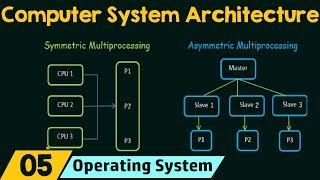
Definition of Multicore Processors
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is a Multicore Processor?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into what multicore processors are. Can anyone share what they think defines a multicore processor?

I think it’s like having multiple CPUs on a single chip?

Exactly! A multicore processor is a single computing chip that has multiple independent processing units known as cores. Each core can work on different tasks at the same time. This allows for parallel execution of tasks.

So, how does this improve efficiency?

Good question! Multicore processors increase performance without ramping up power consumption or generating more heat. This is crucial as single-core processors hit physical limits in clock speeds.

Does this mean multitasking is better with multicore?

Yes, indeed! It enhances multitasking and is particularly effective at handling parallel workloads. Remember the acronym 'PEE' for Performance, Efficiency, and Execution when thinking of multicore processors!

Can you sum up what we've discussed?

Sure! A multicore processor consists of multiple cores on a single chip that work in parallel, allowing improved performance and efficiency while optimizing multitasking capabilities.
Motivation for Multicore Architectures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about what motivated the development of multicore architectures. Why do you think the industry shifted from single-core to multicore processors?

Because they wanted to make computers faster?

That's part of it! As the clock speeds of single-core processors began to approach their physical limits, it became clear that solely enhancing clock speeds wouldn't yield sufficient performance gains anymore. Hence, multicore architectures were introduced.

So, it’s like finding a new way to improve performance without just making things faster?

Exactly! By leveraging multiple cores, it was possible to increase performance while keeping power consumption in check.

What are some examples of tasks that benefit from this?

Great inquiry! Tasks like video rendering, gaming, and data processing benefit immensely from multicore architectures. The parallel execution of these tasks is what enables those improved results. Remember, PII can help you remember: Performance, Integrity, and Improvement.

Can you summarize that new concept?

Absolutely! The shift to multicore processors was motivated by the need for increased performance without higher power usage, tackling the limitations of single-core processors as they hit physical speed barriers.
Benefits of Multicore Processors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s wrap up by discussing the benefits of multicore processors. Can anyone name a few benefits they recall from our discussion?

Better performance and multitasking!

Absolutely! Multicore processors offer enhanced performance by executing multiple tasks simultaneously, which leads to improved multitasking.

Is energy efficiency one of them too?

Yes, good catch! They're also more energy-efficient compared to single-core designs. This is critical in balancing performance and power consumption. One more way to remember is with the acronym 'EPMP'—Efficiency, Performance, Multiprocessing, and Power.

How do they handle complex tasks?

Multicore processors excel at managing complex parallel workloads, facilitating better performance in demanding tasks. So overall, remember this: multicore processors enhance multitasking capabilities, deliver better performance, and improve energy efficiency.

Can you summarize all benefits we talked about?

Certainly! The primary benefits of multicore processors include enhanced performance, energy efficiency, improved multitasking, and better parallel workload management. Remember to leverage these benefits when evaluating processors!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
A multicore processor is a single computing chip containing multiple independent cores that can execute tasks simultaneously. This design addresses physical limits of single-core processors by enhancing performance without a proportional increase in power consumption or thermal output, making it ideal for handling parallel workloads and multitasking effectively.
Detailed
Definition of Multicore Processors
Multicore processors are a pivotal advancement in modern computing. They consist of multiple independent processing units, recognized as cores, within a single chip. Each core can execute tasks in parallel, significantly improving the processor's performance and energy efficiency. The move towards multicore architectures has emerged primarily due to the nearing physical limitations of increasing clock speeds in single-core processors. To continue enhancing computing performance without escalating power consumption or heat generation, multicore designs allow for improved multitasking capabilities and better management of parallel workloads. Consequently, multicore processors have become the standard in contemporary computing environments.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Multicore Processor?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A multicore processor is a single computing component with multiple independent processing units, known as cores, that can execute tasks in parallel.
Detailed Explanation
A multicore processor is essentially a chip that contains several processing units, or cores. Each core can perform tasks independently and simultaneously, which means multiple tasks can be handled at the same time. This parallel execution helps in speeding up the overall performance of computing tasks significantly compared to older, single-core processors that could only handle one task at a time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a multicore processor like a kitchen staff in a restaurant. If you have multiple cooks (cores), they can prepare different dishes (tasks) at the same time, which speeds up the service. In contrast, a single cook can only make one dish at a time, making the process much slower.
Independent Cores and Parallel Execution
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each core can execute tasks in parallel.
Detailed Explanation
The idea of having independent cores is crucial. This means every core functions separately, allowing them to work on different tasks without waiting for one another. For instance, while one core is processing a video, another can be running a web browser, resulting in smoother performance for the user. This parallelism maximizes the efficiency of the processor, as it can utilize all its resources at once.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of students working on different projects at the same time. Each student (core) is focusing on their own project (task), and none of them need to pause or wait for someone else to finish their work. This allows the entire group to accomplish more in the same amount of time.
Key Concepts
-
Multicore Processors: Processors with multiple cores for parallel task execution.
-
Performance: Improvement in computational speed due to multicore architecture.
-
Efficiency: Energy usage reduced while enhancing processing capabilities.
-
Multitasking: Ability to perform several tasks at once through multicore design.
Examples & Applications
A computer rendering 3D graphics uses multiple cores to process different elements of the scene simultaneously.
In video games, multicore processors handle AI processing, rendering, and physics calculations concurrently.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cores in a chip run side by side, processing tasks like a swift tide.
Stories
Imagine a team of chefs, each specialized, preparing different dishes at once in a restaurant. Together, they serve customers faster than a single chef could.
Memory Tools
E.P.E.: Efficiency, Performance and Energy when thinking of multicore processors.
Acronyms
P.E.E
Performance
Efficiency
Execution—core elements of multicore processors.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Multicore Processor
A single computing component with multiple independent processing units, known as cores, capable of executing tasks in parallel.
- Cores
Independent processing units within a multicore processor that can execute tasks concurrently.
- Parallel Execution
The ability to perform multiple operations simultaneously, effectively improving performance.
- Power Consumption
The amount of electrical energy required to operate the processor, a significant factor in processor design.
- Multitasking
The capability of a processor to manage and execute multiple tasks at the same time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
