Stereoscopy and Stereo Vision
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Principle of Stereoscopic Viewing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the principle of stereoscopic viewing. Can anyone tell me why two images enhance our depth perception?

I think it's because our eyes see slightly different perspectives, and our brain combines them.

Exactly! This merging of two overlapping images creates a stereo pair, providing a 3D impression. Now, can you remember a time you experienced this in a movie or a game?

Yes! The VR games I play have that 3D effect, making it feel like I'm really in the game!

Great example! So, why do you think this technique is important in photogrammetry?

It must help in mapping and creating accurate models of landscapes.

Correct! Remember, depth perception is vital for applications such as topographic mapping and urban planning. Let's summarize: stereoscopic viewing uses two images to create depth perception, crucial in photogrammetry.
Understanding Stereoplotters
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed stereoscopic viewing, let's explore stereoplotters. Can anyone tell me what they are used for?

Aren't they used to extract 3D coordinates from stereo images?

Yes! Stereoplotters can be analog, analytical, or digital. What do you think sets them apart?

I guess the technology they use? Like, digital would be more advanced.

Exactly! Digital stereoplotters use automated algorithms for processing, making them very efficient. Can anyone think of why that might be important?

Efficiency could save time and lead to faster project completion.

Exactly right! To summarize, stereoplotters are essential for converting stereo pairs into 3D coordinates, with digital options providing advanced processing capabilities.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section on stereoscopy covers the basic principles of stereo viewing, the role of stereo pairs in depth perception, and the function of stereoplotters in deriving three-dimensional coordinates from stereo images, underscoring the importance of these tools in photogrammetry.
Detailed
Stereoscopy and Stereo Vision
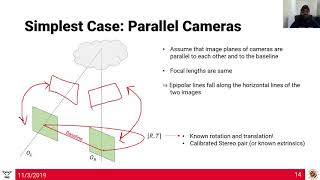
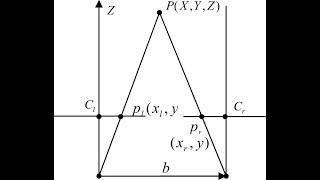
Principle of Stereoscopic Viewing: Stereoscopy hinges on capturing two overlapping images of the same scene from different angles, effectively creating a stereo pair. The human brain interprets these images as a unified 3D view, enhancing depth perception. This principle is crucial for applications like mapping and modeling in photogrammetry.
Stereoplotters: These devices, whether analog, analytical, or digital, are instrumental in deriving 3D coordinates from stereo images. Each type offers unique functionalities, facilitating accurate spatial representation from stereo pairs.
In summary, stereoscopy not only enriches visual representation but also underpins key processes in photogrammetry, making it essential for various engineering applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principle of Stereoscopic Viewing
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Two overlapping images of the same area, taken from different positions, form a stereo pair.
• The human brain perceives depth by merging these two perspectives, creating a 3D impression.
Detailed Explanation
The principle of stereoscopic viewing is fundamental to understanding how we perceive depth visually. When you see two images taken from slightly different angles, your brain processes them together. This process allows you to understand how far away objects are from you, similar to how our eyes work to discern distance. The overlap in these images is crucial because it helps your brain fuse the two perspectives into a single, coherent three-dimensional view.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine watching a 3D movie: you wear glasses that filter two different images sent to each eye. Your brain combines these images, giving you that immersive 3D effect. Stereoscopic viewing in photogrammetry works similarly by using two images to create a depth perception that helps in mapping and understanding the physical world more accurately.
Stereoplotters
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Instruments or software used to extract 3D coordinates from stereo images.
• Types include analog, analytical, and digital stereoplotters.
Detailed Explanation
Stereoplotters are essential tools in photogrammetry that allow us to interpret and analyze stereo images. They help map three-dimensional coordinates from two-dimensional images taken at different angles. There are different types of stereoplotters: analog ones that use physical models and optics, analytical ones that involve mathematical computations to enhance accuracy, and digital ones that leverage software to process images for extracting information.
Examples & Analogies
Think of stereoplotters like a specialized pair of glasses for viewing topographic maps. Just as glasses help you see clearly by adjusting the light reaching your eyes, stereoplotters help visualize and measure the landscape in three dimensions. For example, a cartographer might use a digital stereoplotter to create a detailed topographic map from aerial imagery, allowing them to understand the terrain and features effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Stereoscopy: A method of creating depth perception using two images.
-
Stereo Pair: Two images from slightly different angles.
-
Stereoplotter: A device for obtaining 3D coordinates from stereo images.
Examples & Applications
An example of stereoscopy in use is in 3D movies, where viewers see two images merged to create a sense of depth.
Stereoplotters are used in creating topographic maps by extracting elevation data from stereo aerial images.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
See two images, don't be shy, Depth perception will surely fly!
Stories
Imagine two friends standing opposite each other at a distance, taking photos. When combined, their pictures allow you to see a lively park as if you were there, feeling the depth of trees and people.
Memory Tools
Stereo Pair = See 3D from Two.
Acronyms
S.P.E.E.D. = Stereo Pair Enhances Every Depth perception.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Stereoscopy
The technique of creating the optical illusion of depth from two-dimensional images.
- Stereo Pair
Two overlapping photographs taken from different perspectives to provide depth perception.
- Stereoplotter
A device used for extracting three-dimensional information from stereo images.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
