Aggregate Tests and Standards
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Crushing Strength Test
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with the Crushing Strength Test. Who can tell me what this test evaluates?

It assesses how well aggregates can resist crushing under pressure.

Correct! It’s standardized by IS 2386 (Part 4). Does anyone know why this is important?

Because bad aggregates can result in pavement failure under heavy loads.

Exactly! We need aggregates that can withstand these demands. That's crucial for durability.

Mnemonic aid: Remember 'CRUSH' — Compressive Resistance Under Stress at High-loads.

Nice way to remember it!

Can anyone tell me what the ideal crushing values should be for varying applications?

For wearing surfaces, ACV should be less than or equal to 30%.

Great job! This is how we ensure the quality of the pavement.

In summary, the Crushing Strength Test helps identify suitable materials that can handle heavy traffic.
Abrasion and Impact Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we're discussing the Abrasion Test. What does this test measure?

It measures how resistant the aggregates are to wear.

Good! And why is abrasion resistance vital for road construction?

Because roads face constant friction and wear from vehicles!

Yes! The ASTM C131 standard helps guide us here. Now, how does the Impact Value Test relate?

It assesses toughness under impact, right? It’s crucial for roads subjected to heavy loads.

Exactly! Remember 'A.I.R.' for Abrasion and Impact Resistance.

That’s a catchy way to remember it!

To summarize, both tests evaluate aggregate quality concerning traffic loading conditions.
Soundness and Shape Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the Soundness Test. What do we check for here?

We check how aggregates withstand weathering.

Exactly! This is essential for durability against freeze-thaw cycles. IS 2386 (Part 5) covers this. Why should we care?

If aggregates break down, the whole pavement can fail!

Correct! Now onto Shape Tests. What are we looking for here?

We measure the flakiness and elongation of aggregates.

Right! More cubical shapes provide better interlocking in pavements!

Let’s remember with 'SHAPE' — Strong and Handy Aggregates Provide Efficiency!

That’s easy to recall!

In summary, soundness and shape tests ensure long-lasting and stable pavements.
Water Absorption and Specific Gravity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's cover Water Absorption and Specific Gravity. Why are these tests important?

They help determine how much water aggregates can absorb and their density.

Exactly! How does high water absorption affect aggregate performance?

It could weaken the bond in the pavement and lead to damage!

Absolutely! Remember 'W.A.G.' for Water Absorption and Gravity - they guide aggregation quality.

Got it!

