. Why do you think they are crucial for pavement maintenance?

They help absorb movements due to temperature changes!

Exactly! Without them, cracks may form and lead to water infiltration, resulting in damage over time.

So, they are not just about filling gaps?

Right! They play a vital role in the overall durability of the pavement as well. Remember: ‘C-R-D-W’ to recall their properties, and think of the materials to use wisely.

In conclusion, joint fillers are key to maintaining the structural integrity and service life of concrete pavements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Joint fillers play a critical role in concrete pavements by providing compressibility and resistance to environmental factors. Their proper selection and installation ensure longevity and durability of joint systems.
Detailed
Joint Fillers
Joint fillers are compressible materials that are installed into joint gaps in concrete pavements. Their primary purpose is to accommodate the thermal expansion of concrete slabs while absorbing compressive forces without breaking down over time. They remain in their positions throughout the lifespan of the pavement, ensuring structural integrity and performance.
Key Properties of Joint Fillers
Joint fillers are characterized by several desirable properties: they must be highly compressible, recover their shape after compression, resist extrusion under pressure, and be durable in various environmental conditions. Additionally, they should be water-resistant and resistant to biological degradation.
Common Materials Used
Typical materials for joint fillers include:
- Bituminous Premoulded Fillers: often made from a combination of bitumen and fibers, prevalent in regions like India.
- Cork: favored for its natural compressibility and durability.
- Sponge Rubber/Foam Sheets: lightweight and highly compressible, making them easy to install.
- Cellulose Fiberboard: usually treated with bitumen for enhanced water resistance.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): known for being lightweight and resilient.
Installation Techniques
There are critical techniques to ensure effective installation of joint fillers, such as placing them flush with the slab edges, preventing gaps or misalignments, covering the full slab depth, and using bond breakers to enhance performance.
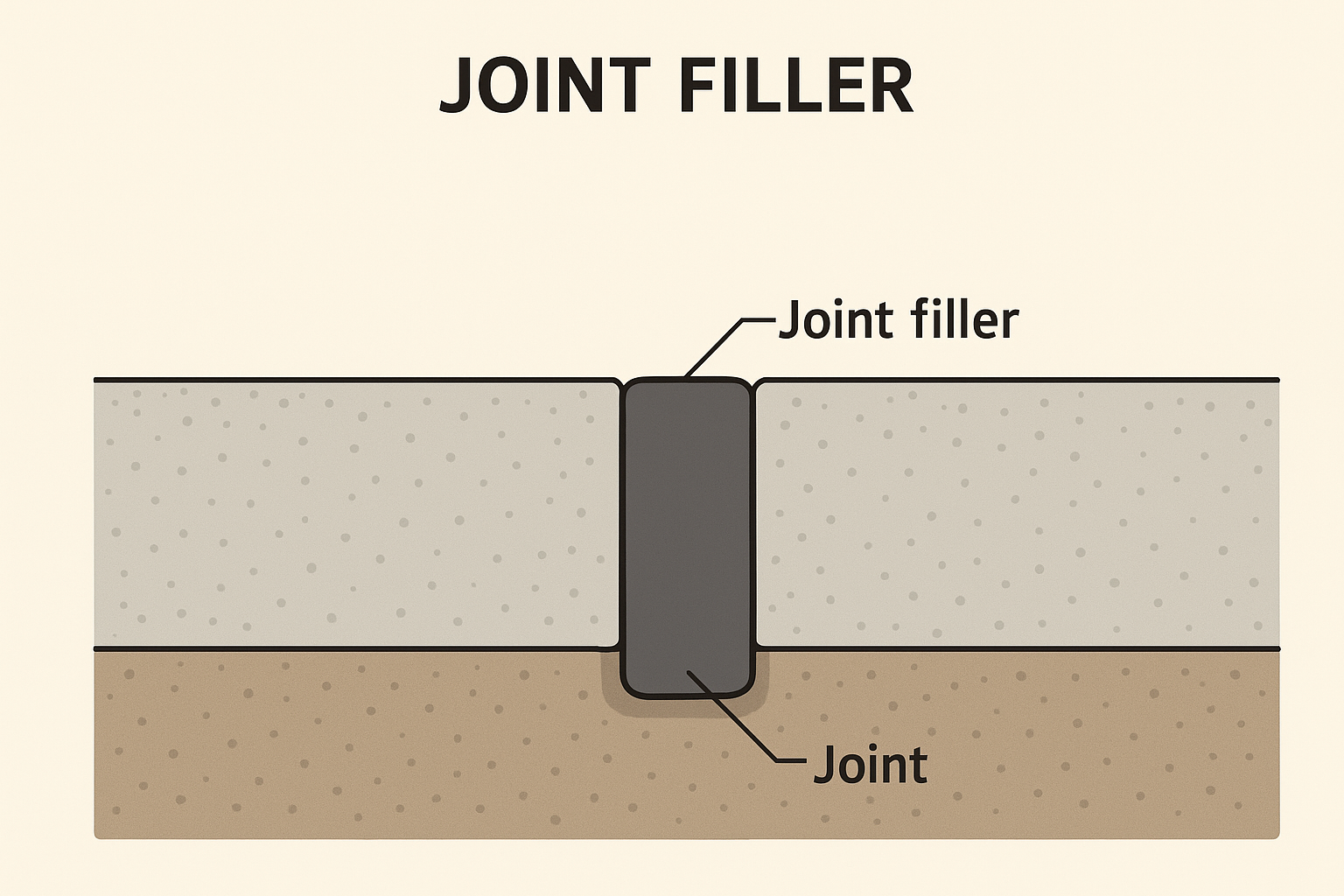
Overall, appropriate design, material selection, and maintenance practices related to joint fillers are pivotal for achieving durable and functional concrete pavements.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Function of Joint Fillers
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Joint fillers are compressible materials inserted in the joint gap to accommodate the expansion of concrete slabs. They remain in place throughout the pavement's life, absorbing compressive forces without disintegrating.
Detailed Explanation
Joint fillers are materials placed in the spaces, or joints, within concrete pavements. Their main purpose is to allow the concrete to expand and contract without causing damage. As temperatures change, concrete naturally expands and shrinks; hence, these fillers must be capable of compressing and absorbing these changes. This means that the fillers should remain intact and functional over the entire lifetime of the pavement, even when subjected to heavy loads or temperature variations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of joint fillers like the cushioning in a running shoe. Just as the cushioning absorbs the impact when you step down, preventing damage to your feet, joint fillers absorb the stresses that occur in concrete due to temperature and load changes, preventing cracks and failures in the pavement.
Desirable Properties of Joint Fillers
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- High compressibility
- Recovery after compression
- Resistance to extrusion
- Durability under environmental conditions
- Non-absorbent or low water absorption
- Resistance to rot or biological degradation
Detailed Explanation
Joint fillers are required to have certain properties to perform effectively. High compressibility ensures they can easily adapt as the concrete expands or contracts. Recovery after compression means that once the pressure is released, the filler returns to its original shape. Resistance to extrusion prevents the filler from being pushed out of the joint under pressure. Durability refers to their ability to withstand weather conditions over time. Being non-absorbent or having low water absorption is crucial to prevent water damage. Finally, resistance to rot means that they should not degrade due to biological factors, like mold or insects.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sponge. A good sponge can compress when you squeeze it and then bounce back to its original shape. Similarly, joint fillers must compress under pressure but return to their shape, ensuring they are always ready to support the concrete when it expands or contracts without getting destroyed by water or mold.
