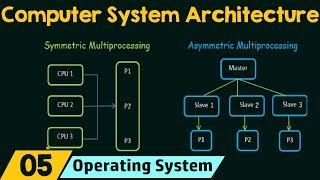
Benefits of Multicore Processing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Multicore Processors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome to our discussion on multicore processing! Can anyone tell me what a multicore processor is?

I think it's a processor that has more than one core.

Exactly! A multicore processor is a single chip that contains multiple independent processing units, known as cores. This allows for parallel execution of tasks. Now, why do you think multicore processors have become so popular?

Maybe because they are faster?

That's a good point! They indeed provide enhanced performance, but they also help with energy efficiency, especially as single-core speeds reach physical limits. Remember the acronym 'PEM' for Performance, Efficiency, and Multitasking. Which of these benefits do you find most interesting?

I think the multitasking is cool! It means I can run multiple applications at once without slowing down.

Right, that truly improves user experience. Remember, multicore processors are designed to optimize the way we handle parallel workloads!
Performance Enhancement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on performance enhancement. How does having multiple cores improve the processing performance of a computer?

Each core can handle a different task, right?

Exactly! Each core can execute separate threads or processes, which increases overall throughput. This is particularly beneficial for applications designed for parallel processing. Can anyone think of an example of such applications?

Games? They need a lot of processing power to run smoothly.

Great example! Games often require significant computational power, and multicore processors can manage this by processing different parts of the game simultaneously. This also ties back to our PEM acronym as we see how it enhances performance. Any other scenarios?

Video editing! It can use multiple threads to process different video files.

Absolutely! Video editing software greatly benefits from multicore processors. Remember that when we talk about performance, parallelism is key. Now, let's summarize today’s discussion.

We learned that multicore processors can simultaneously execute multiple tasks, greatly enhancing performance across a variety of applications.
Energy Efficiency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into energy efficiency. Why do we care about energy efficiency in processors?

Because lower energy consumption means cheaper electric bills and better for the environment.

Precisely! Multicore processors help reduce power consumption without the need for higher clock speeds. What do you think is a common technique used to optimize energy efficiency?

Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)?

Exactly! DVFS adjusts the voltage and frequency based on current workload, allowing cores to lower power usage during lighter tasks. So remember 'DVFS' for effective energy efficiency. How does this relate to the concept of multitasking we discussed earlier?

If the cores are efficient, they can work on many tasks without using too much power.

Yes, it’s about balancing workload across cores without overloading any single core, which is crucial for both performance and energy efficiency. To sum up, we learned how multicore processors are designed to enhance energy efficiency alongside performance.
Multitasking Capabilities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore multitasking capabilities. Why can a multicore processor handle multitasking better than a single-core processor?

Because each core can manage different applications at the same time?

Exactly! With multiple cores, each core can execute a different thread or process. How does this make the user experience better, especially when running applications?

It makes everything run smoother and faster, like browsing the web and using Word at the same time.

Great insight! This capability allows for efficient handling of various applications simultaneously, making it ideal for tasks that require quick switching between programs. Don’t forget our PEM acronym here; all these benefits tie back to enhanced performance, efficiency, and multitasking. Can anyone summarize how multicore processing impacts our daily computing experience?

It allows us to use multiple applications smoothly and saves energy, making our devices faster and more efficient!

