Lab Work on RF Amplifiers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Objective of Lab Work
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today's lab work aims to design and analyze an RF amplifier. The objective is to enhance weak RF signals effectively. Can anyone share why amplifying weak signals is crucial?

It's important because weak signals can easily get lost in noise, especially in communication systems.

Exactly! In RF applications, clarity and strength of the signal are essential for maintaining quality communication. Let's discuss what materials we need for this lab.

We need a transistor or an FET, and also some resistors and capacitors for stabilization, right?

Correct, Student_2! We will also need a signal generator and an oscilloscope to test our circuit. Now, let's dive into the step-by-step procedure.
Materials and Their Purpose
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why is a transistor or FET crucial in our design?

They are the active components that help in signal amplification.

That’s right! And how about resistors and capacitors?

Resistors help in biasing and stabilizing the circuit while capacitors can filter out noise.

Exactly, and this combination ensures our amplifier works effectively. Understanding these roles is essential for successful circuit construction.
The Procedure and Testing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about how we will design the amplifier circuit. What’s the first step?

We need to design the amplifier based on our desired gain and frequency range.

Correct! Once we finish the design phase, we will build the circuit. What comes next?

Apply a weak RF signal to see how well it amplifies.

Exactly! After applying the signal, we will measure the output to check our gain. Why is checking linearity and stability important?

So we can ensure that the amplifier behaves consistently without distortion.

Great observation! Monitoring these parameters confirms our amplifier design's reliability.
Practical Applications of RF Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

After our lab work, how do you think these amplifiers are used in real applications?

They are used in communication systems to boost signals from antennas.

Absolutely! And they can also be used in radar systems to detect objects. Knowing their applications helps us understand the importance of RF amplifier design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The lab work section focuses on the practical aspect of RF amplifier design, detailing the materials required and the step-by-step procedure. It aims to provide students with hands-on experience in building an amplifier circuit, applying weak RF signals, and measuring output for gain, linearity, and stability.
Detailed
Lab Work on RF Amplifiers
Objective
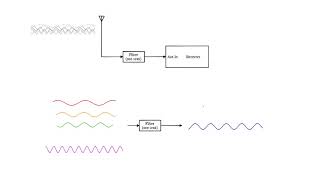
The main objective of this lab work is to design and analyze an RF amplifier capable of boosting weak RF signals. This hands-on experience is crucial in understanding the practical application of theoretical concepts learned in RF amplifier design.
Materials Required
- Transistor or FET (e.g., BJT for common-emitter, FET for common-source)
- Resistors and capacitors needed for biasing and stabilization
- A signal generator and oscilloscope for signal testing
- A power supply for the amplifier circuits
Procedure
- Design the amplifier circuit based on the desired frequency range and amplification requirements.
- Build the amplifier circuit and apply a weak RF signal to its input.
- Measure the output signal to calculate the gain of the amplifier. Check for linearity and stability during this step.
Understanding and applying these steps enables students to bridge theory and practice, ensuring readiness for real-world RF circuit applications.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Objective of the Lab Work
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Objective: Design and analyze an RF amplifier to amplify a weak RF signal.
Detailed Explanation
The primary goal of this lab work is to create and study an RF amplifier circuit. This type of amplifier is specifically designed to boost weak radio frequency signals, which are often too faint for processing in communication systems. The objective emphasizes understanding how to both design the circuit and evaluate its performance effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the RF amplifier as a megaphone for weak sounds. Just as a megaphone takes a soft voice and makes it loud enough to be heard over a crowd, the RF amplifier takes weak radio signals and increases their strength so they can be effectively used in devices like radios or cell phones.
Materials Needed
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Materials:
1. Transistor or FET (e.g., BJT for common-emitter, FET for common-source)
2. Resistors, capacitors for biasing and stabilization
3. Signal generator and oscilloscope
4. Power supply
Detailed Explanation
To carry out the lab work, several components are needed. A transistor or a field-effect transistor (FET) serves as the primary active device for amplification. Resistors and capacitors are crucial for setting up the amplifier's biasing conditions and ensuring stability during operation. A signal generator is required to provide the initial weak RF signal, which the amplifier will boost, while an oscilloscope helps visualize the output signal to determine the effectiveness of the amplifier's performance. Lastly, a power supply is necessary to power the amplifier circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're baking a cake. You need specific ingredients: sugar, flour, eggs, and a recipe (the process). In this lab, the transistors are like the main ingredients (like flour), while the resistors and capacitors are the supporting ingredients, and the signal generator and oscilloscope serve as your kitchen tools to ensure your cake (or RF amplifier) turns out just right.
Procedure for Building the Amplifier
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Procedure:
1. Design the amplifier circuit based on the desired frequency range and gain.
2. Build the amplifier and apply a weak RF signal.
3. Measure the output signal to calculate the gain and check for linearity and stability.
Detailed Explanation
The procedure consists of three main steps. First, you'll design the amplifier circuit, which includes selecting the appropriate configuration (like common-emitter) that suits the desired frequency range and gain characteristics. Next, you will physically build the circuit with the chosen components. After constructing the amplifier, you will apply a weak RF signal from the signal generator. Finally, an important part of the experiment involves measuring the output signal with the oscilloscope to assess the amplifier's gain (how much it boosted the signal) and its linearity (how accurately it amplified the signal without distortion) and stability (whether it operates reliably without oscillations).
Examples & Analogies
Think of this procedure as tuning and testing a new music instrument. First, you select how you want the instrument to sound (design it). Next, you put it together (build it). Then, you play a quiet note to see how much louder it can get and if it stays in tune (measure and check performance).
Key Concepts
-
Objective: The aim is to design and analyze RF amplifiers for weak signal amplification.
-
Materials: Components needed include transistors, resistors, capacitors, signal generators, and oscilloscopes.
-
Procedure: Steps include circuit design, building the circuit, applying signals, and measuring output.
Examples & Applications
In communication systems, RF amplifiers are crucial for enhancing the weak signals picked up by antennas.
In radar technology, RF amplifiers are utilized to amplify signals reflecting off objects to determine their distance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Design, build, apply, and see, the RF signal grow happily.
Stories
In a town of weak signals, there lived an RF amplifier named Ampy, who loved to boost all the sound waves so people could connect easily.
Memory Tools
To remember the steps of the lab: DAB - Design, Assemble, Boost.
Acronyms
LAB - Learning Amplification Basics
Design
Build
Analyze.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- RF Amplifier
A device used to amplify weak radio frequency signals to a higher level.
- Transistor
A semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals.
- FET
Field Effect Transistor; a type of transistor that controls the flow of current using an electric field.
- Oscilloscope
An electronic instrument that graphically displays electrical signals.
- Gain
The ratio of output signal power to input signal power, indicating how much an amplifier boosts a signal.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
