Recording Transactions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Purpose of Recording Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore why recording transactions is the key priority in accounting. Can anyone share their thoughts on this?

It helps keep track of money going in and out of the business.

Exactly! By keeping track of financial transactions, a business can evaluate its financial health. Remember, we often summarize this with the phrase 'Document to Decide!'

What happens if we don’t record some transactions?

Good question! Failing to record transactions accurately can lead to financial discrepancies, which can affect decision-making and compliance. Can anyone think of a real-life example for that?

A business might underestimate its expenses and lose money.

Absolutely! Recording accurately ensures we have a clear picture of the finances.

Will transactions always have a debit and a credit?

Yes, every transaction will have at least two entries: one debit and one credit, which is crucial to the double-entry system! Let’s summarize today: accurate recording helps in tracking, decision-making, and compliance.
The Process of Recording Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into how financial transactions are actually recorded. For example, what do you think the first step is in recording?

You need to write down the transaction as soon as it happens.

Correct! We often record transactions in journals. The format usually includes the date, account titles, amounts, and a brief description. Does anyone recall another important aspect?

Each transaction should have a debit and credit entry!

Right! This is called double-entry bookkeeping. Just remember, for every debit, there must be an equal credit, ensuring balance. Can you think of an example of a transaction that might involve both?

If a store sells a product, it records both the sale and the cash received.

Exactly! And after recording these entries, the next step is classification into ledgers. Before we end, let's repeat: always record immediately and make sure to debit and credit equally!
Interpretation of Recorded Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's touch on why the recording of transactions is important for decision-making. Why do we need to analyze recorded transactions?

To see how we are doing financially and if we need to change anything.

Exactly! By providing accurate financial statements derived from these records, management can make informed choices. Can someone tell me what types of financial statements are typically prepared?

The profit and loss statement and the balance sheet!

Great job! And these statements help assess profitability and financial position, respectively. Keep in mind, 'Record, Analyze, Decide' is a helpful mnemonic. Let’s wrap up today’s discussion by reminding ourselves of the importance of recording transactions!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Recording transactions is a vital objective of accounting, ensuring that all financial activities are documented accurately and completely. This foundation allows for proper classification, summarization, and interpretation of financial data to support decision-making and legal compliance.
Detailed
Recording Transactions
The primary objective of accounting is to systematically record all financial transactions that occur within a business. These transactions can include sales, purchases, income, and expenses. Accurate recording is crucial as it ensures completeness and serves as the first step in the accounting process. The correct documentation of these transactions will allow accountants to classify and summarize the data, leading to the preparation of financial statements, which in turn aid in decision-making and ensure legal compliance.
Significance
The process of recording transactions is pivotal in maintaining the integrity of financial information for a business. It provides a concrete basis for evaluating the financial health of an organization and is essential for meeting legal obligations, such as tax filings and reporting to regulatory authorities. Accurate transaction records also help businesses manage their finances effectively, thereby supporting sustainable growth.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Objective of Recording Transactions
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The primary objective of accounting is to systematically record all financial transactions that occur within a business, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
Detailed Explanation
The main aim of recording transactions in accounting is to create a reliable and organized record of all financial activities that a business engages in. This means that every time money comes in or goes out, it should be logged carefully. By doing so, businesses can ensure that their financial records are accurate and that no important entries are missed. This practice is crucial because it lays the groundwork for all subsequent financial reporting and analysis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of recording transactions like keeping a journal. Just as you would write down significant events in your life to remember them later, businesses write down their financial transactions so they can keep track of how money flows in and out. If you forget to write down an event, it gets lost in time; similarly, missing a financial transaction can lead to significant errors in the financial statements.
Accuracy and Completeness in Recording Transactions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Ensuring accuracy and completeness means that all transactions are recorded exactly as they happened without any errors and that no transactions are left out.
Detailed Explanation
Accuracy in recording transactions ensures that the figures reflect the true state of the financial affairs of the business. For example, if a sale of $1,000 is incorrectly recorded as $10,000, it would misrepresent the income of the company, leading to poor decision-making. Completeness means that every single transaction—whether it’s a sale, expense, or payment—must be included in the records. Missing a transaction can result in an incomplete financial picture, which could lead to erroneous conclusions and actions based on misleading data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’re at a grocery store, and you buy groceries for $150, but you only write it down as $50. This incorrect record keeping could lead you to think you have more money than you actually do, which is similar to how businesses can make decisions based on inaccurate financial records if they do not ensure all transactions are recorded correctly.
Key Concepts
-
Recording Transactions: Essential for accurate financial reporting.
-
Double-Entry System: Ensures balance in accounting records.
-
Financial Statements: Outputs derived from recorded transactions for decision-making.
Examples & Applications
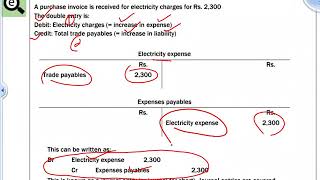
When a company sells a product for $100 in cash, it records a credit to sales revenue and a debit to cash.
If a business pays $50 in rent, it records a debit to rent expense and a credit to cash.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Record, classify, and report - to keep finances in support!
Stories
Imagine a baker who records each cake sold. If she forgets, she may overestimate her profits and underprepare for the supplies needed.
Memory Tools
R.A.D: Record all data to ensure accurate representation!
Acronyms
D.E.C. stands for Debit, Entry, Credit - the structure of recording transactions!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Recording Transactions
The systematic documentation of all financial transactions that occur within a business.
- DoubleEntry System
An accounting system where each transaction is recorded in at least two accounts, one as a debit and the other as a credit.
- Profit and Loss Statement
A financial statement that summarizes revenues, costs, and expenses during a specific period.
- Balance Sheet
A financial statement that presents the financial position of a business at a specific point in time, detailing assets, liabilities, and owner's equity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
