Introduction to Multicore Processors
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Multicore Processors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing multicore processors, which are essentially processors with multiple cores that can execute tasks simultaneously. Can anyone define what we mean by a core?

Is a core like a separate processor that can do its own thing?

Great observation! Yes, each core functions like an independent processor. This means they can handle different tasks or threads at the same time. Let’s remember this using the acronym 'MC' for Multicore.

So, more cores mean better performance?

Exactly! A multicore processor can significantly enhance multitasking capabilities. In simpler terms, having multiple cores allows the computer to divide work and process it simultaneously, leading to more efficient performance.
Motivation for Multicore Architectures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s explore why multicore architectures became necessary. What limitations were single-core processors facing?

They couldn't keep increasing clock speeds without overheating?

Exactly! As we pushed for higher clock speeds, we encountered power and heat issues. That’s where multicore processors come in. They allow more processing power without the pitfalls of high clock speed.

So, multicore is like having a team instead of just one person trying to do everything?

That's a perfect analogy! Just like a team can accomplish more together, multicore processors can tackle multiple tasks efficiently.
Benefits of Multicore Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed what multicore processors are and why they're essential, let’s talk about the benefits. Can anyone list some benefits of multicore processing?

Better multitasking!

Energy efficiency?

And improved performance overall!

All correct! Multicore processors enhance multitasking, are energy-efficient by utilizing less power for parallel tasks, and generally provide a performance boost. This makes them ideal for modern computing demands.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
As clock speeds of single-core processors hit physical limits, multicore processors emerged to boost performance without escalating power consumption. These processors offer benefits like enhanced multitasking, energy efficiency, and better parallel workload handling, making them the standard for contemporary computing.
Detailed
Introduction to Multicore Processors
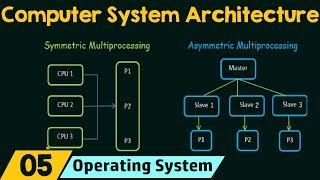
Multicore processors have become integral in modern computing due to the need for improved performance without the drawbacks of increased power consumption or heat generation. A multicore processor consists of multiple independent processing units (known as cores) within a single chip, enabling parallel task execution. With the limitations of single-core processors, multicore architectures provide several benefits, including enhanced performance, energy efficiency, improved multitasking capabilities, and superior management of parallel workloads. This section underscores the transition in processor architecture towards multicore designs and the myriad advantages they present for contemporary computing scenarios.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Multicore Processors
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A multicore processor is a single computing component with multiple independent processing units, known as cores, that can execute tasks in parallel.
Detailed Explanation
A multicore processor is essentially a chip that contains more than one processor core. Unlike a single-core processor, which can only carry out one instruction at a time, multicore processors can process multiple instructions simultaneously, meaning they can handle more tasks at once. This technology leads to faster computational speeds and improved performance for applications, especially those that are designed to take advantage of parallel processing capabilities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a multicore processor like a team of workers in an office. If you have one employee (single-core) working on a task, it might take longer to finish. However, if you have a team of employees (multiple cores) working together on separate tasks simultaneously, they can complete the project much quicker.
Motivation for Multicore Architectures
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As clock speeds of single-core processors approached physical limits, multicore processors were introduced to increase performance without further increasing power consumption or heat dissipation.
Detailed Explanation
As technology progressed, manufacturers found that they couldn't increase the clock speed of single-core processors without causing excessive heat and power usage. This was because of physical limitations inherent in the materials and designs of chips. To improve performance without causing these problems, multicore architectures were developed. By adding more cores, processors can handle more tasks at once while keeping power consumption and heat generation in check.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to speed up a car by making its engine run faster (increasing clock speed) - you can only push it so far before it overheats. Instead, if you add more cars to the race (more cores), you can transport more goods in the same time without risking damage to any single vehicle.
Benefits of Multicore Processing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Enhanced performance, energy efficiency, improved multitasking, and better handling of parallel workloads.
Detailed Explanation
Multicore processors come with several advantages: They enhance performance because multiple tasks can be executed simultaneously. They are also energy efficient because running several cores at lower speeds generates less heat and consumes less power than increasing the speed of a single core. Additionally, multitasking is more effective; for example, a user can run applications like a web browser, word processor, and video player at the same time without significant slowdown. Lastly, multicore processors handle workloads designed for parallel processing much better, allowing various tasks to share work without conflict.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant kitchen where multiple chefs (cores) are working. By having more chefs, the kitchen can prepare different dishes simultaneously (parallel workloads), serve multiple tables effectively (improved multitasking), and use ingredients more efficiently (energy efficiency) than if there was just one chef trying to manage everything.
Key Concepts
-
Multicore Processor: A chip with multiple processing units.
-
Parallel Processing: Executing multiple tasks at once.
-
Clock Speed: Measurement of how fast a processor operates.
-
Efficiency: Performing tasks with minimal waste.
-
Multitasking: Simultaneously handling multiple tasks.
Examples & Applications
A smartphone with a multicore processor can run games while simultaneously allowing users to browse the internet and stream video.
In a server setting, a multicore processor can manage numerous client requests at once, improving load times and responsiveness.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cores galore, tasks to explore, with multiple minds, computing's core.
Stories
Imagine a factory where each worker (core) specializes in different tasks. One handles assembly, another quality control, and yet another packaging. Together, they complete far more than a single worker could.
Memory Tools
MPC - Multicore Processors are Cool! (Multicore, Performance, Computing)
Acronyms
MC = Multitasking Capability
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Multicore Processor
A single computing component with multiple independent processing units (cores) that can execute tasks in parallel.
- Parallel Processing
The simultaneous execution of multiple tasks or threads to improve performance and efficiency.
- Clock Speed
The speed at which a processor can execute instructions, typically measured in GHz.
- Efficiency
The ability to perform work without wasting resources, such as power or time.
- Multitasking
The capability of a processor to perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
