Instruction Set
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
ARM Microcontroller Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to uncover the ARM microcontroller architecture. Who can tell me what RISC stands for?

Isn't it Reduced Instruction Set Computing?

Exactly! ARM is based on RISC architecture, which is focused on achieving high performance and low power consumption. Can anyone think of an application for ARM microcontrollers?

I think they're used a lot in mobile devices!

Great observation! They are extensively used in devices like smartphones and IoT applications, thanks to their efficient design. One of the popular ARM cores you might have heard of is the Cortex series. Can anyone name an ARM microcontroller?

I know! The STM32 series!

That's correct! The STM32 series is a prime example of an ARM microcontroller that features many peripherals. Let’s summarize: ARM microcontrollers excel in high performance and low power efficiency.
AVR Microcontroller Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift our focus to AVR microcontrollers. Who can tell me what makes them beginner-friendly?

I think it's because they are simple and commonly used in projects like Arduino?

Absolutely! AVR microcontrollers, founded by Atmel, stand out due to their simplicity and popularity in hobbyist projects, particularly with Arduino. What does Harvard architecture mean?

It means that they keep program memory and data memory separate, right?

Exactly! This separation leads to faster execution. Can anyone name a popular AVR microcontroller?

The ATmega328 is widely used!

That's a great example! So remember, AVR microcontrollers are primarily 8-bit, making them efficient for small embedded applications.
PIC Microcontroller Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's explore the PIC microcontroller architecture. What stands out about PICs compared to ARM and AVR?

PICs can be either 8-bit or 16-bit, right? And they have a modular design.

Correct! Their modularity allows for versatile configurations, meaning they can adapt to various applications. What about their instruction set?

They use CISC, which allows for more complex instructions.

Spot on! This allows for smaller code size but often requires more cycles to execute each instruction. Can anyone think of where we might find PIC microcontrollers in use?

In industrial automation or consumer electronics?

Exactly! PIC microcontrollers are prevalent in both low-power devices and more demanding applications. In summary, they are adaptable and widely utilized in the industry.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the importance of instruction sets within different microcontroller families, including ARM, AVR, and PIC. It highlights their unique features, how they affect performance, and their suitability for various applications.
Detailed
Instruction Set Overview
The instruction set of microcontrollers is crucial in determining how they operate and interact with the hardware components. In this section, we focus on three major microcontroller families: ARM, AVR, and PIC, each characterized by distinct architectures and instruction sets.
ARM Architecture
ARM microcontrollers utilize a RISC architecture aimed at high performance and low power consumption, incorporating 32-bit and 64-bit instruction sets.
- Cortex Cores: ARM’s Cortex cores like M0, M3, M4, and M7 are well-regarded for balancing performance and efficiency.
- Application Support: ARM supports a vast ecosystem for development, making it popular in consumer electronics and IoT.
Examples: STM32, NXP LPC series, Tiva C series.
AVR Architecture
AVR microcontrollers are built on an 8-bit RISC architecture, valued for their simplicity and efficiency.
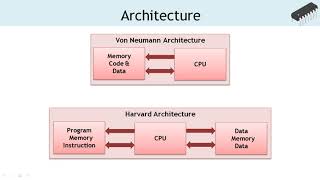
- Harvard Architecture: This separates program and data memory, helping speed up instruction execution.
- Hobbyist-Friendly: AVR architecture is the backbone of platforms like Arduino, making it accessible for beginners.
Examples: ATmega series, ATtiny series.
PIC Architecture
The PIC microcontroller family is known for its modular structure, offering diverse configurations for various applications.
- CISC Architecture: This uses complex instructions, leading to smaller code size, suitable for tight memory conditions.
- Versatile Applications: PIC microcontrollers are used in both low and high-performance systems.
Examples: PIC16 series, PIC18 series, PIC32 series.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences in instruction sets not only improves programming skills but also aids in selecting the right microcontroller for specific applications.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
ARM Instruction Set
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM microcontrollers use a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture with a simple instruction set that improves execution speed and reduces power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
ARM microcontrollers utilize a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture. This means that instead of having a large number of complex instructions, they are designed to have fewer, simpler instructions that can be executed quickly. This approach leads to faster processing speeds since the CPU can execute instructions more efficiently, and it helps lower power consumption, which is crucial for many applications, especially in battery-operated devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are a chef with a simple and precise recipe. Instead of complicated steps that take a long time to prepare, you have clear, straightforward instructions. This allows you to cook quicker and save energy compared to a recipe that has many complex and lengthy instructions. Similarly, the ARM instruction set allows microcontrollers to perform tasks efficiently.
Performance Benefits of the ARM Instruction Set
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The instruction set improves execution speed and reduces power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
By utilizing a streamlined and efficient instruction set, ARM microcontrollers can execute tasks faster compared to those with more complex instruction sets. This increase in execution speed translates to better overall performance for applications. Furthermore, because simpler instructions require less processing power, they consume less energy, which is particularly beneficial in embedded systems that need to operate efficiently for longer periods without recharging.
Examples & Analogies
Think of driving a car on a smooth highway versus a bumpy, winding road. On the smooth highway, you can accelerate quickly and maintain speed with less fuel consumption. The ARM instruction set functions like that smooth highway, allowing the microcontroller to operate efficiently and quickly, conserving energy in the process.
Ecosystem and Development Support for ARM
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM-based MCUs are supported by a vast ecosystem of development tools, libraries, and software platforms.
Detailed Explanation
One of the significant advantages of ARM microcontrollers is their robust ecosystem. There are numerous development tools available that aid programmers in writing, testing, and debugging their code. This includes integrated development environments (IDEs), software libraries, and community support, which can drastically shorten development time and improve the quality of the end product.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the comparison of building a house with or without a toolbox. If you have an organized toolbox with all the necessary tools and guides, your construction process will be faster and more efficient. Similarly, having a supportive ecosystem for ARM microcontrollers makes programming and development much easier for engineers and hobbyists alike.
Key Concepts
-
ARM Microcontrollers: High performance and low power consumption, mainly in IoT and consumer electronics.
-
AVR Microcontrollers: Simplicity and ease for beginners, often seen in Arduino projects.
-
PIC Microcontrollers: Versatile and modular designs suitable for various applications, including industrial use.
Examples & Applications
STM32 is a well-known example of an ARM microcontroller effective for intensive processing tasks.
ATmega328 is a famous AVR microcontroller widely used in the Arduino platform.
PIC16F877A is a frequently used PIC microcontroller in industrial control applications.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ARM's high, AVR's cheap; PICs in systems run deep.
Stories
Imagine a classroom of students: ARM is the studious one excelling in exams, AVR is the friendly one helping others, while PIC multitasks with various projects.
Memory Tools
For remembering microcontroller types, think 'A Simple PIC': A for ARM, S for Simple AVR, P for PIC.
Acronyms
PAC
for PIC
for ARM
for AVR helps me remember the order of the architectures.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Microcontroller (MCU)
A compact integrated circuit that contains a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals designed to perform specific tasks.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing, an architecture designed to achieve high performance through a simplified instruction set.
- AVR
An 8-bit RISC microcontroller architecture developed by Atmel, known for its simplicity and efficiency.
- CISC
Complex Instruction Set Computing, an architecture featuring complex instructions aimed at creating compact code.
- Harvard Architecture
An architecture that separates memory for instructions and data, allowing for faster execution.
- PIC Microcontroller
A family of microcontrollers developed by Microchip Technology known for their modular architecture and versatile applications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
