AVR Microcontroller Architecture
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to AVR Microcontroller Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss AVR microcontroller architecture, which is based on an 8-bit RISC architecture. Can anyone tell me what RISC stands for?

Reduced Instruction Set Computing.

Exactly right! This architecture is known for its simplicity and is used widely in embedded systems. How many of you have heard of Arduino?

I have! It’s really famous for hobbyist projects.

Exactly! The AVR microcontrollers are popular in Arduino due to their easy programming interfaces. Remember, **AVR=Accessible, Versatile, Reliable**—a good mnemonic. Let's move to the core of AVR.

What is the core architecture like?

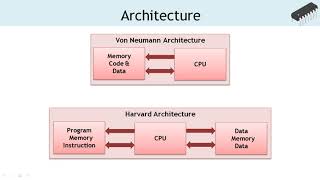
Great question! AVR uses a **Harvard architecture** which separates program memory from data memory. This allows for quicker access during processing.

How does that help performance?

By having separate memories, the microcontroller can fetch instructions and data simultaneously, leading to faster execution. Any other thoughts?

So, it’s faster than microcontrollers with a single memory?

Correct! Now, it’s time to summarize: AVR microcontrollers leverage an 8-bit RISC architecture with Harvard design for efficiency, which is why they're widely adopted in beginners’ projects like Arduino.
Key Features of AVR Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive deeper into the instruction set of AVR microcontrollers. Can anyone explain what makes the instruction set of AVR distinct?

It’s simpler compared to other architectures, right?

Precisely! The **simple 8-bit instruction set** leads to very efficient code execution. What do you think the benefit of having many general-purpose registers is?

It helps in performing operations quickly since there are more registers to work with?

Absolutely! The AVR architecture provides 32 general-purpose registers, enhancing operation speed. Let's remember both of these facts with the acronym **SIMPLE**: **S**imple Instructions, **I**ncreased Memory, **M**ultiple Registers, **P**rogramming Ease, **L**earning Friendly, **E**fficient.

What about their applications in projects?

Excellent point! AVR microcontrollers are a common choice in hobby projects. They facilitate a low-cost entry point into embedded systems. Now let's summarize: The efficiency of AVR microcontrollers comes from their simple instruction set and a high number of registers, making them ideal for hobbyist projects.
Applications of AVR Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the applications of AVR microcontrollers. Where do you think we might see them used?

In small robotics projects and automation?

Exactly! They are indeed popular amongst robotics and automation due to their effectiveness in low-power environments. Can anyone think of any specific examples?

Arduino is a big one, right?

Yes! The ATmega328 is widely used in Arduino boards, making it a staple for DIY electronics. To help remember this, visualize AVR as the '**A**rtist of **V**arious **R**obotics' projects. Can anyone think of other applications?

What about medical devices?

