AVR Microcontrollers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to AVR Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore AVR microcontrollers, which are known for their simplicity and are widely used in small embedded applications. Can anyone tell me what you know about microcontrollers?

I know they are small computers used in devices like remote controls or toys!

I heard AVR is popular among hobbyists, especially with Arduino.

Exactly! AVR microcontrollers are widely embraced by hobbyists, particularly in the Arduino ecosystem. They are ideal for beginners due to their user-friendly design.
AVR Architecture Characteristics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

AVR microcontrollers use an 8-bit RISC architecture. What does RISC mean?

I think it stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computing!

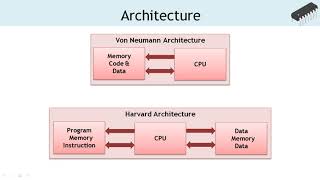
Yes, that's correct! The RISC design allows for a simpler instruction set that enhances execution speed. AVR microcontrollers have a Harvard architecture where the program and data memories are separate, which helps in faster execution.

What does having separate memory do for performance?

Great question! It allows simultaneous access to program and data instructions, improving performance and efficiency.
AVR Microcontrollers in Application
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone give an example of a project using AVR microcontrollers?

I built a light sensor using Arduino with an ATmega chip!

I read that the ATtiny series is for very small projects. Is that true?