Common Materials Used as Joint Fillers
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Bituminous Premoulded Fillers: Made from bitumen and fibers, common in India.
- Cork: Natural, compressible, and durable.
- Sponge Rubber or Foam Sheets: Light, easy to install, and highly compressible.
- Cellulose Fiberboard: Impregnated with bitumen for waterproofing.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): Lightweight and resilient.
Detailed Explanation
Several materials are commonly used for joint fillers, each with specific characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Bituminous premoulded fillers are elastic and often used in areas with high traffic. Cork is a natural option known for its excellent compressibility and durability, making it a reliable choice. Sponge rubber and foam sheets are lightweight and can be easily installed, making them suitable for quick projects. Cellulose fiberboard is reinforced with bitumen for added waterproofing benefits. Lastly, Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is both lightweight and resilient, providing effective support for expansion joints.
Examples & Analogies
Choosing joint filler materials can be likened to picking shoes for different activities. Just like you would select running shoes for jogging and hiking boots for walking in the mountains, different filler materials serve specific needs based on how much pressure, water, or environmental challenges they need to withstand.
Installation Techniques
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Should be placed vertically, flush with slab edges.
- Care must be taken to avoid gaps or misalignments.
- Should cover the full depth of slab (or as per design).
- Bond breakers may be used to avoid adhesion with concrete.
Detailed Explanation
Proper installation of joint fillers is critical to their performance. They should be positioned vertically along the edges of the concrete slabs to ensure they function effectively. Installing them flush helps maintain a clean surface and prevents any gaps, which could reduce their effectiveness. The fillers must also cover the full depth of the joint as per design specifications to fully accommodate any expansion or contraction. Sometimes, bond breakers are applied to the concrete surface to prevent the fillers from sticking to the concrete, which allows for proper movement.
Examples & Analogies
Installing joint fillers can be compared to putting on a fitted case for a phone. Just as the case needs to fit perfectly around the phone to offer protection without gaps, joint fillers must be installed correctly to ensure they effectively protect the pavement and accommodate movement without leaving spaces that could lead to problems.
Key Concepts
-
Joint Fillers: Essential components in concrete for accommodating thermal expansion and preventing water ingress.
-
Desirable Properties: High compressibility, recovery after compression, resistance to extrusion, durability, low water absorption, and resistance to rot.
-
Common Materials: Include bituminous fillers, cork, sponge rubber, cellulose fiberboard, and EPS.
-
Installation Techniques: Must ensure flush placement, avoid gaps, cover full slab depth, and potentially use bond breakers.
Examples & Applications
Using sponge rubber as a joint filler in highway pavements for its compressibility and longevity.
Applying bituminous premoulded fillers in urban areas to prevent rainwater infiltration into pavement joints.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fillers fill gaps in concrete lands, to help the pavement withstand.
Stories
Imagine a concrete road on a hot day; without joint fillers, it would sway and crack, leading to chaos!
Memory Tools
C-R-D-W: Compressibility, Recovery, Durability, Water-resistance.
Acronyms
J-F
Joint Fillers - Just Fill gaps safely!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Joint Fillers
Compressible materials inserted in joint gaps to accommodate the expansion of concrete slabs.
- Compressibility
Ability of a material to be compressed and allow for movement in joint spaces.
- Durability
The capacity of a joint filler to withstand environmental conditions without degradation.
- Water Absorption
The ability of a material to absorb water, which should ideally be low in joint fillers.
- Bituminous Fillers
Filler made from bitumen and fibers, commonly used in joint filling applications.
- Sponge Rubber
A lightweight and highly compressible material often used for joint fillers.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
