Business Entity Concept
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Business Entity Concept
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’re going to discuss a key principle in accounting - the Business Entity Concept. Can anyone tell me what they think this concept refers to?

Does it mean that a business is treated separately from an individual?

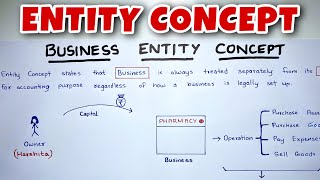
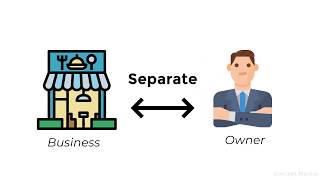
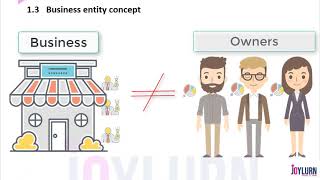
Exactly, Student_1! The Business Entity Concept states that a business is treated as a separate legal entity from its owners. This means we will record all financial transactions from the business's perspective.

So, if the owner invests money in the business, it is recorded differently?

Yes, that’s correct, Student_2! When an owner invests in a business, it's recorded as a liability called capital, reflecting that the business owes this amount to the owner. This separation is crucial for clarity in financial reporting.

What happens if the business gets into debt? Does the owner have to pay it?

Good question, Student_3! Because of the Business Entity Concept, the owners are shielded from the business's debts. The business itself is liable.

To remember this, think about the acronym 'SEPARATE' - for 'Separate Entity' - which reinforces that the business operates independently of its owners.

In summary, the Business Entity Concept is vital for keeping financial records clear and protecting individual owners from business liabilities.
Application of the Business Entity Concept
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore how the Business Entity Concept applies in real-life scenarios. Can anyone provide an example?

If I’ve opened a restaurant and used my savings to buy equipment, how does that work?

Great example, Student_1! In your case, the money you invest for the restaurant should be recorded as capital of the business, not as personal savings. This highlights the separation between your assets and those of the restaurant.

And if I take a loan for the restaurant, how is that recorded?

Excellent question, Student_4! The loan would also be recorded as a liability for the business. Hence, the restaurant must repay the loan, while your personal finances remain protected.

To help you remember this, I suggest the mnemonic 'B.E.T' - for 'Business Equals Transaction' - emphasize that all transactions should reflect the business's perspective.

To wrap up, the Business Entity Concept not only helps in accurate financial reporting, but also ensures that personal assets are safeguarded.
Significance of the Business Entity Concept
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss why the Business Entity Concept is so important. What do you think, Student_3?

It helps in understanding where the business stands financially, right?

Exactly! By treating the business as a separate entity, stakeholders—like investors and creditors—can better assess its financial health without the noise from personal transactions.

Does it also make auditing easier?

Great point, Student_2! It simplifies the auditing process since auditors can clearly distinguish business transactions from personal ones, reducing confusion.

Another way to remember its significance is 'PRECISION' – for 'Professional Reporting and Entity Clarity in Integrated Operations Needs' - which links back to its crucial role in accounting.

In summary, the Business Entity Concept is fundamental not just for maintaining accurate records, but also for ensuring legal protection and trustworthy financial reporting.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This concept is a fundamental accounting principle where a business's financial activities are recorded independently of its owners' personal transactions. This ensures clarity and integrity in financial reporting by treating the business as a separate legal entity.
Detailed
Business Entity Concept
The Business Entity Concept is a core accounting principle which dictates that a business is treated as a distinct entity, separate from its owners or shareholders. This means that all financial transactions must be recorded from the perspective of the business itself rather than from the individuals who own it. For instance, when an owner invests money into the business, this investment is recorded as a liability owed by the business (known as capital) rather than an increase in the owner's personal assets. This separation is essential for various reasons:
- Clarity in Financial Reporting: It provides a clear demarcation between personal and business finances, which is critical for accurate financial reporting.
- Legal Protection: It protects the owners from liabilities incurred by the business, as the business entity itself is responsible for its debts.
- Consistency and Comparability: Facilitating better comparisons with other entities and helping maintain consistency across financial statements.
In conclusion, understanding the Business Entity Concept is crucial for accurate accounting and meaningful financial analysis, ensuring stakeholders can trust financial information without bias from personal transactions.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Business Entity Concept
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The business is treated as a separate entity from its owner. All financial transactions are recorded from the business's perspective, not the owner's.
Detailed Explanation
The Business Entity Concept is a fundamental accounting principle that establishes the business as a distinct entity from its owner. This means that the financial activities and transactions of the business are recorded separately from the personal transactions of the owner. This separation is essential because it ensures that the business's financial statements reflect its true financial position and performance without mixing personal finances.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you own a café. If you personally spend money on a new car, that expense does not appear in the café's financial records. Instead, only transactions related to the café, like purchasing ingredients or paying rent, show up in its books. This separation helps investors and stakeholders see how well the café is doing without confusion from your personal finances.
Recording Transactions from the Business's Perspective
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example: If the owner invests ₹1,00,000 in the business, it is recorded as a liability (Capital) from the business's point of view.
Detailed Explanation
When an owner invests money into the business, such as ₹1,00,000, it's recorded as capital in the business's accounts. This capital is considered a liability because it represents an obligation of the business to the owner. In other words, the business owes this amount back to the owner as it is their investment. By treating this investment as a liability, the accounting system maintains a clear distinction between the owner’s personal net worth and the business’s financial status.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it this way: If you set up a lemonade stand and put in ₹1,00,000 to buy supplies, that money is a loan to your lemonade stand. If you go to a bank and ask for a loan, the bank expects to be paid back. Similarly, your lemonade stand should account for your initial investment as money it owes to you. This ensures that the stand's losses or profits are calculated independently of your personal finances.
Key Concepts
-
Separation of Entity: The principle that a business's financial transactions must be independent of its owners' personal transactions.
-
Capital and Liabilities: The recognition that funds invested by owners are liabilities from the business perspective.
-
Importance for Stakeholders: The concept aids stakeholders such as creditors and investors in understanding a business's financial health.
Examples & Applications
An owner's contribution of ₹1,00,000 to their business is recorded as a capital liability, clearly distinguishing it from the owner's personal wealth.
If a business purchases equipment financed through a bank loan, the loan amount is recorded as a liability, separate from the owner's personal finances.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When business and owners mix, it’s quite a fix; keep them separate, for an accurate mix!
Stories
Imagine a chef who runs a restaurant; if she buys knives with personal funds, it would confuse her profits. Keeping business expenses separate means all cuts and profits are truly hers!
Memory Tools
Remember 'B.E.T' - Business Equals Transactions, underscoring that all transactions reflect the business's financial state.
Acronyms
SEPARATE - Separate Entity, Professional Accounting, Responsible And Trustworthy Examination.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Business Entity Concept
An accounting principle that treats a business as a separate entity from its owners, influencing how transactions are recorded and reported.
- Capital
The financial resources invested by the owner(s) in a business, recorded as a liability from the business's perspective.
- Liability
A financial obligation or debt that a business is responsible for, separate from the owners' personal obligations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