Excellent summary! Multicore processing indeed enhances our computing experience in various impactful ways. Let’s recap the main points we discussed today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The benefits of multicore processing lie in its ability to improve performance and energy efficiency significantly while allowing for efficient multitasking and parallel workload management. This section explores the distinct advantages that multicore architectures bring to modern computing.
Detailed
Benefits of Multicore Processing
Multicore processors, characterized by multiple independent processing units, are essential in advancing computing capabilities. The introduction of multicore architecture addresses the limitations of single-core processors, particularly as their clock speeds reach physical limits.
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Performance: With multiple cores, a multicore processor can execute several threads or processes simultaneously, significantly increasing overall processing power.
- Energy Efficiency: By distributing workload across multiple cores, multicore architectures can maintain lower clock speeds and reduced power consumption compared to ramping up single-core speeds, resulting in energy savings.
- Improved Multitasking: Multicore systems can handle multiple applications running at the same time without significant performance degradation. Each application can utilize a separate core, allowing for smoother multitasking.
- Better Handling of Parallel Workloads: Many modern applications, particularly in data-intensive environments, are designed to exploit parallelism. Multicore architectures are better suited for such workloads, allowing for a more efficient execution of tasks that can run concurrently.
In conclusion, the transition to multicore processors represents a fundamental shift in computer architecture, providing both performance enhancements and energy savings, making them the standard in contemporary computing.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Enhanced Performance
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Multicore processors significantly enhance performance by allowing multiple cores to execute different tasks simultaneously, improving overall computational throughput.
Detailed Explanation
Enhanced performance in multicore processors occurs because different cores can work on separate tasks at the same time. Instead of a single core processing tasks sequentially (one after the other), multicore systems can divide tasks among available cores. For instance, if one core handles a complex calculation while another core manages data input/output, the processor can complete both tasks at a faster rate than a single core could alone.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a multicore processor like a team of chefs in a restaurant. Instead of one chef preparing all the dishes (which would take a long time), multiple chefs can work on different orders simultaneously, leading to a much quicker overall dining experience.
Energy Efficiency
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Multicore processors are generally more energy-efficient compared to single-core designs, allowing tasks to be completed without significantly increasing power consumption and heat generation.
Detailed Explanation
Energy efficiency in multicore processors results from distributing workloads across multiple cores. When tasks are shared, the individual cores can operate at lower frequencies while still completing tasks efficiently. This approach reduces the total power draw of the processor, enabling better energy management—perfect for mobile devices or servers where power costs are critical.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a distribution center that has several workers. If each worker can handle parts of the shipment at a manageable pace, the work gets done efficiently without overworking anyone. If only one person were responsible for all shipments, they might have to speed up, use more energy (get tired), and ultimately take longer.
Improved Multitasking
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
With multiple cores, multicore processors can handle several applications or threads at once, improving the user experience during multitasking.
Detailed Explanation
Multicore processors excel at multitasking because they can divide and manage multiple threads across several cores. For instance, if you are streaming a video, downloading a file, and browsing the web all at the same time, multicore processors can allocate different cores to each task, preventing any slowdown or lag that might occur on a single-core processor.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a digital assistant at an airport. If there are multiple agents available to help travelers, several questions can be handled simultaneously. However, if only one agent is present, they would have to answer each question one by one, leading to longer wait times.
Better Handling of Parallel Workloads
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Multicore processors are well-suited for parallel workloads, where many tasks can be performed at the same time, enhancing performance in multithreaded applications.
Detailed Explanation
Parallel workloads consist of tasks that can be executed concurrently, and multicore processors can manage these efficiently. For example, in scientific computing or video rendering, tasks can be split into smaller chunks that multiple cores can process simultaneously. This allows for quicker results compared to executing each task in sequence on a single core.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a construction project where several teams work on different sections of a building simultaneously. Each team completes their assigned section independently and much faster than if one large team had to do everything in sequential order.
Key Concepts
-
Multicore Processor: A processor that contains multiple cores for concurrent processing.
-
Performance: The overall efficiency and speed at which a processor completes tasks.
-
Energy Efficiency: The effectiveness of a processor in optimizing power usage.
-
Multitasking: The ability of a processor to run several applications at the same time without performance loss.
-
Parallel Workloads: Tasks that maximize resource usage by executing independently in a multicore environment.
Examples & Applications
Running a video game while streaming a video on another application, showcasing multitasking.
Using a video editing software that renders multiple video layers simultaneously for improved performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
More cores lead to more fun, processing tasks can now be done!
Stories
A chef with multiple assistants in the kitchen can prepare meals quicker than a single chef alone, showcasing how multicore processors function in parallel for better efficiency.
Memory Tools
Remember PEM: Performance, Efficiency, and Multitasking are the key benefits of multicore processors.
Acronyms
P.E.M. – Performance, Efficiency, Multitasking.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Multicore Processor
A processing unit with multiple independent cores capable of executing tasks in parallel.
- Performance
The ability of a processor to execute tasks efficiently and swiftly.
- Energy Efficiency
The capability of a system to perform its tasks with minimal power consumption.
- Multitasking
The ability to run multiple applications or processes simultaneously without performance degradation.
- Parallel Workloads
Tasks that can be executed concurrently to optimize performance and efficiency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
