Digital Photogrammetry
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Image Acquisition in Digital Photogrammetry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into digital photogrammetry, starting with image acquisition. Can anyone tell me what platforms we commonly use to capture images digitally?

Drones and satellites!

Exactly! Drones provide high-resolution imagery at a lower cost and can access difficult areas easily. Why do you think this access is important?

It helps in collecting data from places that are hard to reach, like steep terrains or disaster zones.

Great point! This accessibility is crucial for timely data collection in emergency situations. Let's remember the acronym 'DRA' for Drones, Resolution, and Accessibility!

So DRA helps us remember the key benefits of digital acquisition?

Yes! Now that we understand acquisition, let's discuss how we match these images to create models.
Image Matching Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move to image matching. Can someone explain what is meant by feature-based techniques?

I think they involve finding unique points or features in images to match them up?

Correct! Techniques like SIFT and SURF look for these keypoints. They help create a robust model that represents the environment accurately. Why do you think this is important?

If we get the points wrong, the created models will be inaccurate, right?

Exactly! Accuracy is critical for reliable data. As a mnemonic, remember 'FAM' for Feature, Alignment, and Model to connect these ideas!

That makes sense! What about area-based techniques?

Good question! Area-based approaches like NCC compare pixel intensities over a region rather than focusing on individual points. Let's look into their importance next!
Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at two pivotal outputs of digital photogrammetry—the DSM and DTM. Can anyone tell me what the DSM includes?

It includes everything on the surface, like buildings and trees, right?

Absolutely! The DSM is comprehensive and captures the landscape's features. How about the DTM?

The DTM only shows the bare earth, without any of the surface features.

Correct! The DTM is crucial for tasks like flood modeling and terrain analysis. To remember the distinction, think of 'DSB'—Digital Surface and Bare.

So, DSM is the whole landscape while DTM focuses on what’s underneath.

Exactly! Understanding these models is vital for effective civil engineering applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses digital photogrammetry, emphasizing its reliance on digital cameras, drones, and advanced image matching techniques, which have transformed data acquisition and interpretation. Concepts such as Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM) are highlighted, showcasing their distinct roles in providing detailed geographic information.
Detailed
Digital Photogrammetry
Digital photogrammetry represents a modern advancement in the field, leveraging digital technologies to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of spatial data acquisition and analysis. This section begins by discussing Image Acquisition, which now primarily occurs through digital platforms such as cameras mounted on drones and satellites. This shift to digital methods allows for rapid data collection with high precision, essential for various civil engineering applications.
Next, the section outlines various Image Matching Techniques valuable in processing and analyzing captured images. Techniques include
- Feature-based methods like SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform), SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features), and ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF), which focus on identifying and matching distinct features across images.
- Area-based approaches, particularly Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC), which assesses and matches images based on pixel intensity and area.
The creation of Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM) is also discussed.
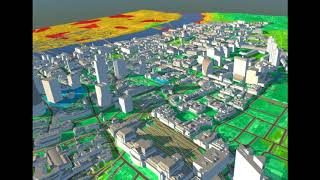
- DSM captures all surface features, such as buildings and vegetation, focusing on the topography of the landscape, while
- DTM focuses solely on the bare earth, which is crucial for analysis of landforms and drainage patterns.
In summary, digital photogrammetry stands as a linchpin in the integration of data from aerial surveys, enabling extensive applications in civil engineering and environmental management.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Digital Photogrammetry
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Modern photogrammetry is almost entirely digital, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
Detailed Explanation
Digital photogrammetry refers to the modern practice of using digital technology to capture images and process them to obtain measurements and create models of physical objects or areas. This shift from traditional methods, which often relied on film and manual techniques, has dramatically enhanced the speed and precision of photogrammetric work. By leveraging digital tools, data can be processed more quickly and accurately, leading to improved results.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine taking photos of a landscape with a smartphone. The digital camera instantly stores high-quality images, allowing users to edit, enhance, and analyze the photos right away. Similarly, in digital photogrammetry, these captured images provide immediate access to valuable data that can help in mapping and modeling.
Image Acquisition Methods
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Image Acquisition through digital cameras, drones, satellites.
Detailed Explanation
Image acquisition in digital photogrammetry involves capturing images using various tools such as digital cameras, drones, and satellites. Each of these devices has unique advantages. Drones can access hard-to-reach locations and capture high-resolution imagery from different angles, while satellites can cover much larger areas at a broader scale. This diversity in acquisition methods allows for more comprehensive data collection, increasing the variety of applications in surveying and mapping.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how different cameras are used for different occasions. A DSLR might be used for a wedding to capture high-quality portraits, while a GoPro could be used to film extreme sports activities where flexibility and portability are key. Similarly, choosing between drones, cameras, or satellites for photogrammetry depends on the specific needs of the project.
Image Matching Techniques
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Image Matching Techniques: Feature-based: SIFT, SURF, ORB; Area-based: Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC).
Detailed Explanation
Image matching techniques are essential in digital photogrammetry to identify corresponding points and features across multiple images. Feature-based methods like SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) and SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features) detect and match distinct points between images, ensuring that the same features are recognized despite changes in angle or scale. Area-based methods, such as Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC), evaluate pixel intensity patterns to find correspondences in a broader area. These techniques enhance the accuracy in constructing 3D models from images.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how facial recognition works on smartphones. It identifies key facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth (like SIFT and SURF identifying features) to verify the user’s identity. Similarly, in photogrammetry, algorithms match features across images to ensure the correct reconstruction of 3D spaces.
Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM)
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
DSM includes all surface features (buildings, trees). DTM represents bare earth surface.
Detailed Explanation
In digital photogrammetry, models are categorized into two types: Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM). A DSM captures all visible features on the surface, including buildings and vegetation, providing a comprehensive view of the environment. In contrast, a DTM focuses solely on the bare earth surface, stripping away all objects. These models are vital for various applications, such as flood modeling, urban planning, and creating topographical maps.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine editing a photograph of a city skyline. The final image can either show everything in detail, including buildings and trees (like a DSM), or you could use editing software to remove all the structures, leaving just the land contours visible like a DTM. This differentiation in models serves different planning and analysis purposes.
Key Concepts
-
Digital Surface Model (DSM): A representation of the Earth's surface including all features.
-
Digital Terrain Model (DTM): A model representing only the bare earth.
-
Image Matching Techniques: Approaches for aligning images to create 3D models.
-
Feature-based Techniques: Finding unique identifiers in images for matching.
-
Area-based Techniques: Matching pictures using patterns in pixel intensity.
Examples & Applications
A city planner uses DSM to assess potential sites for new buildings, factoring in existing structures.
A geologist utilizes DTM for analyzing landforms and determining potential areas for erosion.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
DSM's the surface, DTM's the ground; one shows all, the other's profound.
Stories
A drone flew high over a city, capturing both buildings and trees for the DSM, while another flew low, measuring just the bare earth for the DTM to help with land planning.
Memory Tools
Remember 'FAME' for Feature, Area, Matching, and Efficiency to grasp the core principles of image techniques.
Acronyms
Use 'DRA' for Drones, Resolution, Accessibility as a reminder of how digital tools enhance data gathering.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Digital Surface Model (DSM)
A 3D representation of the Earth's surface that includes all surface features like buildings and trees.
- Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
A 3D representation that reflects the bare earth surface without any objects or vegetation.
- Image Matching Techniques
Methods used to align and match pairs of photos to create accurate 3D models.
- Featurebased Techniques
Approaches that identify and match unique features within images to establish correspondences.
- Areabased Techniques
Methods that match images based on the intensity and pattern of pixel values over areas.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
