Classifying Transactions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Importance of Classifying Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the classification of transactions. Can anyone share why categorizing transactions is important in accounting?

I think it helps in understanding the financial health of a business.

Exactly! Classifying transactions allows stakeholders to analyze financial data effectively. Remember, it's like organizing a messy drawer, making it easier to find what you need quickly.

What categories do financial transactions fall into?

Great question! Financial transactions are primarily classified into assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. This categorization provides a clear picture of the company's financial structure.

How does it affect financial statements?

When we classify transactions correctly, it allows us to prepare accurate financial statements like the balance sheet and profit and loss account, ensuring that we meet legal requirements and compliance standards.

To recap, classifying transactions is crucial for clarity in financial reporting and effective decision-making.
How Transactions are Classified
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how we classify transactions based on their nature. What are the main categories?

Assets, liabilities, income, and expenses?

That's right! Let's break those down. Who can explain what an asset is?

Assets are what a business owns, like cash or equipment.

Exactly! And liabilities are what the business owes to others. Can someone give an example of a liability?

A loan or accounts payable.

Correct! Now, let's talk about income. How does it differ from expenses?

Income is money received from sales, while expenses are costs incurred.

Exactly! Income increases equity, while expenses decrease it. Remember the acronym 'AILE' for Assets, Income, Liabilities, and Expenses!

To summarize, classifying transactions into these categories is fundamental for proper accounting and reporting.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section elaborates on the classification of financial transactions within the accounting framework, explaining its importance for accurate reporting and financial analysis. The process of categorizing transactions aids in preparing financial statements and enhances the interpretability of financial data.
Detailed
Classifying Transactions
Classifying transactions is a vital phase of the accounting process following the initial recording of transactions. Once transactions are recorded in a journal, they are organized into specific categories within the ledger. This classification is essential for generating coherent financial statements, such as the balance sheet and profit and loss account.
Key Points
-
Importance of Classification: Classification ensures that financial data is organized, making it easier to summarize and interpret overall business performance.
- It prevents errors and facilitates streamlined reporting.
- Stakeholders can easily access categorized financial data that reflect the company's operational health.
- Types of Classifications: Transactions are typically classified into several categories:
- Assets: Resources owned by the organization, like cash and equipment.
- Liabilities: Obligations owed to third parties.
- Income: Revenues generated from business activities.
- Expenses: Costs incurred in the process of generating income.
- Process Overview: The classification process helps in:
- Accurately preparing financial statements, crucial for decision-making.
- Ensuring compliance with accounting standards, which is pivotal for external reporting.
Through thoughtful classification, businesses can gain insights into their operational efficiency and financial stability, ultimately guiding strategy and growth.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Classifying Transactions
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
After transactions are recorded, they are classified into specific accounts in the ledger. This helps in organizing financial data and preparing financial statements.
Detailed Explanation
Once transactions are recorded in journals, the next important step is to classify them. Classification means sorting the recorded transactions into specific categories that relate to different aspects of the business's finances. It is essential because it helps keep the financial data structured and accessible. This organization enables accountants to prepare financial statements, which provide insights into the financial health of the business. Essentially, classification is like filing important documents into folders according to their topics to make them easier to find and review.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where books are organized into categories like fiction, non-fiction, and reference. If all the books were just piled together randomly, it would be challenging to find any particular book. Similarly, in accounting, if financial transactions were not classified into specific accounts, it would be challenging to understand how much money a business is making, what it owes, or how much is being spent.
The Ledger System
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This helps in organizing financial data and preparing financial statements.
Detailed Explanation
The ledger is a crucial component of the accounting system where classified transactions are recorded. Each account in the ledger corresponds to a specific category, such as cash, inventory, or expenses. By having these categorized accounts, accountants can easily track the financial activities related to each area of the business. When preparing financial statements, these organized accounts provide the necessary information, allowing for a straightforward compilation of data needed to analyze the company's financial situation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ledger as a detailed recipe book. Each recipe represents a different aspect of your cooking (like baking, frying, or grilling) and includes all the ingredients and steps needed. When you want to make something specific, you refer to the right recipe instead of combing through a jumbled mess of random ingredients. Similarly, the ledger allows accountants to quickly find relevant financial data without having to sift through unorganized transactions.
Key Concepts
-
Classification: The process of categorizing financial transactions into organized groups.
-
Assets: Resources owned by a business, critical for understanding financial health.
-
Liabilities: A company's financial obligations, relevant for assessing risk.
-
Income: Revenue generated, important for evaluating business performance.
-
Expenses: Costs incurred, essential for profit analysis.
Examples & Applications
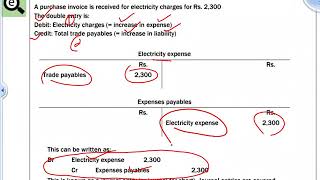
A company purchases inventory for $10,000. This transaction is classified as an asset.
A business incurs $2,000 in salaries as an expense, affecting the profit and loss account.
A company takes a loan of $5,000, classified as a liability in their balance sheet.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Assets are treasures, liabilities are debts, expenses shrink profits, income’s the best bets.
Stories
Imagine a merchant with a shop (assets) needing to pay back a big loan (liabilities). They sell goods and earn money (income) but must pay for supplies (expenses) to stay afloat.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A.L.I.E.' for Assets, Liabilities, Income, and Expenses to easily recall the classifications.
Acronyms
A-L-I-E - A for Assets, L for Liabilities, I for Income, E for Expenses.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Assets
Resources owned by a business that have economic value.
- Liabilities
Obligations or debts that a business owes to outside parties.
- Income
Funds received by a business from its operations.
- Expenses
Costs incurred by a business in the process of earning revenue.
- Financial Statements
Formal records of the financial activities and position of a business.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