In conclusion, understanding these properties helps ensure that we choose high-quality aggregates for construction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses various aggregate tests and standards, including their objectives and applicable codes, highlighting how these assessments determine aggregate quality and suitability for road construction.
Detailed
Aggregate Tests and Standards
This section details the essential tests and standards employed to evaluate road aggregates, fundamental in ensuring effective pavement construction. Each test is designed to assess specific physical properties that determine the suitability and performance of aggregates used in road projects.
- Crushing Strength Test:
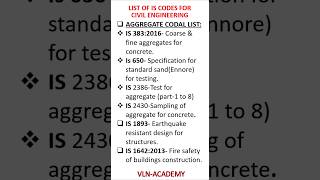
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4)
- Objective: Assesses the aggregate's ability to resist crushing under compressive load, a critical factor for pavement durability.
- Abrasion Test:
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4) / ASTM C131
- Objective: Measures the wear resistance of aggregates, important for high-traffic surfaces.
- Impact Value Test:
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4)
- Objective: Evaluates the toughness of aggregates under impact forces, critical for resisting dynamic loads.
- Soundness Test:
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 5)
- Objective: Tests the durability of aggregates against weathering effects, ensuring long-term performance.
- Shape Tests (Flakiness and Elongation):
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 1)
- Purpose: Classifies aggregates based on geometric shape, which influences the workability and strength of the road base.
- Water Absorption & Specific Gravity:
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 3)
- Purpose: Determines the porosity and density-related properties of aggregates, affecting mix design and performance.
Understanding these tests helps in the selection of quality aggregates that contribute to the overall performance and longevity of road surfaces.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Crushing Strength Test
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.1 Crushing Strength Test
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4)
- Objective: To assess resistance to crushing under compressive load.
Detailed Explanation
The Crushing Strength Test is designed to determine how well aggregate materials can withstand compressive forces. In other words, it tests the ability of the aggregate to resist being crushed when subjected to heavy loads, such as those experienced in road construction. The standard used for this test is IS 2386 (Part 4), ensuring that the materials evaluated meet certain national guidelines for performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to crush a rock with your hand. If it's a sturdy boulder, it won’t budge, showing high strength. On the other hand, if it's a brittle piece of chalk, it breaks easily. Similarly, in this test, strong aggregates resist crushing under loads just like the boulder.
Abrasion Test
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.2 Abrasion Test
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4) / ASTM C131
- Objective: To determine aggregate wear resistance.
Detailed Explanation
The Abrasion Test assesses how well aggregates resist wear when subjected to friction and mechanical action. This is important because aggregates in road construction are constantly exposed to traffic and environmental factors that can wear them down over time. The IS 2386 (Part 4) and ASTM C131 standards outline the procedures for conducting this test, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of shoes walking on a rough road. If they're made from durable material, they’ll last longer and show less wear. In the same way, the abrasion test helps ensure that the aggregate used in roads can endure the constant wear from vehicles.
Impact Value Test
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.3 Impact Value Test
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 4)
- Objective: To determine aggregate’s toughness under impact.
Detailed Explanation
The Impact Value Test evaluates an aggregate's ability to withstand sudden shocks or impacts, which is critical in construction as aggregates often face dynamic loads, such as the weight of vehicles hitting them. By following IS 2386 (Part 4), this test provides a standardized measure of toughness and resilience.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a rubber ball dropped on a concrete floor. It bounces back because it's tough enough to absorb the impact. Conversely, if you drop a fragile glass ornament, it shatters. Similarly, this test reveals whether the aggregate can endure the impact without breaking.
Soundness Test
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.4 Soundness Test
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 5)
- Objective: To check aggregate durability under weathering.
Detailed Explanation
The Soundness Test measures how well aggregates resist deterioration when subjected to weathering conditions, such as freeze-thaw cycles or wetting-drying conditions. Using IS 2386 (Part 5) as the standard, it ensures that the aggregates can maintain their integrity over time despite exposure to changing environmental conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge exposed to water over time. If it starts to break down or lose its shape, it’s not sound. In road construction, sound aggregates will provide lasting stability, much like a durable sponge that can hold water without falling apart.
Shape Tests
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.5 Shape Tests
- Flakiness and Elongation: IS 2386 (Part 1)
- Purpose: To classify aggregates based on geometric shape.
Detailed Explanation
Shape Tests, including those for flakiness and elongation, are conducted according to standard IS 2386 (Part 1). These tests help classify aggregates by their shape, which can affect their packing and interlocking ability in a construction mix. Aggregate shapes influence the strength and stability of road surfaces.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine assembling a puzzle. The shapes of each piece can determine how well they fit together and how strong the overall structure will be. Similarly, well-shaped aggregates fit together better, leading to stronger and more stable pavements.
Water Absorption & Specific Gravity
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
6.5.6 Water Absorption & Specific Gravity
- Standard: IS 2386 (Part 3)
- Purpose: To determine porosity and density-related properties.
Detailed Explanation
The tests for Water Absorption and Specific Gravity, standardized in IS 2386 (Part 3), help determine the porosity and density characteristics of aggregates. Water absorption indicates how much moisture the aggregates can hold, while specific gravity provides a measure of density, both of which are crucial for deciding the suitability of aggregates in road construction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge again. A dry sponge absorbs a lot of water, while a more solid material might not absorb any at all. Similarly, understanding how much water an aggregate can absorb helps predict how it will perform when mixed into pavement.
Key Concepts
-
Crushing Strength Test: Assesses the CRS of aggregates.
-
Abrasion Test: Evaluates wear resistance.
-
Impact Value Test: Measures toughness under dynamic loads.
-
Soundness Test: Checks durability against weathering.
-
Shape Tests: Classifies aggregates by geometry.
-
Water Absorption: Indicates porosity.
-
Specific Gravity: Measures density.
Examples & Applications
Aggregates with an ACV of 25% are suitable for heavy load pavements.
A high abrasion value indicates a poor quality aggregate for bituminous surfacing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To avoid roads so very thin, keep tests running to win!
Stories
Imagine a road made from fluffy clouds; the wind and rain wear them away like kids on a playground. So, we test the aggregates to find the tough ones!
Memory Tools
A.I.W.S: Abrasion, Impact, Water absorption, Shape. Remembering tests for aggregate quality.
Acronyms
C.A.I.S.W (Crushing, Abrasion, Impact, Shape, Water absorption) tests for quality!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Crushing Strength Test
A test to determine the ability of aggregates to resist crushing under applied loads.
- Abrasion Test
A test that measures the wear resistance of aggregates.
- Impact Value Test
A test that evaluates the toughness of aggregates under impact loads.
- Soundness Test
A test to assess the durability of aggregates against weathering.
- Shape Tests
Tests to classify aggregates based on their geometric shapes.
- Water Absorption
The measurement of the water holding capacity of aggregates.
- Specific Gravity
A measure of the density of aggregates compared to the density of water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
