The Accounting Process
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Recording of Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're starting with the first step in the accounting process, which involves the recording of transactions. Why do you think it's essential to record these transactions as they happen?

I think it's important so that we don't forget any transactions later.

Exactly! Accurate recording helps maintain a complete record. Each transaction needs a debit and credit entry. Who can tell me why we record both?

Because of the double-entry system, right? Each transaction affects at least two accounts.

Exactly! Remember, the acronym DUAL can help you recall this principle: D - Debit, U - User (two accounts), A - Account, L - Ledger. Let's move on to classifying these recorded transactions.
Classifying Transactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss classifying transactions. After we record, we need to sort these into specific accounts in the ledger. What types of accounts do we usually work with?

Assets, liabilities, income, and expenses!

Great job! Classifying transactions helps us organize financial data. Can anyone explain why this organization is beneficial?

It makes it easier to prepare financial statements and understand the overall financial health of the business.

Exactly! Remember, organizing helps in quick assessments. Now, let's discuss how we summarize this classified data.
Summarizing Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

After classifying transactions, we summarize the data into financial statements. What kind of statements do we often prepare?

The profit and loss account and the balance sheet.

Correct! These statements provide critical insights into the business's performance. Can anyone share how the profit and loss account differs from the balance sheet?

The profit and loss account shows our revenues and expenses over a period, while the balance sheet shows assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at a specific point in time.

Well put! Keep in mind the acronym PS for Profit & Statement: the 'S' stands for summarizing the performance in a time frame. Finally, we interpret this financial data.
Interpreting Financial Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about interpreting the financial data we’ve summarized. Why is this step crucial?

It's important because it helps stakeholders understand the financial health of the business.

Yes! Analysis can guide decisions about budgeting, investing, and strategies moving forward. Who remembers a key tool we might use in analysis?

Ratio analysis! We can compare figures from financial statements to gain insights.

Exactly! Always compare past performance with current data for better informed decisions. To summarize, today we learned about recording, classifying, summarizing, and interpreting. By remembering the acronym RCSI, you can keep these steps in mind. Any questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the essential steps of the accounting process, including recording transactions, classifying them into ledgers, summarizing data into financial statements, and interpreting these statements to evaluate a business's financial health.
Detailed
The Accounting Process
Overview
The accounting process consists of four critical steps that enable organizations to manage their finances effectively. This process is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring informed decision-making.
Steps in the Accounting Process
- Recording of Transactions: The first step in the accounting process is to record all business transactions as they happen. Each transaction involves both debit and credit entries, which are documented in journals.
- Classifying Transactions: After recording, these transactions are classified into specific accounts in the ledger. This classification organizes financial data, making it easier to prepare financial statements.
- Summarizing Data: Once transactions are classified, the data is summarized into key financial statements, such as the profit and loss account and the balance sheet, which provide insights into the overall financial health of the business.
- Interpreting Financial Data: The final step involves analyzing these financial statements to interpret the organization's financial performance. This interpretation aids in making strategic business decisions and evaluating overall performance.
Importance of the Accounting Process
The accounting process is vital for ensuring accuracy in financial reporting and for providing stakeholders with relevant information required for effective decision-making and compliance with legal regulations.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Recording of Transactions
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
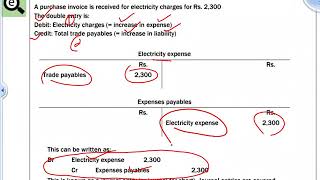
The first step in accounting is to record business transactions as they occur in the books of accounts. This is done through journals, where each transaction is recorded with a debit and a credit entry.
Detailed Explanation
The recording of transactions is the initial phase in the accounting process. It involves documenting every financial event that occurs in a business as it happens. This is done using journals, where each transaction is entered with a debit amount and a corresponding credit amount. The importance of this step lies in capturing accurate information right away, which serves as the foundation for all subsequent accounting activities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this step like jotting down notes during a class lecture. Just as you write down key points immediately to ensure you don’t forget them, businesses record transactions in journals so that they have a clear and accurate account of what happened from the very beginning.
Classifying Transactions
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
After transactions are recorded, they are classified into specific accounts in the ledger. This helps in organizing financial data and preparing financial statements.
Detailed Explanation
Once all business transactions have been recorded in the journal, the next step is to classify them into specific categories within the ledger. This means organizing the transactions into different accounts like assets, liabilities, expenses, and revenue. This classification is crucial as it helps in tracking the financial information systematically, which is essential for preparing financial statements later on.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine sorting your emails into different folders – work emails, personal emails, promotional emails, etc. By categorizing your emails, you can easily find what you need when you need it. Similarly, classifying financial transactions allows businesses to locate and analyze their financial data efficiently.
Summarizing Data
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
After classifying data in the ledger, the information is summarized into financial statements like the profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Detailed Explanation
Following the classification of transactions, the next step is to summarize this financial data into comprehensive financial statements, which are essential for assessing the overall financial health of the business. These financial statements commonly include the profit and loss account (which shows revenue and expenses) and the balance sheet (which shows assets, liabilities, and equity). This summarizing step gives stakeholders a clear picture of how the business is performing over a specific period.
Examples & Analogies
Think of summarizing data like creating a report card for a student at the end of the term. The report card succinctly shows the student's performance in different subjects, allowing parents and teachers to assess overall academic achievement easily. In accounting, financial statements serve a similar purpose by summarizing a business's financial activities.
Interpreting Financial Data
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The final step involves analyzing the financial statements to interpret the financial health of the business. This helps in making business decisions and evaluating performance.
Detailed Explanation
The last step of the accounting process is interpreting the financial data presented in the financial statements. This involves analyzing various metrics such as profitability, liquidity, and solvency to gauge the business's financial health. Understanding these aspects is vital for business owners and managers as it informs their decision-making processes regarding investment, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Examples & Analogies
Interpreting financial data can be compared to a doctor analyzing a patient’s health reports to make a diagnosis. Just as the doctor looks at various tests and reports to understand the patient's condition and decide on treatment, business managers assess their financial statements to understand the company’s situation and decide on future actions.
Key Concepts
-
Recording: Documenting financial transactions accurately.
-
Classifying: Organizing transactions into accounts for better data management.
-
Summarizing: Aggregating data into financial statements for clear presentation.
-
Interpreting: Analyzing financial statements to inform decision-making.
Examples & Applications
When a company sells a product for cash, it records the transaction as a debit to the cash account and a credit to the sales account.
Classifying expenses into categories like salaries, rent, and utilities helps in preparing detailed financial statements.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
First record, then classify, summarize to clarify, analyze to decide, and let profits fly!
Stories
Imagine a baker who records every donut sold, categorizing them by flavor for future baking, summarizing monthly sales, and interpreting trends to decide on new recipes.
Memory Tools
Use RCSI to remember the steps: Record, Classify, Summarize, Interpret.
Acronyms
RCSI as in Record, Classify, Summarize, Interpret
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Recording
The act of documenting financial transactions in the books of accounts using debit and credit entries.
- Classifying
The organization of recorded transactions into specific accounts within the ledger.
- Summarizing
The process of aggregating classified financial data into financial statements.
- Interpreting
The analysis of financial statements to assess the financial health and performance of a business.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
