Introduction to Microcontrollers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What are Microcontrollers?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we’re going to dive into microcontrollers, or MCUs. Can anyone tell me what a microcontroller is?

Is it some kind of computer chip?

Good observation! A microcontroller is indeed a compact integrated circuit that combines a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals into a single chip designed to carry out specific functions.

What kind of tasks do they perform?

They’re used in various applications, such as automotive systems, home appliances, and robotics. Essentially, wherever you find embedded systems, there's likely a microcontroller at work!

To help you remember, think 'MCU: Miniature Computing Unit'!

That’s a great way to remember it!

At the end of this session, keep in mind that microcontrollers are essential for efficient and effective performance of the devices we interact with every day.
Architecture of Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to the architecture of microcontrollers. Why do you think their architecture is significant?

I think it's about how well they do their specific tasks?

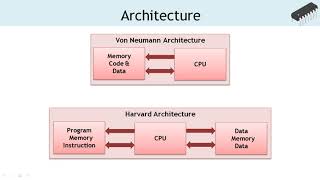
Exactly! The architecture directly influences functionality, performance, and power efficiency of the microcontroller. For instance, ARM, AVR, and PIC are some of the popular families—each crafted for diverse tasks.

What makes them different?

Great question! Each family varies based on performance metrics and application suitability. ARM controllers, for example, are often used for high-performance tasks combined with low power consumption.

Remember: 'Three A's for knowing microcontrollers: Architecture, Applications, and Attributes!'

That's easy to remember!

Let's recap: Microcontrollers like ARM, AVR, and PIC come with distinct architectures that cater to different needs, affecting their overall performance.
Components of Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s identify the key components found in microcontrollers. Can anyone name a component?

The processor?

Yes! The CPU is critical since it executes instructions. In addition to the CPU, we have memory types like Flash for program code, SRAM for temporary data, and EEPROM for persistent data.

What about I/O?

Great point! I/O interfaces allow microcontrollers to communicate with external devices, controlling sensors and displays.

As a memory aid, think of ‘C-Memory-IO’ to remember the core aspects: CPU, Memory, and I/O!

That’s a fun way to remember it!

In summary, microcontrollers comprise a CPU, various types of memory, and vital I/O interfaces, all working harmoniously to perform tasks efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces microcontrollers as compact integrated circuits that encompass a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals. They are widely used in various applications, including consumer electronics and robotics, and their architecture significantly impacts their performance and efficiency.
Detailed
Introduction to Microcontrollers
A microcontroller (MCU) is a highly integrated device consisting of a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals all on a single chip, designed to execute specific tasks effectively. Microcontrollers play a crucial role in embedded systems, which range across numerous fields such as automotive, home appliances, robotics, medical devices, and more. Their internal architecture influences their functionality, performance, and power efficiency, making the understanding of their components and architecture vital for developers. In this chapter, we will dive into the structure of microcontrollers, explore key architectural differences among popular families like ARM, AVR, and PIC, and detail the essential components they contain.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Microcontroller?
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A microcontroller (MCU) is a compact integrated circuit (IC) that contains a processor, memory, and I/O peripherals on a single chip.
Detailed Explanation
A microcontroller is essentially a small computer on a chip. It integrates all the key components needed to function as a computer: the processor which does the calculations, memory for storing data, and input/output peripherals that allow it to communicate with other devices. This compact design makes microcontrollers ideal for specific tasks in various electronic devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a microcontroller like a Swiss Army knife. Just like a Swiss Army knife has various tools (such as a knife, screwdriver, and scissor) all in one compact device, a microcontroller has a processor, memory, and I/O interfaces all in one chip, designed for specific tasks.
Applications of Microcontrollers
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Microcontrollers are designed to perform specific tasks and are widely used in embedded systems for applications such as automotive systems, home appliances, robotics, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Detailed Explanation
Microcontrollers are prevalent in many everyday devices, performing dedicated functions that make them useful. For example, in an automotive system, a microcontroller might control the anti-lock braking system. In home appliances, it could manage the timing of a microwave. In robotics, microcontrollers allow robots to process sensor data and respond accordingly. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications across industries.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smart thermostat that learns your temperature preferences and adjusts the heating or cooling accordingly. Inside, it likely has a microcontroller that manages the sensors (to detect the current temperature) and the output (to control the heating system), ensuring your home remains comfortable.
The Importance of Microcontroller Architecture
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The microcontroller's architecture and components play a significant role in determining the functionality, performance, and power efficiency of the system in which they are embedded.
Detailed Explanation
The architecture of a microcontroller defines how its components interact and function together. This includes how data moves within the microcontroller, how it processes instructions, and how it interfaces with the outside world. Different architectures can lead to significant differences in performance and power usage. Hence, the choice of architecture is crucial for ensuring that the end product meets the desired specifications for efficiency and effectiveness.
Examples & Analogies
Consider choosing a vehicle for a specific driving need. A sports car is designed for speed and performance on clear roads, while a rugged SUV is built for off-road durability and handling. Similarly, different microcontroller architectures are suited for different applications, depending on whether you need high-speed processing, low power consumption, or a balance of both.
Overview of the Chapter Content
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this chapter, we explore the internal structure of microcontrollers, key architectural differences between popular microcontroller families (ARM, AVR, and PIC), and the essential components of a microcontroller.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter will provide a comprehensive overview of how microcontrollers are designed and built, with a focus on popular families like ARM, AVR, and PIC. We'll look into the specific features, strengths, and weaknesses of these families, enabling you to understand which microcontroller might be best suited for various tasks. This foundational knowledge is essential for anyone looking to engage deeply in embedded system design.
Examples & Analogies
When learning to cook, knowing about different types of kitchen equipment—like a slow cooker, a frying pan, and a pressure cooker—can help you choose the right tool for the recipe you're following. Similarly, understanding different microcontroller architectures will help you select the right one for your electronic project.
Key Concepts
-
Microcontroller: An integrated circuit that combines a processor, memory, and peripherals.
-
Embedded Systems: Systems that use microcontrollers to execute specific tasks.
-
Architecture: The design and structure of the microcontroller that influences performance and functionality.
Examples & Applications
Microcontrollers are used in automotive systems for engine control.
Home appliances like microwaves integrate microcontrollers for operational control.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Microcontrollers are nifty little chips, executing tasks with precise little trips.
Stories
Imagine a tiny robot controlled by a microcontroller, effortlessly guiding its path in a maze—this chip executes the plan!
Memory Tools
Remember 'MCU' for Miniature Computing Unit, defining its compact nature!
Acronyms
Try 'I-C-P' for Input, Communication, and Processing—all are crucial functions of microcontrollers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Microcontroller (MCU)
A compact integrated circuit containing a processor, memory, and peripherals designed for specific tasks.
- Embedded Systems
Devices that use microcontrollers for various applications, functioning as part of larger systems.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing, a CPU design philosophy aimed at simplifying instructions and enhancing performance.
- CISC
Complex Instruction Set Computing, which allows more complex instructions in assembly language.
- Flash Memory
Non-volatile memory used to store program code, retaining data even without power.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
