ARM Microcontroller Architecture
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ARM Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

ARM microcontrollers are part of the RISC architecture family, which stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computing. Can anyone tell me the benefits of using RISC architecture?

I think RISC architectures are generally faster because they have simpler instructions.

Yes, and they consume less power too, right?

Exactly! This balance of power efficiency and performance makes ARM microcontrollers popular in various applications. Let’s break down the ARM core components, starting with the ARM Cortex series. Can anyone name a few types of Cortex cores?

There’s the Cortex-M0 and Cortex-M4, I believe.

What about the Cortex-M3?

Great! Each of these cores has specific features tailored for different applications. The Cortex-M series, in particular, is prevalent in embedded systems. Let's recap: ARM microcontrollers are known for performance and efficiency due to their RISC architecture.
ARM Instruction Set and Performance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the instruction set of ARM microcontrollers. Who can explain why having a simple instruction set benefits performance?

A simpler instruction set often means that instructions can execute faster since there's less complexity.

This also means lower power consumption, right? The microcontroller can operate cooler.

Correct! The use of a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture is crucial. This leads to better execution speed and efficiency. Can anyone think of an application where this might be important?

In IoT devices, where they need to constantly send and receive data while conserving battery.

Absolutely! The ARM architecture's simplicity enhances its adaptability in various IoT applications. As we move to the next section, keep in mind how this impacts ARM's wide application support.
Examples of ARM Microcontrollers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at some specific examples of ARM microcontrollers. Can anyone name a few?

STM32 is a common one!

And the NXP LPC series.

Perfect! These microcontrollers are widely used in consumer devices and embedded systems. What features make the STM32 stand out?

It has good processing power and a lot of peripheral support!

