ARM Core
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ARM Microcontroller Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today, we are focusing on ARM microcontrollers. Can someone tell me what a microcontroller is?

A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit that contains a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals.

Exactly! Now, ARM microcontrollers are based on RISC architecture. RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computing. Why do you think this approach benefits performance?

It likely reduces the complexity of instructions, allowing for faster execution.

Correct! This simplicity in instruction helps in enhancing execution speed. ARM cores like Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, and Cortex-M7 cater to different needs. Let's remember them with an acronym: PPC - Performance, Power, and Cost-effectiveness.

So ARM microcontrollers are efficient in performance and power consumption?

Absolutely! And they are used in various applications from consumer electronics to IoT. Can anyone name a few examples of ARM microcontrollers?

STM32 and NXP LPC series!

Great! STM32 is one of the most used. To summarize, ARM microcontrollers play a crucial role in embedded system design due to their RISC architecture which allows for efficient execution and power management.
ARM Cortex Cores
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last session, we covered ARM microcontrollers' basic architecture. Now, let's dive deeper into the ARM Cortex cores. What's the significance of these cores?

They are the heart of ARM microcontrollers, enabling them to perform efficiently.

Right! The Cortex cores are structured to balance power and performance. For example, the Cortex-M4 is commonly used in applications requiring signal processing. How do you think the choice of core impacts application performance?

Choosing a core like Cortex-M7 would improve performance in more demanding applications compared to a simpler core.

Exactly! Different applications have different needs, and using the appropriate Cortex core can maximize efficiency. Remember, selecting the right component is critical in system design since it affects both functionality and cost.

Does that also influence the power requirements?

Yes! Lighter cores like the Cortex-M0 consume less power, making them ideal for battery-operated devices. In summary, understanding ARM Cortex cores helps us make informed choices in embedded systems design.
Applications and Support Ecosystem
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the wide range of applications for ARM microcontrollers. Why do you think they are so popular in industries?

Because they work efficiently in different environments and applications!

True! Their versatility makes them suitable for everything from automotive systems to consumer electronics. What can you say about the software ecosystem associated with ARM microcontrollers?

There are lots of development tools and software platforms available, which makes programming easier!

Exactly! This support ecosystem simplifies development and speeds up deployment. A good mnemonic for remembering this is 'A CESS', which stands for Application, Core, Ecosystem, Support, and Scalability. Who can relate this back to what we've learned?

We see how different ARM cores have flexibility, and with broad software support, it makes building projects simpler!

Perfectly summarized! ARM microcontrollers provide extensive application support alongside robust developmental resources, making them indispensable in the embedded system landscape.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section provides an overview of ARM microcontroller architecture, focusing on ARM Cortex cores, their instruction set, and the extensive range of applications. It elaborates on the advantages of ARM microcontrollers, including low power consumption and high performance.
Detailed
ARM Core
The ARM microcontroller architecture is primarily based on RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) principles, designed to balance performance, power efficiency, and ease of use. ARM-based systems are commonly found in consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial automation, and IoT applications, exemplifying their versatility. The heart of these microcontrollers is the array of ARM Cortex cores, such as Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, and Cortex-M7. Each core is designed for specific applications, allowing developers to choose the best option based on their needs.
Key Features of ARM Microcontrollers:
- Instruction Set: They utilize a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture with a simplified instruction set, significantly improving execution speed and reducing power consumption.
- Wide Application Support: ARM microcontrollers are backed by a robust ecosystem of development tools and resources that facilitate software development.
Example ARM Microcontrollers:
- STM32 (by STMicroelectronics)
- NXP LPC series
- Texas Instruments Tiva C series
In summary, ARM microcontrollers represent a critical element in embedded system design due to their balanced performance, power efficiency, and extensive support potential.
Youtube Videos

