Practical Applications of RF Amplifiers and Filters
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Applications of RF Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss where RF amplifiers are most commonly used. Can anyone think of an application?

In communication systems, right? They amplify the signals.

Exactly! RF amplifiers boost weak signals received by antennas in communication systems. They're crucial for effective transmission.

What about radar systems? Do they use RF amplifiers?

Yes, great point! Radar systems amplify signals to detect objects over long distances. It’s one of their primary uses!

What about in signal processing? I think they might be used there too?

Absolutely! In signal conditioning, RF amplifiers help amplify desired signals while removing unwanted noise.

So, what are three key applications of RF amplifiers discussed today? Let’s summarize.

Communication systems, radar systems, and signal processing.

Exactly! Excellent work.
Applications of RF Filters
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus now to RF filters. Can anyone tell me what types of RF filters we discussed?

There are band-pass filters, low-pass filters, and band-stop filters!

Correct! Band-pass filters are particularly important in radio receivers. They isolate desired frequency bands. What about low-pass filters?

They remove high-frequency noise in audio and data transmission systems.

Exactly, well said! Now, can anyone remind me of when we would use a band-stop filter?

They’re used to eliminate specific frequency bands that cause interference.

Yes! Interference filtering is a major application for band-stop filters. Let’s summarize: what are the applications of the filters we discussed?

Band-pass for isolating frequencies, low-pass for noise reduction, and band-stop for interference.

Fantastic summary everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
RF amplifiers and filters are critical in numerous systems, including communications and radar. Amplifiers boost weak signals, while filters select or reject frequencies. Understanding their applications is vital for effective RF circuit design.
Detailed
Practical Applications of RF Amplifiers and Filters
RF amplifiers and filters are integral in numerous applications within communication systems, radar, and signal processing. RF amplifiers amplify weak signals to ensure they can be transmitted effectively, particularly in communication systems, where signals received by antennas often need significant boosts to avoid distortion. In signal processing, RF amplifiers help condition signals, amplifying those that are desired while reducing noise interference.
On the other hand, RF filters are crucial for selecting specific frequency bands and rejecting unwanted frequencies. Band-pass filters serve in radio receivers and transmitters to isolate the frequency bands of interest, allowing clear communication. Low-pass filters find their usage in audio and data systems to eliminate high-frequency noise, improving overall signal quality. Band-stop filters act to remove interference by targeting specific frequency bands that detract from signal integrity. Understanding these practical applications aids in designing effective RF systems, balancing the need for signal amplification and filtering within desired parameters.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Applications of RF Amplifiers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
RF Amplifiers:
- Communication Systems: Used to amplify weak signals received by antennas in communication systems.
- Signal Processing: Used in signal conditioning to amplify desired signals and remove unwanted noise.
- Radar Systems: Amplify radar signals to detect objects over long distances.
Detailed Explanation
RF amplifiers are critical in various fields, especially in communication. In communication systems, they amplify weak signals that come from antennas, which is essential because signals collected from antennas can be very faint. In signal processing, RF amplifiers help to boost the signals we want while minimizing or eliminating any noise that may interfere with these signals. Furthermore, in radar systems, they play a pivotal role in enhancing the signals that bounce back from objects, which helps in detecting those objects from far away.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the RF amplifier as a megaphone for a person's voice: if someone is speaking softly (analogous to a weak signal), the megaphone takes that gentle sound and amplifies it so that people far away can hear clearly. Similarly, in radar systems, it's like sending out a strong voice to ensure even distant listeners can respond to it.
Applications of RF Filters
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
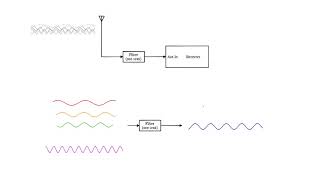
RF Filters:
- Band-Pass Filters: Used in radio receivers and transmitters to isolate desired frequency bands.
- Low-Pass Filters: Used to remove high-frequency noise in audio and data transmission systems.
- Band-Stop Filters: Used in applications where specific frequency bands need to be eliminated, such as interference filtering.
Detailed Explanation
RF filters are specialized circuits designed to control which signals are passed through while blocking others. Band-pass filters are commonly found in radio devices where they help to select only specific frequencies for clear reception and transmission. Low-pass filters will allow only low-frequency signals to go through while filtering out high frequencies, which is great for audio and data systems to prevent interference from noise. Band-stop filters, on the other hand, specifically target and remove certain frequencies that may be causing undesired interference or noise.
Examples & Analogies
Think of RF filters as bouncers in a club. A band-pass filter lets in people (signals) who fit a certain style (frequency range) while keeping everyone else out. Low-pass filters are like club rules that only allow people dressed in casual wear (low frequencies) while preventing suits and ties (high frequencies). Conversely, band-stop filters kick out a specific group, such as those wearing a particular color (unwanted interference), ensuring a more enjoyable experience for everyone inside.
Key Concepts
-
RF Amplifiers: Key components for amplifying weak signals in communication systems.
-
Signal Processing: The use of RF amplifiers to enhance desired signals and suppress noise.
-
Band-Pass Filters: Vital for isolating specific frequency bands in receivers and transmitters.
-
Low-Pass Filters: Important for eliminating high-frequency noise in audio.
-
Band-Stop Filters: Used for removing specific unwanted frequencies.
Examples & Applications
RF amplifiers in a mobile phone boost signals received from cell towers to ensure clear communication.
Low-pass filters in audio equipment reduce high-frequency noise, improving sound quality by allowing only lower frequencies to pass.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In filters, frequency’s the key, keep the low or the high; but let the desired ones be free.
Stories
Imagine a busy highway. The RF amplifier is a tollbooth that allows only the right number of cars—signals—to drive through smoothly, while the filters are the traffic police ensuring only certain cars can enter the premium lanes.
Memory Tools
To remember the applications, think of RFS—Radar, Filters, Signal processing.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'CARS' for remembering RF amplifier applications
Communication
Amplification
Radar Systems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- RF Amplifier
A device used to amplify weak radio frequency signals in various applications, such as communication systems and radar.
- Filter
A circuit that allows certain frequency ranges to pass through while attenuating unwanted frequencies.
- BandPass Filter
A type of filter that allows a specific range of frequencies to pass while attenuating frequencies outside this range.
- LowPass Filter
A filter that permits frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency and attenuates higher frequencies.
- BandStop Filter
A filter that attenuates a specific range of frequencies while allowing frequencies outside this range to pass.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