Right again! Their low cost and efficiency make them suitable for such applications. Let's sum it up: AVR microcontrollers excel in hobbyist projects, and product prototyping due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness—think Arduino!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The AVR microcontroller architecture, developed by Atmel, is based on an efficient 8-bit RISC design. It stands out for its Harvard architecture, allowing separate program and data memories, which enhances execution speed. The widespread use of AVR microcontrollers in hobbyist projects, particularly with Arduino, reflects their accessibility and effectiveness for beginners.
Detailed
AVR Microcontroller Architecture
AVR microcontrollers, initially designed by Atmel (now part of Microchip Technology), utilize an 8-bit RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture. Known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, they are particularly suitable for small embedded systems and projects targeted at beginners. Key features of AVR architecture include:
- AVR Core: Availing a Harvard architecture which separates program memory from data memory, enabling faster execution rates.
- Instruction Set: Featuring a straightforward 8-bit instruction set facilitates efficient code execution and allows for 32 general-purpose registers, making operations swift compared to other microcontrollers in its category.
- Popularity Among Hobbyists: AVR's design has made it a favorite in platforms like Arduino, which promotes ease of programming and development for new entrants into embedded systems.
Example AVR microcontrollers include:
- ATmega Series: E.g., ATmega328, known for applications such as Arduino.
- ATtiny Series: Smaller, more energy-efficient microcontrollers designed for simpler tasks.
These characteristics underline the AVR architecture's significance in various embedded applications, particularly in the burgeoning maker movement.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of AVR Microcontrollers
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers, developed by Atmel (now part of Microchip), are based on an 8-bit RISC architecture. AVR microcontrollers are popular due to their simplicity, ease of use, and low cost, making them ideal for beginners and small embedded projects.
Detailed Explanation
AVR microcontrollers were developed by Atmel and utilize an 8-bit RISC architecture, which allows for simpler and efficient processing. Their popularity stems from their user-friendliness, which is particularly beneficial for beginners in electronics and embedded systems. Their low cost also makes them a favorable choice for small projects, especially in educational and hobbyist settings.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine learning to cook with a simple recipe in a beginner's cookbook. The straightforward instructions and easily available ingredients parallel AVR microcontrollers, which are designed to be accessible for those new to microcontroller programming, much like a beginner's recipe book makes cooking approachable.
AVR Core Architecture
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The AVR microcontroller uses a Harvard architecture, where the program and data memories are separate, allowing for faster execution.
Detailed Explanation
Harvard architecture means that an AVR microcontroller has separate memory storage for instructions (the program) and for data. This distinct separation allows the microcontroller to access instructions and data simultaneously, leading to faster processing speeds compared to architectures that use a single memory space, where accessing one can interrupt the other.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a librarian who has two separate rooms for books and files. If someone is looking for a book, they don’t have to wait for a file to be retrieved from the same room, allowing for quicker service. Similarly, the AVR's separate memory for program and data allows it to execute operations more swiftly.
Instruction Set of AVR Microcontrollers
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers use a simple 8-bit instruction set and are known for their efficient code execution. The architecture offers 32 general-purpose registers, making it faster than other microcontrollers in its class.
Detailed Explanation
The instruction set of AVR microcontrollers is built around 8-bit commands, which are relatively straightforward compared to other more complex instruction sets. These instructions allow the microcontroller to perform tasks efficiently, making it suitable for applications where quick execution is critical. The presence of 32 general-purpose registers aids in speeding up processes by allowing multiple operations to be managed simultaneously.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a small team working on a project where each team member has a specific task but they can all quickly exchange notes and ideas among themselves. This collaboration, similar to how general-purpose registers operate, highlights how AVR microcontrollers can handle multiple data points quickly and efficiently, leading to better overall project success.
Popularity in Hobbyist Projects
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AVR microcontrollers are particularly popular in platforms like Arduino, which simplifies the development process.
Detailed Explanation
AVR microcontrollers are widely used in platforms like Arduino, enhancing their accessibility. The Arduino platform provides a user-friendly interface and a wide collection of libraries, making it much easier for beginners to program and utilize these microcontrollers in their projects. This support fosters a large community of hobbyists and educators who can collaborate and share knowledge and projects.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community garden where newcomers can borrow tools and attend workshops. Just like the community garden helps people learn gardening without the intimidation of starting alone, the Arduino platform with AVR microcontrollers allows newcomers to create projects without extensive prior knowledge, fostering a supportive learning environment.
Examples of AVR Microcontrollers
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example AVR Microcontrollers:
- ATmega series (e.g., ATmega328, ATmega32)
- ATtiny series (smaller, lower-power MCUs)
Detailed Explanation
The ATmega and ATtiny series represent popular lines of AVR microcontrollers. The ATmega series, such as ATmega328 and ATmega32, are commonly used in various applications due to their balance of performance and resource availability. On the other hand, the ATtiny series offers smaller, energy-efficient options ideal for applications where space and power consumption are critical such as in portable devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ATmega series as a collection of versatile kitchen appliances suitable for various cooking styles, while the ATtiny series functions more like compact, specialized tools that are perfect for small kitchen spaces but still very effective for specific tasks.
Key Concepts
-
AVR Microcontroller Architecture: An efficient architecture that employs an 8-bit RISC design, ideal for beginners in embedded systems.
-
Harvard Architecture: This architecture segregates program and data memory, enhancing execution speed.
-
Instruction Set: Simple 8-bit instruction set facilitating efficient code execution.
-
General-Purpose Registers: The presence of 32 registers accelerates processing capabilities.
-
Hobbyist Applications: AVR microcontrollers are frequently used in platforms like Arduino.
Examples & Applications
The ATmega328 microcontroller is used extensively in Arduino boards, allowing users to easily program and control various devices.
ATtiny series microcontrollers are utilized in low-power applications such as small electronics and sensors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AVR with ease, programmers please, in projects they aim to seize.
Acronyms
Remember A-V-R**
A**vailable for all
**V**ersatile in use
**R**eliable through projects.
Stories
Once in a land of circuits, the AVR was the hero, known for crafting brilliant projects with ease—hobbyists learned to control robots and lights, bringing them to life with joy.
Memory Tools
To recall what AVR can do, think of the acronym 'E.R.E.C.': Educational, Robust, Efficient, and Cost-effective.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AVR Microcontroller
An 8-bit RISC microcontroller architecture used for various applications, known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- Harvard Architecture
A computer architecture that separates storage and treatment of data and instructions, facilitating faster processing.
- Instruction Set
The set of instructions that a microcontroller can execute, defining its programming capabilities.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing, an architecture designed to execute a small number of instructions quickly.
- GeneralPurpose Registers
Registers that can be used by the CPU for various operations, increasing processing speed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
