Load Balancing in Multicore Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Load Balancing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to discuss load balancing in multicore systems. Can anyone tell me why load balancing is important in multicore architectures?

To make sure all the cores are used evenly!

Exactly! By distributing tasks evenly, we can maximize the performance of each core. Now, there are two main methods of load balancing: static and dynamic. Does anyone know the difference?

Static means tasks are assigned before execution, while dynamic adjusts them during execution?

Great summary! Static load balancing distributes tasks based on initial knowledge of workloads, while dynamic load balancing adapts to changing conditions during execution. This flexibility helps improve performance. Remember it as 'Static sets, Dynamic adjusts.'
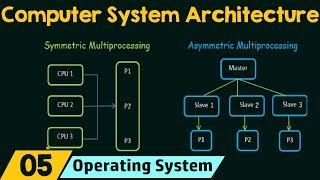
Static Load Balancing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into static load balancing. Why do you think it's limited?

If the workload changes, the initial assignments might not work well?

Precisely! Static load balancing does not account for workload changes after tasks are assigned. Does anyone remember other advantages or issues with such a method?

It's simple to implement, but it might lead to inefficiencies!

Correct! It’s simple but can lead to some cores being overloaded and others idle. That's why understanding these balances is vital.
Dynamic Load Balancing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s explore dynamic load balancing. Why might this be more advantageous than static?

It can adapt to changing workloads throughout execution!

Exactly! It allows for real-time adjustments. This can improve system efficiency significantly. Can anyone think of a scenario where this might be necessary?

If different users are running applications that slow down at different times!

Right! Such scenarios would benefit greatly from dynamic load balancing as it recalibrates task assignments based on current core loads.
Comparing Static and Dynamic Load Balancing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's summarize the key differences between static and dynamic load balancing. What can someone highlight?

Static is done before running the tasks, and dynamic happens during execution.

Dynamic can adapt better, especially when workloads vary!

Perfect! To remember easily, think of 'Static is planned, Dynamic is flexible.' Understanding these can help optimize multicore processing effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Effective load balancing is crucial in multicore systems as it optimizes the use of processing cores by distributing tasks evenly. This can be achieved through static load balancing, where tasks are divided before execution, and dynamic load balancing, which adjusts task distribution based on real-time core workloads.
Detailed
Load Balancing in Multicore Systems
Load balancing is an essential technique in multicore systems aimed at distributing computational tasks evenly across all available processing cores. The primary objective of load balancing is to maximize performance while avoiding scenarios where some cores are overburdened and others are underutilized.
Key Concepts
- Static Load Balancing: This method involves allocating tasks to cores based on predefined characteristics of the workload before execution begins. While this approach may simplify initial distribution, its effectiveness can be limited by unpredictable workload variations.
- Dynamic Load Balancing: In contrast, dynamic load balancing adapts task distribution during execution based on the real-time workloads on different cores. This method can improve efficiency significantly since it accounts for changes in workload and can redistribute tasks to minimize delays and maximize throughput.
Significance
Load balancing is fundamental in enhancing the performance of multicore systems, ensuring that all cores contribute effectively to task completion and system responsiveness.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Load Balancing Overview
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Load balancing ensures that tasks are evenly distributed across all cores to maximize performance and avoid some cores being underutilized while others are overburdened.
Detailed Explanation
Load balancing is a critical concept in multicore systems where multiple cores are designed to handle tasks. The goal of load balancing is to distribute these tasks evenly among the available cores. This prevents situations where some cores are working harder than others, leading to inefficient performance. By balancing the workload, the system can operate more effectively and utilize its resources optimally.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a group of workers at a factory. If one worker is doing all the heavy lifting while others are sitting idle, the factory's output is reduced. Load balancing is like assigning tasks evenly among all workers, so everyone is busy and the output is maximized.
Static Load Balancing
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Static Load Balancing: The distribution of tasks is done before execution begins, based on known characteristics of the tasks.
Detailed Explanation
Static load balancing involves preassigning tasks to cores before the execution of a program starts. This means the tasks are divided based on their complexity and expected workload, allowing the system to allocate the right amount of work to each core. Since this method does not adapt to changes during execution, it works best when the workload is predictable and consistent.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a teacher assigning homework to students based on their known strengths. If a student is good at math, they might receive more math problems, while others get different subjects based on their skills. Similarly, in static load balancing, cores receive tasks based on their predefined capabilities.
Dynamic Load Balancing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Dynamic Load Balancing: Tasks are distributed during execution, based on the current load on each core. This approach can respond to variations in workload more effectively.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic load balancing, unlike its static counterpart, allows for task distribution during the execution of programs. This means that the system can monitor the load on each core and redistribute tasks if some cores are overburdened while others are underutilized. This adaptability enhances overall system performance, particularly in environments with unpredictable workloads.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant where servers must take care of different tables. If one server has too many customers and cannot attend to everyone promptly, the manager might reassign some tables to another server who is less busy. This is akin to dynamic load balancing, as the workload is adjusted based on current conditions to improve service efficiency.
Key Concepts
-
Static Load Balancing: This method involves allocating tasks to cores based on predefined characteristics of the workload before execution begins. While this approach may simplify initial distribution, its effectiveness can be limited by unpredictable workload variations.
-
Dynamic Load Balancing: In contrast, dynamic load balancing adapts task distribution during execution based on the real-time workloads on different cores. This method can improve efficiency significantly since it accounts for changes in workload and can redistribute tasks to minimize delays and maximize throughput.
-
Significance
-
Load balancing is fundamental in enhancing the performance of multicore systems, ensuring that all cores contribute effectively to task completion and system responsiveness.
Examples & Applications
In a web server handling multiple requests, static load balancing might allocate requests based on round-robin, while dynamic load balancing can adjust allocations based on current request times and server loads.
In a multicore system running different applications, tasks might be assigned statically during startup but can shift during runtime based on application demands.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To balance the load, let cores share the road, evenly spread to lighten the load.
Stories
Imagine a team of chefs in a restaurant; static load balancing is assigning each chef a specific dish at the start, while dynamic load balancing allows them to switch dishes as needed based on customer demand.
Memory Tools
Static is Set, Dynamic is Dance - one is fixed, the other prance!
Acronyms
S for Static, D for Dynamic - remember the difference with SD!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Load Balancing
The process of distributing computational tasks evenly across multiple processing units or cores to optimize performance.
- Static Load Balancing
A method where tasks are assigned to processors before execution, based on known workload characteristics.
- Dynamic Load Balancing
A method of reallocating tasks among processing units during execution based on current workload conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
