Common-Emitter (CE) Amplifier
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Common-Emitter Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into the common-emitter amplifier, a critical component in RF circuits. Can anyone tell me what they think makes this amplifier essential in electronics?

I think it has something to do with amplifying weak signals.

Absolutely, that's right! The CE amplifier is particularly good at amplifying weak RF signals. Can anyone summarize its voltage gain feature?

It provides high voltage gain, which helps in making weak signals stronger.

Great summary! The voltage gain can be calculated using the equation Av = -R_C / r_e. Let's remember that for later calculations.
Characteristics of Common-Emitter Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore the characteristics of the common-emitter amplifier. What do we know about its input and output impedance?

It has moderate input and output impedance, I think!

Correct! This moderate impedance makes it suitable for various applications without excessive loading. Can anyone explain how we would calculate its gain?

Using the formula Av = -R_C / r_e?

Exactly! Understanding this gain equation is crucial for designing effective amplifiers.
Applications of Common-Emitter Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the common-emitter amplifier's functionality, where do you think we might use this in real-world applications?

I think it's used in communication systems, like radios.

Great insight! CE amplifiers are indeed extensively used in radios and communication systems for amplifying incoming signals. Can anyone else think of another application?

Radar systems could also use these amplifiers to detect objects.

Excellent! Radar systems benefit from the ability of the CE amplifier to amplify signals over long distances.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The common-emitter (CE) amplifier configuration is pivotal in RF engineering, offering significant voltage gain while maintaining moderate input and output impedance. It plays a crucial role in low-power RF circuit designs, with its gain determined by the collector resistance and internal emitter resistance.
Detailed
Common-Emitter (CE) Amplifier
The Common-Emitter (CE) Amplifier is a fundamental configuration used in RF (Radio Frequency) circuit designs. Its importance lies in its capability to provide a high voltage gain, making it widely applicable in low-power RF circuits. In this configuration, the emitter terminal is common to both the input and output circuits, which allows for efficient signal amplification.
Characteristics of Common-Emitter Amplifier
- High Voltage Gain: The CE amplifier is capable of amplifying weak signals significantly, which is critical in RF applications where signals may be at very low levels.
- Moderate Input and Output Impedance: This configuration presents moderate impedance at both the input and output, making it versatile for various circuit designs.
- Gain Equation: The voltage gain (Av) can be expressed as:
\[ A_v = -\frac{R_C}{r_e} \]
where \( R_C \) is the collector resistance and \( r_e \) is the internal emitter resistance. This relationship illustrates how gain is influenced by these two parameters, allowing designers to adjust the amplifier's performance according to specific needs.
In summary, the common-emitter amplifier's design allows for effective amplification of RF signals, with its key features strongly linking to its operational performance in amplifying low-power circuits.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Common-Emitter Amplifier
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The common-emitter amplifier is a basic configuration used in both low- and high-frequency applications. It provides voltage gain and is widely used in low-power RF circuits.
Detailed Explanation
The common-emitter amplifier is one of the fundamental configurations for building amplifiers. It's known for its ability to amplify voltage, making it a popular choice for both low and high-frequency applications. This type of circuit is commonly found in low-power radio frequency (RF) devices, implying it's utilized when the power level of the signals is relatively low.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a common-emitter amplifier as a megaphone at a concert. Just like a megaphone amplifies a speaker's voice to make it louder and clearer for the audience, a common-emitter amplifier amplifies weak RF signals, making them suitable for processing or transmission.
Characteristics of Common-Emitter Amplifier
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Characteristics:
■ High voltage gain.
■ Moderate input and output impedance.
Detailed Explanation
The common-emitter amplifier has several defining characteristics: it typically offers a high voltage gain, meaning it can greatly increase the voltage of an input signal. This feature is beneficial in many electronic applications where weak signals need to be boosted. Additionally, it has moderate input and output impedance, which aids in compatibility with different components in an electronic circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the amplifier's high voltage gain like a speaker that is able to produce a loud sound despite being fed a soft signal. The moderate impedances are similar to a middle-level adjustment on a sound mixer that balances how much input is needed vs. how much output is produced.
Gain Equation of Common-Emitter Amplifier
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
■ Gain Equation:
Av=−RCreA_v = -\frac{R_C}{r_e}
Where R_C is the collector resistance, and r_e is the internal emitter resistance.
Detailed Explanation
The gain of a common-emitter amplifier can be quantified with the equation Av = -RC/re. Here, RC refers to the collector resistance, and re represents the internal emitter resistance. This equation indicates how the amplifier's voltage gain is influenced by these resistances: a higher collector resistance will result in a greater gain, while a higher internal emitter resistance will reduce it. The negative sign denotes the phase inversion of the output signal relative to the input signal.
Examples & Analogies
You can liken this equation to a plumbing system. The collector resistance (RC) is like the size of the pipe, while the emitter resistance (re) is like a faucet partially closed. If you make the pipe larger (increasing RC), more water can flow through (higher voltage gain). Conversely, if the faucet is partially closed (increased re), less water can flow (lower voltage gain).
Key Concepts
-
Voltage Gain: The capability of an amplifier to enhance input signal strength, with the CE amplifier offering high voltage gain.
-
Impedance: A characteristic of the amplifier that affects how it integrates into circuits, with the CE amplifier known for moderate impedance.
-
Gain Equation: Mathematical representation of the relationship between collector resistance and internal emitter resistance, guiding amplifier design.
Examples & Applications
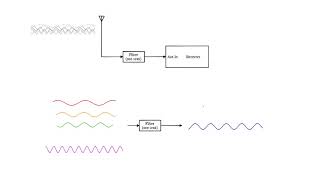
In a radio receiver, a common-emitter amplifier can amplify weak signals received by the antenna, making them strong enough for processing.
In radar systems, CE amplifiers boost extremely weak reflected signals bounced off objects, allowing accurate detection over long distances.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the world of RF signal might, / Common-emitter amplifies with great height.
Stories
Imagine a weak signal trying to talk. The CE amplifier hears it loud and clear, boosting its voice like a friend in a crowded hall.
Memory Tools
Remember 'High IMPact' for the Common-Emitter's 'High Voltage Impact' on weak signals with Moderate Impedance.
Acronyms
C.E.A. - Common for connection, Emitter is the active part, Amplifier does the boost!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CommonEmitter (CE) Amplifier
A configuration of amplifier where the emitter terminal serves as the reference point for both input and output, providing high voltage gain.
- Voltage Gain
The ratio of output voltage to input voltage in an amplifier, commonly expressed as Av.
- Impedance
The opposition that a circuit presents to the flow of electric current, encompassing both resistive and reactive components.
- Collector Resistance (R_C)
The resistance connected to the collector terminal of a transistor in a common-emitter configuration, impacting gain.
- Internal Emitter Resistance (r_e)
The small resistance associated with the emitter that plays a crucial role in determining the amplifier's gain.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
