Igneous Rocks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Igneous Rocks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about igneous rocks, a critical type of rock used in road construction. Can anyone tell me how igneous rocks are formed?

Aren't they formed from molten lava or magma that cools down?

Exactly! That's right, Student_1. They cool and solidify from magma or lava. This process is what gives them their unique properties, such as hardness and strength. Can anyone name an igneous rock?

Isn't granite an igneous rock?

Correct! Granite, along with basalt, is a prime example of igneous rocks used in construction. Let's remember this by associating 'Granite is Great for roads!'

What makes them suitable for roads?

Good question! Their hardness allows them to withstand heavy loads, making them ideal for high-load pavements. So, remember, igneous rocks are tough, reliable, and widely used!
Types of Igneous Rocks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive a little deeper. Can anyone share what type of igneous rock they know?

Besides granite, I think basalt is also one!

Exactly! Both granite and basalt are widely used in road construction due to their durability. Remember 'G for Granite and B for Basalt'! What do you think makes basalt different from granite?

I think basalt is usually darker than granite.

That's right! Basalt is typically darker and denser. Both rocks have unique strengths, and understanding these differences helps us make better choices in construction materials. So, keep in mind—color and density matter!

How do we decide which one to use for roads?

It depends on the load requirements and the environment the road will be in. If it's heavy traffic, we lean towards granite for its strength!
Application of Igneous Rocks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now look at how igneous rocks are applied in road construction. Who can tell me why they are preferred in high-load areas?

They must be very strong and durable!

Absolutely! Their strength and resistance to weathering make them ideal. Think 'Igneous, the Strong Road's Best Friend!'. Are there specific projects where these rocks would shine?

Maybe in highways or busy city roads?

Correct again! Highways and roads that experience heavy truck traffic benefit from igneous rocks like granite and basalt for durability.

So, if there's a lot of traffic, we should use igneous rocks, right?

Exactly! Always remember—heavy loads require strong materials!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
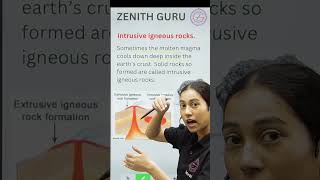
Igneous rocks, formed from cooled molten magma or lava, are predominant in road construction due to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand heavy loads. The section highlights examples such as granite and basalt and discusses their significance in high-load pavements.
Detailed
Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of molten magma or lava, making them one of the primary classifications of rocks. They are known for their hardness, strength, and overall durability, making them particularly suitable for high-load pavement applications in road construction.
Properties of Igneous Rocks
- Hardness and Strength: Igneous rocks are among the hardest types of rocks, offering superior strength and durability to pavements subjected to heavy traffic loads.
- Common Types: Two significant examples of igneous rocks are granite and basalt. Both are utilized widely in road construction for their structural integrity.
- Uses in Construction: Due to their robust nature, igneous rocks are typically used in high-load areas, ensuring stability and longevity of paved surfaces.
Understanding the properties and applications of igneous rocks helps engineers select the appropriate materials for road construction, ensuring performance and durability under varying conditions.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Examples of Igneous Rocks
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Igneous Rocks
- Examples: Granite, basalt
Detailed Explanation
Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks, formed from the cooling and solidification of molten materials called magma or lava. Common examples include granite and basalt. Granite is known for its use in construction projects due to its durability and aesthetic appeal, while basalt is often found in areas with volcanic activity. Both types are hard and strong, making them suitable for various applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of igneous rocks like cookies fresh out of the oven. Just as cookies solidify after being heated and remove the heat, igneous rocks form when molten rock cools down and solidifies. Granite is like a gourmet cookie with various flavors and chunks (quartz, feldspar, and more), while basalt is more like a classic chocolate chip cookie—simple but robust.
Properties of Igneous Rocks
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Properties: Hard, strong, durable
Detailed Explanation
Igneous rocks are characterized by their hardness, strength, and durability. These properties arise from the process of crystallization that occurs when molten rock cools. The minerals that form in igneous rocks are tightly packed together, which contributes to their overall strength and resistance to wear and weathering. This makes igneous rocks ideal for construction materials, particularly in high-load pavements.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to crush an ice cube versus a solid, frozen cake. The ice cube (which represents sedimentary rock) is easy to break, while the solid cake (like igneous rock) requires a lot more force due to its firmness and density. This analogy helps illustrate why igneous rocks are often used in heavy-duty construction.
Applications of Igneous Rocks
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Use: High-load pavements
Detailed Explanation
Igneous rocks are commonly used in high-load pavements because of their strength and durability. Their ability to withstand heavy traffic and environmental stresses makes them suitable for roads and highways. High-load pavements are essential for maintaining safety and the longevity of road infrastructure, particularly in areas with intense vehicular activity.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a busy highway where large trucks frequently travel. To ensure the road doesn’t wear out too quickly, builders use igneous rocks to construct the pavement, much like how a football field might be made from synthetic turf that can withstand the wear and tear from games. The durable nature of igneous rocks ensures that roads can handle heavy loads without deteriorating quickly.
Key Concepts
-
Formation of Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks form when magma or lava cools and solidifies.
-
Properties of Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks exhibit hardness and strength, making them ideal for construction.
-
Common Types: Granite and basalt are two primary examples of igneous rocks used in road construction.
Examples & Applications
Granite is often used in road construction due to its high strength and durability.
Basalt is widely selected for its density and ability to withstand weathering.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Igneous rocks are tough and strong, in road construction, they belong!
Stories
Once upon a time, granite and basalt decided to enter a race. Granite, being tougher, often won the respect of road builders, while basalt, being denser, claimed the heavy traffic lanes. Together, they made the perfect road team!
Memory Tools
G and B for Granite and Basalt - great allies in road construction.
Acronyms
HSD
Hard
Strong
Durable - properties of igneous rocks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Igneous Rocks
Rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of molten magma or lava.
- Granite
A common type of igneous rock known for its strength, often used in construction.
- Basalt
A dense, dark igneous rock used in high-load pavements due to its durability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