Absolutely! The ATtiny series is specifically designed for low-power applications and is perfect for compact projects. AVR microcontrollers, particularly in Arduino, lower the entry barrier for learning embedded systems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The AVR microcontroller architecture is based on an 8-bit RISC design, providing efficient code execution and making it a popular choice for beginners and in platforms like Arduino. The architecture's distinct features, including a Harvard design and a simple instruction set, support diverse embedded applications.
Detailed
In this section, we explore AVR microcontrollers, a family of microcontrollers developed by Atmel (now part of Microchip). Based on an 8-bit RISC architecture, AVR microcontrollers are celebrated for their simplicity, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for beginner projects and hobbyist applications. The architecture employs a Harvard design, enabling separate program and data memories. This separation allows for faster code execution and offers 32 general-purpose registers that contribute to the efficiency of the instruction set — characterized as simple yet effective for embedded systems. They are notably prominent in platforms like Arduino, which enhance development accessibility. Examples of AVR microcontrollers include the ATmega and ATtiny series, showcasing their versatility in various projects.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of AVR Microcontrollers
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers, developed by Atmel (now part of Microchip), are based on an 8-bit RISC architecture. AVR microcontrollers are popular due to their simplicity, ease of use, and low cost, making them ideal for beginners and small embedded projects.
Detailed Explanation
AVR microcontrollers are primarily designed to be user-friendly and affordable, especially for those who are just starting with embedded systems. Their 8-bit RISC architecture allows for efficient processing of instructions, making them suitable for applications that don't require complex computing tasks. This approach significantly lowers the barrier to entry for hobbyists and students, as they can create projects without needing advanced knowledge.
Examples & Analogies
Think of AVR microcontrollers like a basic toolkit for a beginner in woodworking. Just as a simple set of tools allows a novice to start building furniture without needing professional equipment, AVR microcontrollers provide the necessary functions for small scale electronics projects without the complexity of more advanced systems.
AVR Core Features
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The AVR microcontroller uses a Harvard architecture, where the program and data memories are separate, allowing for faster execution.
Detailed Explanation
In a Harvard architecture, program instructions and data have distinct pathways and storage areas. This separation means that while the CPU is fetching the next instruction from program memory, it can simultaneously access data from data memory. Consequently, this allows the microcontroller to execute instructions more quickly and efficiently, enhancing performance in handling tasks.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a librarian who is also a writer. If they have one desk where they keep both their reference books and their own writings, they must spend time switching between looking for information and writing. However, if they have two separate desks—one for reference materials and one for writing—they can work much faster without interruptions. Similarly, the AVR's separate memory for instructions and data lets it 'work' more efficiently.
Instruction Set and Execution
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers use a simple 8-bit instruction set and are known for their efficient code execution. The architecture offers 32 general-purpose registers, making it faster than other microcontrollers in its class.
Detailed Explanation
The simple 8-bit instruction set of AVR microcontrollers is designed to perform functions with minimal complexity, allowing quicker processing. The 32 general-purpose registers are small storage spaces within the CPU that temporarily hold data and instructions. This allows the microcontroller to access frequently used data quickly, which speeds up computation. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where processing speed is critical.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a chef who has several small bowls ready on the counter to hold ingredients for cooking. Instead of running back to the pantry every time they need something, having the ingredients close at hand allows them to prepare meals efficiently. Likewise, the general-purpose registers in the AVR microcontroller help it to quickly retrieve and execute instructions without needing to access slower memory repeatedly.
Popularity and Application
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers are particularly popular in platforms like Arduino, which simplifies the development process.
Detailed Explanation
The AVR architecture has found immense popularity due to its integration into the Arduino platform, which provides an accessible way for individuals to engage with technology. Arduino offers a simplified programming interface and a rich community of support, allowing users to create projects without extensive technical onboarding. This accessibility has made AVR microcontrollers a favorite among hobbyists, educators, and students, fostering creativity and innovation.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a cooking class that provides a simple recipe along with all the necessary tools and ingredients prepared in advance. Students can follow the steps and focus on learning to cook without worrying about sourcing complex ingredients or tools. Similarly, Arduino provides all the necessary resources to simplify working with AVR microcontrollers, enabling users to focus on building their projects instead of struggling with complex setups.
Example AVR Microcontrollers
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example AVR Microcontrollers: ATmega series (e.g., ATmega328, ATmega32) and ATtiny series (smaller, lower-power MCUs).
Detailed Explanation
The ATmega series of AVR microcontrollers, including popular models like ATmega328 and ATmega32, are widely used in both hobbyist projects and industrial applications. These microcontrollers balance performance and power consumption, making them versatile for various tasks. The ATtiny series, on the other hand, is designed for low-power applications where size and energy efficiency are crucial. This allows designers to choose the right microcontroller based on specific project requirements, whether they need robust performance or minimal power usage.
Examples & Analogies
Think about smartphone models: some phones are designed for high performance with many features, while others may focus on being compact and energy-efficient for everyday use. Similarly, the ATmega series serves demanding applications, while the ATtiny series is tailored for simpler, less demanding tasks.
Key Concepts
-
8-bit Architecture: AVR microcontrollers utilize an 8-bit architecture making them efficient for many small-scale applications.
-
Simplicity and Efficiency: AVR microcontrollers are known for their simplicity, which allows beginners to grasp embedded systems more easily.
-
Harvard Architecture: The use of a Harvard architecture separates program memory from data memory, enhancing performance.
-
Hobbyist Popularity: AVR microcontrollers are recognized for their widespread use in hobbyist projects, particularly through platforms like Arduino.
Examples & Applications
The ATmega328P microcontroller is commonly used in Arduino boards, enabling simple development of various digital projects.
The ATtiny series is suitable for compact, low-power applications such as remote controls or tiny sensors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AVR's simple, it makes us grip, in projects small, lets our tech flip.
Stories
Once there was a chip named ATmega, who loved helping hobbyists build their creations, from blinking lights to tiny robots—learning made easy in the Arduino nation.
Memory Tools
Remember RISC: ‘Reduce the Instructions, Speedy Computing’ to help recall the AVR design philosophy.
Acronyms
AVR stands for ‘Atmel Versatile Robotics’, a nod to its practical uses in friendly electronics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AVR Microcontroller
An 8-bit microcontroller architecture developed by Atmel, known for its simplicity and efficiency in embedded applications.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing; a CPU design philosophy that uses a small set of simple instructions for faster processing.
- Harvard Architecture
A computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data, allowing simultaneous access.
- ATmega
A series of AVR microcontrollers by Atmel designed for a wide range of applications, particularly popular in Arduino projects.
- ATtiny
A series of small and low-power AVR microcontrollers used in compact embedded systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