Exactly! This support is vital for developing complex applications. In summary, ARM microcontrollers have versatility across applications due to their architecture and ecosystem.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section examines the ARM microcontroller architecture, highlighting its RISC design, instruction set, and key features that contribute to its popularity in embedded systems. It also discusses various ARM Cortex cores and provides examples of popular ARM microcontrollers.
Detailed
ARM Microcontroller Architecture
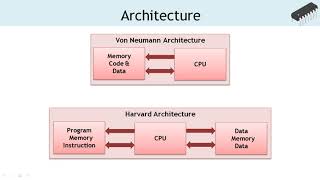
ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) microcontrollers are characterized by their use of a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture, known for achieving a balance between high performance and low power consumption. This architecture is particularly advantageous for a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics and IoT devices. The main components of ARM microcontrollers include:
- ARM Core: These microcontrollers utilize ARM Cortex cores (like Cortex-M0, M3, M4, and M7), which offer various features tailored for performance and power efficiency.
- Instruction Set: ARM microcontrollers implement a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture with a simplified instruction set that optimizes execution speed while minimizing power requirements.
- Wide Application Support: With a robust ecosystem that includes development tools and software libraries, ARM microcontrollers support extensive application development.
Examples of ARM microcontrollers include:
- STM32 (by STMicroelectronics)
- NXP LPC series
- Texas Instruments Tiva C series
Understanding ARM microcontroller architecture is crucial for selecting the appropriate MCU for projects, especially in scenarios where power efficiency and performance are critical.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to ARM Microcontrollers
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) microcontrollers are based on a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture and are known for their high performance, low power consumption, and scalability. ARM-based microcontrollers are widely used in a broad range of applications from consumer electronics to industrial automation and IoT.
Detailed Explanation
ARM microcontrollers stand out because they use a streamlined instruction set, which allows them to execute tasks more efficiently. The RISC architecture means that the processors do not have a lot of complex instructions, resulting in faster performance and reduced power usage. These qualities make ARM microcontrollers ideal for various applications, including consumer devices such as smartphones and appliances, as well as in industrial settings like automated machinery and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ARM microcontrollers like a sports car designed for speed and efficiency. Just as a sports car has a streamlined design with fewer, but more effective components that enhance its speed and reduce fuel consumption, ARM microcontrollers are designed to perform tasks quickly and with minimal power usage.
ARM Core Features
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM microcontrollers use the ARM Cortex cores (e.g., Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7) that are designed to offer a balance between performance, power efficiency, and ease of use.
Detailed Explanation
The ARM Cortex cores are a family of processors that cater to different needs - from high performance to low power. The naming like Cortex-M0 to Cortex-M7 indicates a range of options where M0 is simpler and lower powered, while M7 is intended for more demanding tasks. This variety means that developers can choose the right Cortex processor based on the specific requirements of their application, whether they need high speed, high efficiency, or a combination of both.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine choosing a vehicle based on your daily activities. If you mostly drive in the city (requiring efficiency) you might choose a small electric car (Cortex-M0). However, if you often go on long road trips (requiring power), you might opt for a hybrid SUV (Cortex-M7). This flexibility in choosing the right ARM Cortex core allows developers to best fit the microcontroller to their project's needs.
Instruction Set Characteristics
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM microcontrollers use a 32-bit or 64-bit RISC architecture with a simple instruction set that improves execution speed and reduces power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
The ARM architecture's instruction set enables simpler and faster processing since it relies on fewer cycles to perform each task. The use of either 32-bit or 64-bit data width allows ARM microcontrollers to handle larger data types and perform complex calculations more efficiently. This combination greatly enhances both the speed of operation and the energy efficiency, which are crucial for battery-powered devices and applications where performance is critical.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the way you read a recipe. If the recipe is concise with clear steps, you can cook faster without getting confused. ARM’s simple instruction set is like that clear recipe—it allows the microcontroller to perform tasks quickly and efficiently, minimizing wasted energy and time.
Wide Application Support
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ARM-based MCUs are supported by a vast ecosystem of development tools, libraries, and software platforms.
Detailed Explanation
One of the significant advantages of using ARM microcontrollers is the extensive support they receive. Developers have access to numerous tools, such as integrated development environments (IDEs), libraries, and frameworks, which simplify the development process. This level of support reduces the time and effort needed to create applications, allowing developers to focus on innovation and functionality rather than troubleshooting issues.
Examples & Analogies
It's like planning a trip with lots of online resources available. You have maps, travel guides, and recommendation sites all helping you streamline your journey. Similarly, ARM microcontrollers have a wealth of resources that aid developers in efficiently creating their projects.
Examples of ARM Microcontrollers
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example ARM Microcontrollers:
- STM32 (by STMicroelectronics)
- NXP LPC series
- Texas Instruments Tiva C series
Detailed Explanation
Several manufacturers produce microcontrollers based on the ARM architecture, each offering different features suited for various applications. STM32 microcontrollers are renowned for their high-performance capabilities; NXP LPC series is favored in consumer electronics, while Texas Instruments' Tiva C series is often used in industrial applications. Each of these families contains various models tailored to specific needs, showcasing the versatility and adaptability of ARM architecture in real-world applications.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a smartphone brand that offers various models for different user needs. Some models are designed for basic usage, while others cater to advanced photo editing or gaming. Similarly, STM32, NXP LPC, and Texas Instruments models provide options for diverse applications, from everyday tasks to complex requirements.
Key Concepts
-
RISC Architecture: ARM microcontrollers use a simplified instruction set for efficient processing.
-
ARM Cortex Cores: These cores exist in various flavors, each optimized for different performance needs.
-
Power Efficiency: ARM microcontrollers are designed to minimize power consumption while maximizing performance.
-
Wide Application Use: ARM microcontrollers are versatile and find applications in consumer electronics, IoT, and more.
Examples & Applications
STM32 microcontrollers are widely used in consumer devices due to their performance and efficiency.
NXP LPC series microcontrollers cater to low-power applications while providing extensive features.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ARM is smart, RISC makes it fast; low power, high performance, built to last.
Stories
Imagine a marathon runner with lightweight shoes, sprinting past others. That’s why ARM’s RISC architecture makes it fast and agile while being power-efficient.
Memory Tools
Remember RISC as 'Run Instructions Swiftly and Clear.'
Acronyms
ARM stands for 'Advanced Resource Management.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ARM
Advanced RISC Machine, a family of computer processors based on a RISC architecture.
- RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing, a CPU design philosophy that emphasizes simplicity and efficiency.
- Cortex
A series of ARM processor cores designed for efficiency in embedded applications.
- Ecosystem
A collection of hardware, software, tools, and resources that support the development of applications using ARM microcontrollers.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