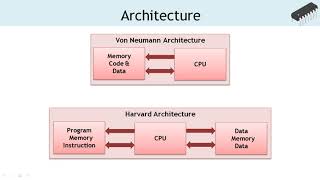



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to ARM Cores
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM microcontrollers use the ARM Cortex cores (e.g., Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7) that are designed to offer a balance between performance, power efficiency, and ease of use.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the ARM Cortex cores, which are fundamental components of ARM microcontrollers. These cores are designed to provide an ideal mix of high performance and low energy consumption. There are several types of Cortex cores, such as Cortex-M0, M3, M4, and M7, each targeting different applications and levels of performance. This variety allows designers to select the most suitable core based on the specific needs of their embedded systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ARM cores like a range of vehicles. The Cortex-M0 is like a compact car that is very fuel-efficient and perfect for city driving, while the Cortex-M7 is like a sports car that offers high performance for demanding situations. Just as you choose a car based on your requirements (family transport vs. racing), engineers choose an ARM core based on the application’s performance and efficiency needs.
RISC Architecture
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM microcontrollers use a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture with a simple instruction set that improves execution speed and reduces power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
ARM microcontrollers implement a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture, which is characterized by a streamlined set of instructions designed for efficiency. This architecture can operate with both 32-bit and 64-bit data, allowing for faster data processing. Because the instruction set is simpler compared to other architectures, ARM microcontrollers can complete tasks quicker, which not only increases performance but also makes them less power-intensive. This efficiency is crucial in battery-powered devices where extending battery life is important.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the difference between a chef who knows a few simple recipes very well and another chef who knows many complicated recipes but struggles to execute them quickly. The RISC architecture is like the simple recipe chef—focused on mastering a few fundamental operations to achieve excellent results faster and with less wasted effort.
Ecosystem and Support
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM-based MCUs are supported by a vast ecosystem of development tools, libraries, and software platforms.
Detailed Explanation
The ARM microcontroller ecosystem is extensive, offering numerous development tools, libraries, and software platforms to developers. This ecosystem includes integrated development environments (IDEs), debugging tools, and a range of libraries that simplify coding and allowed developers to build applications more efficiently. The diversity of tools available means that even new developers can engage with ARM microcontrollers effectively due to the abundance of resources that facilitate learning and development.
Examples & Analogies
Consider learning to play a musical instrument. A student with access to many resources such as lessons, sheet music, and practice tools will likely progress faster than a student who’s trying to learn on their own with minimal guidance. Similarly, the comprehensive ecosystem surrounding ARM microcontrollers enables developers to learn, create, and troubleshoot more efficiently, leading to more successful projects.
Key Concepts
-
ARM microcontrollers are based on RISC architecture, enhancing performance and reducing power consumption.
-
ARM Cortex cores are used for specific applications, offering flexibility between performance and energy efficiency.
-
The ecosystem surrounding ARM microcontrollers includes numerous development tools and resources.
-
Examples of ARM microcontrollers include STM32, NXP LPC series, and Texas Instruments Tiva C series.
Examples & Applications
The STM32 series microcontrollers are popular in many embedded applications including automation and consumer electronics.
NXP LPC series is extensively used in IoT applications due to its low power consumption and efficient processing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ARM microcontroller, small and bright, makes devices work just right.
Stories
Once upon a time in an electronic world, ARM microcontrollers were the tiny knights saving power while boosting performance, defending embedded systems.
Memory Tools
PPC - Performance, Power, Cost-effectiveness when referring to ARM microcontrollers.
Acronyms
A CESS - Applications, Core, Ecosystem, Support, Scalability for ARM microcontrollers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ARM
Advanced RISC Machine, a family of computer processors based on RISC architecture.
- Cortex
A series of ARM processor cores designed for specific applications balanced between performance and power consumption.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing, an architecture that simplifies instructions to enhance execution speed.
- Ecosystem
The collection of tools, libraries, and resources available for a specific technology or platform.
- Efficiency
The ability to achieve maximum productivity with minimum wasted effort or expense.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
