CPU Organization
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Types of CPUs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the various types of CPU organizations. Can anyone tell me what a single-core CPU might be like?

I think it has only one core, so it can only work on one task at a time.

Exactly! The single-core CPU is simpler and can handle one instruction at a time. Now, how about multi-core CPUs? What do you think they do?

They can perform multiple instructions simultaneously because they have more than one core!

Well said! This parallel processing capability allows multi-core CPUs to significantly improve performance. Let's summarize these two types. A single-core CPU handles one task at a time, while multi-core CPUs can run several tasks at once, improving efficiency.
Superscalar CPUs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into the concept of superscalar CPUs. What do you think sets a superscalar CPU apart from the other types?

It can execute multiple instructions in the same cycle, right?

Exactly! Superscalar architectures have multiple execution units, allowing them to process several instructions at once. This is different from single-core and even multi-core configurations, which focus on handling multiple tasks rather than processing multiple instructions concurrently.

So, it’s about speeding up the instruction process instead of just handling more tasks?

Yes! This approach significantly enhances throughput, making superscalar CPUs some of the most efficient in modern computing.
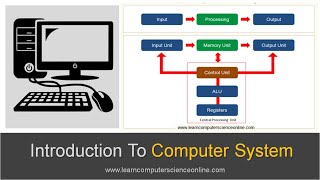
Internal Components of CPU
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift focus to the internal components of the CPU. Can anyone name a crucial part of the CPU?

The ALU! It does all the calculations.

Correct! The ALU, or Arithmetic Logic Unit, performs arithmetic and logical operations. What about the Instruction Register?

It stores the current instruction that's being executed!

Exactly! And the Program Counter is also vital because it tells us where to find the next instruction. Remember the acronym IPC – Instruction, Program Counter, ALU – which represents these components. Can anyone summarize the role of these components together?

They work together to process instructions efficiently, coordinating execution with the control logic.

Well summarized! These components are fundamental in making the CPU function effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section on CPU organization explains the various configurations of processors, including single-core, multi-core, and superscalar architectures. It highlights the internal components of the CPU, such as the Instruction Register, Program Counter, and Arithmetic Logic Unit.
Detailed
CPU Organization
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the core component of any computer system, often referred to as its brain. This section categorizes the types of CPU organization into three main types:
- Single-core CPU: This type consists of one processing unit capable of handling one task at a time. Despite its limitations in performance, it remains widely used in basic computing tasks.
- Multi-core CPU: Multi-core processors contain multiple processing units (cores) within a single chip, allowing for parallel processing. This organization boosts performance as multiple instructions can be executed simultaneously.
- Superscalar CPU: A more advanced architecture that can execute more than one instruction per clock cycle, enhancing the throughput of instruction processing.
In addition to these classifications, the section outlines several critical internal components of the CPU:
- Instruction Register (IR): Holds the current instruction being executed.
- Program Counter (PC): Indicates the memory address of the next instruction to be executed.
- Accumulators: Registers that store intermediate results of arithmetic and logic operations.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs all arithmetic and logical operations within the CPU.
- Control Logic: Coordinates and manages the operations of the CPU.
Understanding CPU organization is vital as it significantly influences a computer's performance and efficiency.
Youtube Videos
![How does Computer Hardware Work? 💻🛠🔬 [3D Animated Teardown]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/d86ws7mQYIg/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of CPU Organization
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
CPU is the brain of the system and may be organized as:
1. Single-core – One processing unit.
2. Multi-core – Multiple cores for parallel processing.
3. Superscalar – Can execute more than one instruction per cycle.
Detailed Explanation
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is often referred to as the brain of a computer because it executes instructions and processes data. The organization of a CPU can vary in structure: 1. A single-core CPU has just one processing unit which can handle one task at a time. 2. Multi-core CPUs contain multiple cores, allowing for parallel processing where multiple tasks can be handled simultaneously. 3. Superscalar CPUs can execute more than one instruction during a single clock cycle, increasing computational speed by efficiently utilizing instruction-level parallelism.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy restaurant kitchen. A single-core CPU is like a chef trying to manage all orders alone, cooking one dish at a time. In contrast, a multi-core CPU is like having several chefs, each cooking different dishes at the same time, speeding up the overall service. A superscalar CPU is like having a team of chefs who each can specialize in specific tasks (like one for grilling, one for frying, etc.), allowing them to complete multiple tasks in the same time frame.
Internal Units of the CPU
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Internal units include:
● Instruction Register (IR)
● Program Counter (PC)
● Accumulators
● ALU and Control Logic
Detailed Explanation
Within the CPU, several internal units play critical roles. The Instruction Register (IR) holds the current instruction being executed, allowing the CPU to know what operation to perform. The Program Counter (PC) keeps track of the address of the next instruction, ensuring the CPU executes instructions in the correct sequence. Accumulators are temporary storage areas in the CPU used for holding intermediate results of calculations. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is responsible for performing all arithmetic and logical operations, while the Control Logic directs the operation of the CPU by coordinating the activities of all units.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the CPU as a team of skilled workers in a factory. The Instruction Register (IR) is like a queue of tasks; the Program Counter (PC) indicates which task comes next. The accumulators are workbenches where parts of tasks get assembled (like pieces of a puzzle). The ALU is the machine that performs all necessary transformations, while the Control Logic serves as the supervisor ensuring everyone knows their responsibilities and the workflow is efficient.
Key Concepts
-
CPU Organization: Structure and types of CPU designs including single-core, multi-core, and superscalar.
-
Instruction Register (IR): Holds the current instruction being executed.
-
Program Counter (PC): Points to the next instruction to be executed.
-
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic and logical operations.
-
Control Logic: Coordinates the operations within the CPU.
Examples & Applications
A single-core CPU is found in basic devices like calculators, managing simple tasks.
A multi-core CPU is used in modern laptops, allowing users to run multiple applications at once, significantly enhancing user experience.
A superscalar CPU can be found in high-performance computing systems, capable of executing several instructions within a single clock cycle.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Single-core is slow, one task at a go. Multi-core runs more, handling tasks galore!
Stories
Imagine a chef (single-core) in a restaurant, preparing one dish at a time. Now visualize a team of chefs (multi-core) working in sync, creating several dishes at once. Superscalar is like having each chef prep multiple ingredients simultaneously!
Memory Tools
IPC for CPU components: I = Instruction Register, P = Program Counter, C = ALU.
Acronyms
MAP for remembering CPU types
= Multi-core
= ALU
= PC.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Singlecore CPU
A CPU with a single processing unit capable of handling one instruction at a time.
- Multicore CPU
A CPU with multiple processing units (cores) that can run multiple instructions simultaneously.
- Superscalar CPU
A CPU architecture that can execute more than one instruction in the same cycle.
- Instruction Register (IR)
A register that holds the current instruction being executed by the CPU.
- Program Counter (PC)
A register that contains the address of the next instruction to be executed.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
A digital circuit within the CPU that performs arithmetic and logical operations.
- Control Logic
The component of a CPU that manages the execution of instructions and the flow of data.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
